Summary
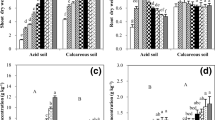
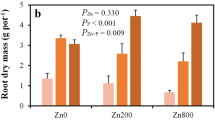
In a pot experiment, Zn-uptake by tomato plants grown on an alluvial soil was increased by P application. When Zn was applied to the soil, no effect was obtained for P application on Zn-uptake. On a calcareous soil, Zn-uptake was increased by P application whether Zn was applied to the soil or not. On both soils, no effect was obtained for Zn application on P-uptake by plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham F T 1963 Relationship between phosphorus and micronutrients in plants. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27, 389–391.
Bingham F T and Garber M J 1960 Solubility and availability of micronutrients in relation to phosphorus fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 24, 209–213.
Bingham F T and Martin J P 1956 Effects of soil phosphorus on growth and minor element nutrition of citrus. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 20, 382–385.
Bingham F T, Martin J P and Chastain J A 1958 Effects of phosphorus fertilization of California soils on minor element nutrition of citrus. Soil Sci. 86, 24–31.
Beohle J Jr and Lindsay W L 1969 Micronutrients. The Fertilizer Shoe-Nails. Pt. 6,In The Limelight-Zinc. Fertilizer Solutions 13 (1), 6–12.
Brown A L, Krantz B A and Eddings J L 1970 Zn−P interaction as measured by plant response and soil analysis. Soil Sci. 110, 415–420.
Christensen N W and Jackson T L 1981 Potential for phosphorus toxicity in zinc-stressed corn and potato. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 45, 904–909.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1969 A micronutrient soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn and Cu. Agron. Abstr. p 84.
Loneragan J F, Grove T S, Robson A D and Snowball K 1979 Phosphorus toxicity as a factor in Zn−P interactions in plants. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 43, 966–972.
Olsen S R, Cole C V, Watanabe F S and Dean L A 1954 Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. U.S. Dept. Agric. Circ. 939.
Orabi A A, Abdallah A, Mashadi H and Barakat A H 1981 Zinc-phosphorus relationship in the nutrition of corn plants (Zea mays L.) grown on some calcareous soils. Plant and Soil 59, 51–59.
Orabi A A, Mashadi H, Abdallah A and Morsy M 1981 Effect of zinc and phosphorus on the grain yield of corn (Zea mays L.) grown on a calcareous soil. Plant and Soil 63, 291–294.
Piper C S 1950 Soil and Plant Analysis. Interscience Publishers, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orabi, A.A., Ismail, A.S. & Mashadi, H. Zinc-phosphorus relationship in the nutrition of tomato plants as affected both by the soil and by the rate of applied zinc. Plant Soil 69, 67–72 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02185704
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02185704