Abstract
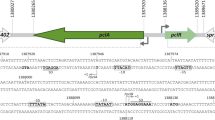
Streptococcal C5a peptidase (SCP), encoded byscpA inStreptococcus pyogenes, is a surface molecule which is able to cleave and inactivate the chemotactic factor C5a. ThescpA gene is part of thevir regulon and subject to positive regulation by the Mga protein. It is down-regulated compared to another Mga-activated gene,emm. A chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene was used to measurescpA promoter activity. Previous work had shown that when a large portion of thescpA promoter region was deleted, expression of CAT increased relative to the wild-type. This deleted region was found to contain an inverted repeat. In this study we show that the inverted repeat in the leader mRNA is the site of transcription termination, which down-regulates expression ofscpA. This is a novel mechanism for regulation of gene expression inS. pyogenes. A specific deletion of the inverted repeat in thescpA promoter-CAT reporter construct was made using inverse PCR. Expression was measured from single-copy chromosomal integrants. When the inverted repeat was deleted, expression increased. Furthermore, Northern hybridization confirmed the existence of a truncated transcript, consistent with a transcription termination mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1989) Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Biswas I, Gruss A, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (1993) High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 175:3628–3635
Bollet C, Gevaudan MJ, deLamballerie X, Zandotti C, deMicco P (1991) A simple method for the isolation of chromosomal DNA from Gram-positive or acid-fast bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1955
Caparon MG, Scott JR (1987) Identification of a gene that regulates expression of M protein, the major virulence determinant of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8677–8681
Caparon MG, Geist RT, Perez-Casal J, Scott JR (1992) Environmental regulation of virulence in group A streptococci: transcription of the gene encoding M protein is stimulated by carbon dioxide. J Bacteriol 174:5693–5701
Chen CC, Cleary PP (1989) Cloning and expression of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene inEscherichia coli: linkage to the type 12 M protein gene. Infect Immun 57:1740–1745
Chen CC, Cleary PP (1990) Complete nucleotide sequence of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene ofStreptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem 265:3161–3167
Chen C, Bormann N, Cleary PP (1993) VirR and Mry are homologous trans-acting regulators of M protein and C5a peptidase expression in group A streptococci. Mol Gen Genet 241:685–693
Dougherty BA, van de Rijn I (1994) Molecular characterization ofhasA from an operon required for hyaluronic acid synthesis in group A streptococci. J Biol Chem 269:169–175
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Fischetti VA (1989) Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev 2:285–314
Horinouchi S, Weisblum B (1982) Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol 150:815–825
Hudson MC, Stewart GC (1986) Differential utilization ofStaphylococcus aureus promoter sequences byEscherichia coli andBacillus subtilis. Gene 48:93–100
LaPenta D, Zhang XP, Cleary PP (1994)Streptococcus pyogenes type IIa IgG Fc receptor expression is co-ordinately regulated with M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase. Mol Microbiol 12:873–879
Majumdar D, Avissar YJ, Wyche JH (1991) Simultaneous and rapid isolation of bacterial and eukaryotic DNA and RNA: a new approach for isolating DNA. Biotechniques 11:94–101
Okada N, Geist RT, Caparon MG (1993) Positive transcriptional control ofmry regulates virulence in the group A streptococcus. Mol Microbiol 7:893–903
Perez-Casal J, Caparon MG, Scott JR (1991) Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene ofStreptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol 173:2617–2624
Perez-Casal J, Price JA, Maguin E, Scott JR (1993) An M protein with a single C repeat prevents phagocytosis ofStreptococcus pyogenes: use of a temperature-sensitive shuttle vector to deliver homologous sequences to the chromosome ofS. pyogenes. Mol Microbiol 8:809–819
Podbielski A (1992) Ubiquitous occurrence ofvirR andscpA genes in group A streptococci. Med Microbiol Immunol 181:227–240
Podbielski A, Peterson JA, Cleary P (1992) Surface protein-CAT reporter fusions demonstrate differential gene expression in thevir regulon ofStreptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol 6:2253–2265
Richardson JP (1993) Transcription termination. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 28:1–30
Robbins JC, Spanier JG, Jones SJ, Simpson WJ, Cleary PP (1987)Streptococcus pyogenes type 12 M protein gene regulation by upstream sequences. J Bacteriol 169:5633–5640
Scott JR, Cleary P, Caparon MG, Kehoe M, Heden L, Musser JM, Hollingshead S, Podbielski A (1995) New name for the positive regulator of the M protein of group A streptococcus. Mol Microbiol 17:799
Shaw WV (1975) Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloram-phenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol 43:737–755
Simpson WJ, Cleary PP (1987) Expression of M type 12 protein by a group A streptococcus exhibits phaselike variation: evidence for coregulation of colony opacity determinants and M protein. Infect Immun 55:2448–2455
Simpson WJ, LaPenta D, Chen C, Cleary PP (1990) Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by thevirR locus. J Bacteriol 172:696–700
Steiner K, Malke H (1995) Transcription termination of the streptokinase gene ofStreptococcus equisimilis H46A: bidirectionality and efficiency in homologous and heterologous hosts. Mol Gen Genet 246:374–380
Wexler DE, Cleary PP (1985) Purification and characteristics of the streptococcal chemotactic factor inactivator. Infect Immun 50:757–764
Wexler DE, Chenoweth DE, Cleary PP (1985) Mechanism of action of the group A streptococcal C5a inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:8144–8148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pritchard, K.H., Cleary, P.P. Differential expression of genes in thevir regulon ofStreptococcus pyogenes is controlled by transcription termination. Molec. Gen. Genet. 250, 207–213 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174180
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174180