Summary
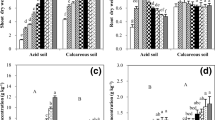
In a soil pot culture experiment conducted under greenhouse conditions, two varieties of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp) were found to be differentially susceptible to phosphorus-induced zinc deficiency. Although phosphate application, in the absence of applied zinc, caused growth disorder in both the varieties, the symptoms were more virulent, appeared early and were induced with both 25 and 75 ppm phosphorus in variety HFC-42-1, as against FOS-1, in which case zinc deficiency symptoms appeared under P75Zn0 treatment only. Contrary to the expectation the more susceptible variety was found to have higher zinc concentration in its shoots and thus the differential susceptibility of these varieties of cowpea could not be related to their zinc absorption characteristics. High phosphate application caused efflux of zinc during 16–32 day growth in both the varieties. However, higher sensitivity to phosphorus-induced zinc disorder in variety HFC-42-1, appeared to be due to nearly 2 times higher P concentration in this variety as against FOS-1. The results indicate that variety HFC-42-1 has a greater need for zinc because of its inherent capacity to accumulate more phosphorus. Dry matter yield and phosphorus and zinc content in the varieties were also differentially affected by the applications of both phosphate as well as zinc. re]19760504
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambler, J. E. and Brown, J. C., Causes of differential susceptibility to zinc deficiency in two varieties of navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agron. J.61, 41–43 (1969).
Boawn, L. C. and Brown, J. C., Further evidence for a P-Zn imbalance in plants. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.32, 94–97 (1968).
Boawn, L. C. and Leggett, G. E., Phosphorus and zinc concentrations in Russett Burbank potato tissue in relation to development of zinc deficiency symptoms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.28, 229–232 (1964).
Brown, J. C., Ambler, J. E., Chaney, R. L. and Foy, C. D., Differential responses of plant genotypes to micronutrients.In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Publ. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Inc. Madison, Wisc. U.S.A. 389–478 (1972).
Edwards, J. H. and Kamprath, E. J., Zinc accumulation and growth of corn seedlings as affected by endosperm removal. Agron. J.67, 809–812 (1975).
Ellis, B. G., Response and susceptibility.In Zinc deficiency — a symposium. Crops Soils18, 10–13 (1965).
Gregory, F. G. and Crowther, F., A physiological study of varietal differences in plants. Part I. A study of the comparative yields of barley varieties with different manurings. Ann. Bot.42, 757–770 (1928).
Johnson, C. M. and Ulrich, A., Analytical methods for use in plant analysis. Bull. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. No.766 (1959).
Millikan, C. R., Plant varieties and species in relation to the occurrence of deficiencies and excesses of certain nutrient elements. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci.27, 220–233 (1961).
Millikan, C. R., Effects of different levels of zinc and phosphorus on the growth of subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L.). Aust. J. Agric. Res.14, 180–205 (1963).
Olsen, S. R., Micronutrient interactions.In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Pub., Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Inc. Madison Wisc. U.S.A. 243–264 (1972).
Paulsen, G. M. and Rotimi, O. A., Phosphorus-zinc interaction in two soybean varieties differing in sensitivity to phosphorus nutrition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.32, 73–76 (1968).
Safaya, N. M., Phosphorus-zinc interaction in relation to absorption rates of phosphorus, zinc, copper, manganese and iron in corn (Zea mays L.). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J.40, 719–722 (1976).
Safaya, N. M., Shukla, U. C. and Khanna, S. S., Behaviour of zinc in soils and plants. Fert. News19, 21–27 (1974).
Safaya, N. M., Shukla, U. C. and Khanna, S. S., Nutritional physiology of zinc and symptoms of its deficiency in some field crops. Fert. News20, 31–35 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safaya, N.M., Singh, B. Differential susceptibility of two varieties of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp) to phosphorus-induced zinc deficiency. Plant Soil 48, 279–290 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02187240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02187240