Abstract
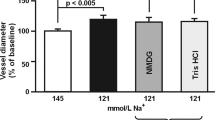
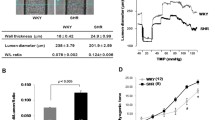
These studies were undertaken to examine the effect of alkalosis to modify “pressure-induced” activation of isolated cerebral arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and their normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) controls. At pH 7.4 andPCO2 of 34 torr elevation of transmural pressure from 0–140 mm Hg resulted in myogenic activation preceeded by membrane depolarization in both SHR and WKY. The degree of developed myogenic tone in SHR was elevated above WKY. Aklalosis (pH 7.4–7.7) depolarized and activated SHR cerebral arteries to a greater extent than WKY. Furthermore, both the electrical and mechanical responses to elevation in transmural pressure were exaggerated in SHR compared to WKY at pH 7.7 (PCO2 constant at 34 torr).
Manipulation ofPCO2 at constant pH of 7.4 had similar effects on “pressure-induced” myogenic tone in both SHR and WKY. Thus, cerebral arteries from both SHR and WKY depolarize and develop myogenic tone in response to increasing transmural pressure. This response is augmented in SHR, but to a much greater extent upon elevation of extracellular pH, whilePCO2 is maintained within normal limits. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry DI, Strandgaard S, Graham DI, Braendstrup O, svendsen UG, Vorstrup S, Hemmingsen R, Bolwig TG (1982) Cerebral blood flow in rats with renal and spontaneous hypertension: resetting of the lower limit of autoregulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2:347–353
Halpern W, Mongeon SA, Root DT (1984) Stress, tension and myogenic aspects of small, isolated extraparenchymal rat arteries. In: Stephens NL (ed) Smooth muscle contraction. Dekker, New York
Harder DR (1982) Effect of H+ and elevatedPCO2 on membrane electrical properties of cat cerebral arteries. Pflügers Arch 394:182–185
Harder DR (1984) Pressure dependent membrane depolarization in cat middle cerebral arteries. Circ Res 55:197–202
Harder DR (1986) Pressure-induced myogenic activation of cat cerebral arteries is dependent upon intact endothelium. Circ Res (in press)
Harder DR, Hermsmeyer K (1983) Membrane mechanism in arterial hypertension. Hypertension 5:404–408
Harder DR, Madden JA (1985) Cellular mechanisms of force development in cat middle cerebral artery by reducedPCO2. Pflügers Arch 403:420–404
Harder DR, Brann L, Halpern W (1983) Altered membrane electrical properties of smoth muscle cells from small cerebral arteries of hypertensive rats. Blood vessels 20:154–160
Harder DR, Smeda J, Lombard J (1985) Enhanced myogenic depolarization in hypertensive cerebral arterial muscle. Circ Res 57:319–322
Jones JV, Fitch W, MacKenzie ET, Strandgaard S, Harper AM (1976) The lower limit of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in the baboon. Circ Res 39:555–557
Mulvaney MJ, Hansen PK, Aalkgaer C (1978) Direct evidence that the greater contractility of resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive rats is associated with a narrowed lumen, a thicker media and increased number of smooth muscle cell tissue. Circ Res 43:854–862
Siegal G (1982) The effect of external pH on Na+ and K+ permeabilities in the smooth muscle fibre membrane of canine cerebral vessels. J Physiol 329:56P-57P
Strandgaard S (1976) Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in hypertensive patients. The modifying influence of prolonged antihypertensive treatment on the tolerance to acute, drug induced hypotension. Circulation 53:720–727
Strandgaard S, Paulson OB (1984) Cerebral autoregulation. Stroke 15:413–416
Standgaard S, Jones JV, MacKenzie ET, Harper AM (1975) Upperlimit of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in experimental renovascular hypertension in the baboom. Circ Res 37:164–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
D. R. Harder is an Established Investigator of the American Heart Association and a Research Career Scientist of the Veterans Administration. This study supported by NIH grants 33833 and 31871 and the Veterans Adminstration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeda, J.S., Lombard, J.H., Madden, J.A. et al. The effect of alkaline pH and transmural pressure on arterial constriction and membrane potential of hypertensive cerebral arteries. Pflugers Arch. 408, 239–242 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181465
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181465