Summary
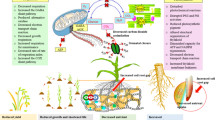
The effect of waterlogging on water use and nutrient uptake in sunflower and sorghum was investigated in relation to stage of development of the crops and the timing and duration of waterlogging. Waterlogging at the vegetative and floral initiation stages of plant growth induced a reduction in water use of sunflower, with corresponding declines in leaf expansion and leaf water potential; in sorghum, the transpiration rates were much lower than for sunflower and relatively unaffected by waterlogging. Waterlogging at anthesis, however, caused an immediate reduction in water use in sunflower with a similar but delayed effect in sorghum. The differences in response of these two species are discussed in relation to the relative importance of water stress and nutrient uptake. Plant analysis at maturity indicated that waterlogging at any growth stage reduced both total and seed phosphorus in sunflower; similar effects were recorded with sorghum, with the exception of anthesis waterlogging which did not reduce nutrient uptake. Waterlogging effects on plant potassium levels were variable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drew M C and Sisworo E J 1979 The development of waterlogging damage in young barley plants in relation to plant nutrient status and change in soil properties. New Phytol. 82, 301–314.
Gales K 1977 Water relationships of waterlogged plants. Ann. Rep. Agric. Res. Council Letcombe Lab. 1976, 76–77.
Jackson W T 1956 The relative importance of factors causing injury to shoots of flooded tomato plants. Am. J. Bot. 43, 637–639.
Kozlowski T T and Pallardy S G 1979 Stomatal responses ofFraxinus pennsylvanica seedlings during and after flooding. Physiol. Plant 46, 155–158.
Kramer P J 1965 Effects of deficient aeration on the roots of plants. Proc. Conf. Drainage for Efficient Crop Production. Am. Soc. Eng Publ. (St. Joseph Michigan), 13–14.
Labanauskas C K, Stolzy L H, Zentmyer G A and Szuszkiewicz T E 1968 Influence of soil oxygen and soil water on the accumulation of nutrients in Avocado seedlings (Persea americana Mill.). Plant and Soil 29, 391–406.
Letey J, Stolzy L H, Blank G B and Lunt O R 1961 Effects of temperature on oxygen diffusion rates and subsequent shoot growth, root growth and mineral content of two plant species. Soil Sci. 92, 314–321.
Letey J, Stolzy L H, Lunt O R and Younger V B 1964 Growth and nutrient uptake of Newport Bluegrass as affected by soil oxygen. Plant and Soil 20, 143–148.
Leyshon A J and Sheard R W 1974 Influence of short term flooding on the growth and plant nutrient composition of barley. Can. J. Soil Sci. 54, 463–473.
Lindner R C and Harley C P 1942 A rapid method for the determination of nitrogen in plant tissue. Science 96, 565–566.
Miller G L and Miller E E 1948 Determination of nitrogen in biological materials. Anal. Chem. 20, 481–488.
Orchard P W and Jessop R S 1984 The response of sorghum and sunflower to short-term waterlogging. I. Effects of stage of development and duration of waterlogging on growth and yield. Plant and Soil 81 119–132.
Orchard P W and So H B 1985 The response of sorghum and sunflower to short-term waterlogging. II. Changes in the soil environment under waterlogged conditions. Plant and Soil 88, 407–420.
Orchard P W, So H B and Jessop R S 1985 The response of sorghum and sunflower to short term waterlogging. III. Root growth effects. Plant and Soil 88, 421–430.
Pereira J S and Kozlowski T T 1977 Variations among woody angiosperms in response to flooding. Physiol. Plant 41, 184–192.
Sena Gomes A R and Kozlowski T T 1980 Growth responses and adaptation ofFraxinus pennsylvanica seedlings to flooding. Plant Physiol. 66, 267–271.
Sojka R E and Stolzy L H 1980 Soil oxygen effects on stomatal response. Soil Sci. 130, 350–358.
Sojka R E and Stolzy L H 1981 Stomatal response to soil oxygen. Calif. Agric. 35, 18–19.
Trought M T C and Drew M C 1980 The development of waterlogging damage to wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). II. Accumulation and redistribution of nutrients by the shoot. Plant and Soil 56, 187–199.
Wien C, Lal R and Pulver E F 1979 Effects of transient flooding on growth and yield of some tropical crops.In Soil Physical Properties and Crop Production in the Tropics. Ed. R Lal and D J Greenland. John Wiley and Sons Chichester pp. 235–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orchard, P.W., Jessop, R.S. & So, H.B. The response of sorghum and sunflower to short-term waterlogging. Plant Soil 91, 87–100 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181821
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181821