Abstract
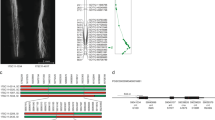
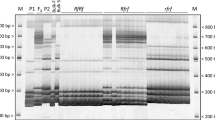
Pollen development requires both sporophytic and gametophytic gene expression. We are using a map-based cloning technique to isolate sporophytic genes which, when mutant, cause pollen abortion and a male sterile (ms) phenotype in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). We have genetically characterized onems locus (ms14) using RFLP analysis and identified flanking markers. High-resolution genomic physical mapping indicates that thems14 locus is located in a ∼300 kb region. We have identified a YAC clone with an insert size of ∼610 kb that contains thems14-linked markers, reflects the organization of the physical map and therefore most probably contains thems14 gene. In addition, we present evidence that the relationship between physical and genetic distance in this chromosomal region changes abruptly from ∼105–140 kb/cM to less than 24 kb/cM, and suggest that the TG393-TG104 region is a hotspot for recombination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MGM, Dirkse WG, Steikema WJ, Pereira A (1993) Transposon tagging of a male steility gene inArabidopsis. Nature 363:715–717
Albertsen MC, Fox TW, Trimnell MR (1993) Tagging, cloning and characterizing a male fertility gene in maize. Amer J Bot Abst 80:16
Antequera F, Bird AP (1988) Unmethylated CpG islands associated with genes in higher plant DNA. EMBO J 7:2295–2299
Arondel V, Lemieux B, Hwang I, Gibson S, Goodman HN, Somerville CR (1992) Map-based cloning of gene controlling omega-3 fatty acid desaturation inArabidopsis. Science 258:1353–1355
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Balint-Kurti J, Jones DA, Jones JDG (1995) Integration of the classical and RFLP linkage maps of the short arm of tomato chromosome 1. Theor Appl Genet 90:17–26
Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994)RPS2 ofArabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856–1859
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Toward a saturated linkage map in tomato based on isozymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112:887–898
Bird AP (1987) CpG islands as gene markers in the vertebrate nucleus. Trends Genet 3:342–347
Chang C, Kwok SF, Bleecker AB, Meyerowitz EM (1993)Arabidopsis ethylene-response geneETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science 262:539–545
Churchill GA, Giovannoni JJ, Tanksley SD (1993) Pooled-sampling makes high-resolution mapping practical with DNA markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:16–20
Civardi L, Xia Y, Edwards KJ, Schnable PS, Nikolau BJ (1994) The relationship between genetic and physical distances in the clonedal-sh2 interval of theZea mays L. genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8268–8272
Clayberg CD (1970) Mapping male-sterile genes on chromosome 11. Report Tomato Genet Coop 20:13
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1984) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1989a) Analysis of tomato DNA by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 7:17–27
Ganal MW, Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989b) Pulsed field gel electrophoresis and physical mapping of large DNA fragments in theTm-2a region of chromosome 9 in tomato. Mol Gen Genet 215:395–400
Giovannoni JJ, Noensie EN, Ruezinsky DM, Xianghuai L, Tracy SL, Ganal MW, Martin GB, Pillen K, Alpert K, Tanksley SD (1995) Molecular genetic analysis of theripening-inhibitor andnon-ripening loci of tomato: a first step in genetic map-based cloning of fruit ripening genes. Mol Gen Genet 248:195–206
Giraudat J, Hauge BM, Valon C, Smalle J, Parcy F, Goodman HM (1992) Isolation of theArabidopsis ABI3 gene by positional cloning. Plant Cell 4:1251–1261
Jahnen W, Lush WM, Clarke WM (1989) Inhibition of in vitro pollen tube growth by isolated S-glycoproteins ofNicotiana alata. Plant Cell 1:501–510
Kaul MLH (1988) Male sterility in higher plants. Springer-Verlag, New York
Larsen F, Gundersen G, Prydz H (1992) Choice of enzymes for mapping based on CpG islands in the human genome. Gene Anal Techniques 9:80–85
Martin GB, Brommonschenkel SH, Chunwonse J, Frary A, Ganal MW, Spivey R, Wu T, Earle ED, Tanksley SD (1993a) Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science 262:1432–1436
Martin GB, De Vincente MC, Tanksley SD (1993b) High-resolution linkage analysis and physical characterization of thePto bacterial resistance locus in tomato. Molec Plant-Microbe Interact 6:26–34
McCormick S (1993) Male gametophyte development. Plant Cell 5:1265–1275
Messeguer R, Ganal MW, Steffens JC, Tanksley SD (1991) Characterization of the level, target sites and inheritance of cytosine methylation in tomato nuclear DNA. Plant Mol Biol 16:753–770
Moffatt BA, Somerville C (1988) Positive selection for male-sterile mutants ofArabidopsis lacking adenine phosphoribosy transferase activity. Plant Physiol 86:1150–1154
Paterson AH, Wing RA (1993) Genome mapping in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnology 4:142–147
Putterill J, Robson F, Lee K, Simon R, Coupland G (1995) TheCONSTANS gene ofArabidopsis promotes flowering and encodes a protein showing similarities to zinc finger transcription factors. Cell 80:847–857
Rick CM (1948) Genetics and development of nine male-sterile tomato mutants. Hilgardia 18:599–633
Rick CM (1980) Tomato Linkage Survey. Report Tomato Genet Coop 30:2–17
Sarfatti M, Katan J, Fluhr R, Zamir D (1989) An RFLP marker in tomato linked to theFusarium oxysporum resistance gene12. Theor Appl Genet 78:755–759
Segal G, Sarfatti M, Schaffer MA, Ori N, Zamir D, Fluhr R (1992) Correlation of genetic and physical structure in the region surrounding the12 Fusarium oxysporum resistance locus in tomato. Mol Gen Genet 231:179–185
Southern E (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, De Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton T, Giovannoni J, Grandillo S, Martin G, Messeguer R, Miller L, Paterson A, Pineda O, Roder M, Wing R, Wu W, Young N (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Van Daelen RAJJ, Gerbens F, Van Ruissen F, Aarts J, Hontelez J, Zabel P (1993) Long-range physical maps of two loci (Aps-1 andGP79) flanking the root-knot nematode resistance gene (Mi) near the centromere of tomato chromosome 6. Pl Mol Biol 23:185–192
Weide R, Van Wordragen MF, Lankhorst RK, Verkerk R, Hanhart C, Liharska T, Pap E, Stam P, Zabel P, Koornneef M (1993) Integration of the classical and molecular linkage maps of tomato chromosome 6. Genetics 135:1175–1186
Wing RA, Zhang HB, Tanksley SD (1994) Map-based cloning in crop plants. Tomato as a model system: I. Genetic and physical mapping ofjointless. Mol Gen Genet 242:681–688
Zamir D, Tanksley SD (1988) The tomato genome is comprised largely of fast-evolving, low copy-number sequences. Mol Gen Genet 213:254–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorman, S.W., Banasiak, D., Fairley, C. et al. A 610 kb YAC clone harbors 7 cM of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) DNA that includes themale sterile 14 gene and a hotspot for recombination. Molec. Gen. Genet. 251, 52–59 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174344
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174344