Abstract
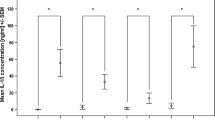
In an attempt to define potential immunological dysfunctions in schizophrenia, we determined the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R) in a whole-blood assay after stimulation with phytohemagglutinin (PHA) as well as the serum concentrations of sIL-2R. Because CD4 +CD45RO+T cells are the main producers of IFN-γ, we determined the percentage of these cells, as well as of pan T, CD4+T, and CD8+T cells, by flow cytometry. A whole-blood count was performed in addition. Two groups of patients were examined, paranoid-type and residual-type schizophrenics. The numbers of both monocytes and neutrophils, but not of lymphocytes, were increased significantly in the schizophrenic sample. The IFN-γ production of the schizophrenics as a whole group, and of the paranoid patients, was reduced significantly in comparison with the control group (p≤0.05). The residual patients produced less IFN-γ than the controls, but more than the paranoid patients. The latter differences did not reach statistical significance. The production of IL-4, which physiologically antagonizes the production of IFN-γ, was not significantly higher in the patient group. No changes in the lymphocyte subpopulations were observed. The production of IL-2 showed a trend toward reduction in paranoid patients, but not in residual schizophrenics. The serum sIL-2R levels were elevated slightly in schizophrenics when compared with controls. In order to rule out a possible effect of cortisol on cytokine production, 20 schizophrenic were compared with 20 age- and gendermatched controls. However, neither elevated cortisol levels were detected in the schizophrenic sample, nor significant intercorrelations between cortisol levels and cytokine production, or levels of sIL-2R, respectively. In summary, our data reinforce the possibility of immune dysfunction in schizophrenia and point to the possible relevance of disease subgroups in this respect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bessler H, Levental Z, Karp L, Modai I, Djaldetti M, Weizman A (1995) Cytokine production in drug-free and neuroleptic-treated schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 38:297–302
Coffey CE, Sullivan JL, Rice JR (1983) T-lymphocytes in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 18:113–119
DeLisi LE (1986) Neuroimmunology: clinical studies of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. In: Nasrallah HA, Weinberger DR (eds) Handbook of schizophrenia, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 377–396
Fowell D, McKnight A, Powrie F, Dyke R, Mason D (1991) Subsets of CD4+ T-cells and their role in the induction and prevention of autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 123:37–64
Ganguli R, Rabin BS (1989) Increased serum interleukin-2 receptor in schizophrenic and brain-damaged subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:291–292
Ganguli R, Rabin BS, Belle SH (1989) Decreased interleukin-2 production in schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 26:424
Ganguli R, Brar JS, Solomon W, Chengappa KNR, Rabin BS (1992) Altered interleukin-2 production in schizophrenia: association between clinical state and autoantibody production. Psychiatry Res 44:113–123
Ganguli R, Brar JS, Chengappa KNR, DeLeo M, Yang ZW, Shurin G, Rabin BS (1995a) Mitogen-stimulated interleukin-2 production in never-medicated, first-episode schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:668–671
Ganguli R, Brar JS, Rabin BS (1995b) Clozapine-induced increase in plasma levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors (comment) Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:878
Henneberg A, Riedl B, Dumke H-O, Kornhuber HH (1990) T-lymphocyte subpopulations in schizophrenic patients. Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 239:283–284
Hornberg M, Arolt V, Wilke I, Kruse A, Kirchner H (1995) Production of intererons and lymphokines in leukocyte cultures of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 15:232–242
Katila H, Cantell K, Hirvonen S, Rimon R (1989) Production of interferon alpha and gamma by lymphocytes from patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2:361–365
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Kirchner H, Kleinicke Ch, Diegel W (1982) A whole blood technique for testing production of human interferon by leukocytes. Immunol Method 48:213–219
Kolyaskina GI (1983) Blood lymphocytes in schizophrenia-immunological and virological aspects. Adv Biol Psychiatry 12: 142–149
Kronfol Z, House JD (1991) Immunity, cortisol and psychiatric disorders. In: Kurstak E (ed) Psychiatry and biological factors. Plenum, New York, pp 223–227
Maes M, Meltzer HY, Bosmans E (1994) Immune-inflammatory markers in schizophrenia: comparison to normal controls and effects of clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand 89:346–351
Masserini C, Vita A, Basile R, Morselli R, Boato P, Peruzzi C, Pugnetti L, Ferrante P, Cazzullo CL (1990) Lymphocyte subsets in schizophrenic disorders. Schizophr Res 3:269–275
McAllister CG, Rapaport MH, Pickar D, Paul SM (1989a) Effects of short-term administration of antipsychotic drugs on lymphocyte subsets in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:956–957
McAllister CG, Rapaport MH, Pickar D, Podruchny TA, Christison G, Alphs LD, Paul SM (1989b) Increased numbers of CD5+B-lymphocytes in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:890–894
Mendelson J, Glascow LA (1966) The in vitro and in vivo effects of cortisol on interferon production and action. J Immunol 96: 345–349
Moises HW, Schindler L, Leroux M, Kirchner H (1985) Decreased production of interferon gamma in leukocyte cultures of schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 72:45–50
Müller N, Hofschuster E, Ackenheil M, Eckstein R (1993) T-cells and psychopathology in schizophrenia: relationship to the outcome of neuroleptic therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand 87:66–71
Müller N, Hofschuster E, Ackenheil M, Hofschuster E, Hempel W, Eckstein R (1991) Cellular immunity in schizophrenic patients before and during neuroleptic treatment. Psychiatry Res 37(2):147–160
Peleman R, Wu J, Fargeas C, Delespesse G (1989) Recombinant interleukin-4 suppresses the production of interferon-γ by human mononuclear cells. J Exp Med 170:1751
Pollmächer T, Hinze-Selch D, Mullington J, Holsboer F (1995) Clozapine-induced increase in plasma levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors (letter). Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:877
Rabin BS, Ganguli R, Cunnick JE, Lysle DT (1988) The central nervous system-immune system relationship. Clin Lab Med 8:253–268
Rapaport MH, Lohr JB (1994) Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptors in neuroleptic naive schizophrenic subjects and in medicated subjects with and without tardive dyskinesia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 90:311–315
Rapaport MH, McAllister CG, Pickar D, Nelson DL, Paul SM (1989) Elevated levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:291–292
Sanders ME, Makoba MW, Sharrow SO, Stephany D, Springer TA, Young HA, Shaw S (1988) Human memory T-lymphocytes express increased levels of 3 cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2 and LFA-1) and 3 other molecules (UCHL-1, Cdw29 and Pgp-1) and have enhanced interferon-gamma production. J Immunol 140:1401–1407
Villemain F, Chatenoud L, Galinowski A, Homo-Delarche F, Ginestet D, Loo H, Zarifian E, Bach JF (1989) Abberant T-cell mediated immunity in untreated schizophrenic patients: deficient interleukin-2 production. Am J Psychiatry 146:609–616
Villemain F, Chatenoud L, Guillibert E, Pelicier Y, Bach JF (1987) Decreased production of interleukin-2 in schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 469:669–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilke, I., Arolt, V., Rothermundt, M. et al. Investigations of cytokine production in whole blood cultures of paranoid and residual schizophrenic patients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Nuerosci 246, 279–284 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190280
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190280