Summary
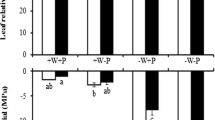
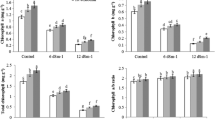
The effects of three levels of N (0, 50 and 100 ppm) and four salinity regimes (0.5, 1.5, 2.5 and 3.5 mmhos/cm) on the growth and mineral composition of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) were investigated in a greenhouse experiment. Bean plants treated with N produced more dry weight and contained higher N than the untreated check. Growth and N uptake by bean plants generally decreased with increasing irrigation water salinity at all N levels. High salinity caused severe burning of the margins of older leaves and stunting of growth. At the low salinity levels (0.5 and 1.5 mmhos/cm), N additions had no effect on growth; however, the suppressing effects of higher salinity were alleviated somewhat with N fertilization.
The concentration and uptake of Cl and Na increased with increasing salinity; probably the relatively high accumulations of Cl and Na were responsible for growth reductions at high salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abtahi, A. 1978 Soil and ground water salinity and their relations to physiography. Iran. J. Agric. Res.6, 21–32.
Bernstein, L., Francois, L. E. and Clark, R. A. 1974 Interactive effects of salinity and fertility on yields of grains and vegetables. Agron. J.66, 412–421.
Bremner, J. M. 1965 Total nitrogen.In Method of Soil Analysis. Ed. C. A. Black pp. 1149–1178. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin.
Cackett, K. E. 1965 Winter production of seed beans in the lowland. Rhod. Agric. J.62, 69–73.
Chapman, H. D. and Pratt, P. F. 1961 Methods of Analysis for Soils, Plants and Waters. Univ. of Calif., Div. Agric. Sci.
Edje, O. T., Mughogho, L. K. and Ayonoadu, U. W. U. 1975 Response of dry beans to varying N levels. Agron. J.67, 251–255.
Hamid, A. and Talibudeen, O. 1976 Effect of sodium on the growth and ion uptake by barley, sugarbeet and broad beans. J. Agric. Sci.86, 49–56.
Khalil, M. A., Amer, F. and Elgabaly, M. M. 1967 A salinity-fertility interaction study on corn and cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.31, 683–686.
Long, E. M. 1943 The effect of salt additions to the substrate on the uptake of water and nutrients by roots of approach-grafted tomato plants. Am. J. Bot.30, 594–601.
Lunin, J. and Gallatin, M. H. 1965 Salinity-fertility interactions in relation to the growth and composition of beans: I. Effect of N, P, and K. II. Varying levels of N and P. Agron. J.4, 339–345.
Masefield, G. B. 1968 Seasonal effects on the root nodulation of legumes. Exp. Agric.4, 335–338.
Masefield, G. B. 1971 The root nodulation of tall and dwarf peas and beans. Exp. Agric.7, 123–127.
Nassery, H. and Jones, R. L. 1976 Salt retention by bean hypocotyl. J. Exp. Bot.27, 1279–1289.
Ogo, T. and Morikawi, S. 1965 Relationships between certain nitrogen fractions in leaf blade of crops and salt tolerance (1). Shimane Agric. Coll. Bull.13A, 559 p.
Ravikovich, S. and Porath, A. 1967 The effect of nutrients on salt tolerance of crops. Plant and Soil26, 49–71.
Ries, S. K. 1971 The relationship of protein content and size of bean with growth and yield. Proc. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci.96, 557–560.
Wadleigh, C. H. and Ayers, A. D. 1945 Growth and biochemical composition of bean plants as conditioned by soil moisture tension and salt concentration. Plant Physiol.20, 106–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sameni, A.M., Maftoun, M., Bassiri, A. et al. Growth and chemical composition of dry beans as affected by soil salinity and N fertilization. Plant Soil 54, 217–222 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181847
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181847