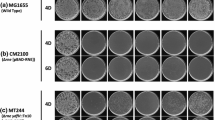
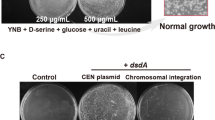
Abstract
In the yeastYarrowia lipolytica the levels of the alkaline extracellular protease (AEP) and acid extracellular protease (AXP) are controlled by the pH of the growth medium. When the pH of growth medium is kept close to 4.0, levels of AXP are high and those of AEP are low, whereas at pH above 6.0 the opposite is true. Mutations which mimic the effects on the protease system of growth at alkaline pH have been identified in two genes,RPH1 andRPH2, inY. lipolytica. Detailed genetic studies showed that mutations in these two genes are dominant in heterozygous diploids, and that their effects are additive in haploid double mutants. These mutants show that pH regulates AEP expression independently from other metabolic signals. These mutants are not detectably affected in their growth rates, nor in internal pH homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arst HN Jr, Bignell E, Telburn J (1994) Two new genes involved in signalling ambient pH inAspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 245:787–790
Bagg A, Neilands JB (1987) Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron(II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon inEscherichia coli. Biochemistry 26:5471–5477
Beckerich JM, Fournier P, Gaillardin C, Heslot H, Rochet M, Treton B (1984) In: Ball C (ed) Genetics and breeding of industrial micro-organisms. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 115–157
Blanchin-Roland S, Cordero Otero RR, Gaillardin C (1994) Two upstream activation sequences control the expression of theXPR2 gene in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica. Mol Cell Biol 14:327–338
Caddick MX, Brownlee AG, Arst HN Jr (1986) Regulation of gene expression by pH of the growth medium inAspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 203:346–353
Cimprich P, Slavik J, Kotyk A (1995) Distribution of individual cytoplasmic pH values in a population of the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 130:245–251
Dorn G (1965) Genetic analysis of the phosphatases inAspergillus nidulans. Genet Res 6:13–26
Foster JW, Hall HK (1992) Effect ofSalmonella typhimurium ferric uptake regulator (fur) mutations on iron- and pH-regulated protein synthesis. J Bacteriol 174:4317–4323
Foster JW, Park YK, Bang IS, Karem K, Betts H, Hall HK, Shaw E (1994) Regulatory circuits involved with pH-regulated gene expression inSalmonella typhimurium. Microbiology 140:341–352
Goffeau A, Layman CWS (1981) The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 639:197–223
Gritz L, Davies J (1983) Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression inEscherichia coli andSacchromyces cerevisiae. Gene 25:179–188
Haworth RS, Fliegel L (1993) Intracellular pH inSchizosaccharomyces pombe — comparison withSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biochem 124:131–140
Hoffman CS, Winston F (1987) A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation ofEscherichia coli. Gene 57:267–272
Imai T, Nakajima I, Ohno Y (1994) Development of a new method of evaluation of yeast vitality by measuring intracellular pH. J Amer Soc Brew Chem 52:5–8
Nicaud J-M, Fabre E, Gaillardin C (1989) Expression of invertase activity inYarrowia lipolytica and its use as a selective marker. Curr Genet 16:253–260
Ogrydziak DM, Scharf SJ (1982) Alkaline extracellular protease produced bySaccharomycopsis lipolytica CX161-1B. J Gen Microbiol 128:1225–1234
Ogrydziak DM, Demain LA, Tannenbaum SR (1977) Regulation of extracellular protease production inCandida lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 497:525–538
Ogrydziak DM (1988) Development of genetic maps of non-conventional yeasts. J Basic Microbiol 28:185–196
Olson ER (1993) Influence of pH on bacterial gene expression. Mol Microbiol 8:5–14
Orejas M, Espeso EA, Tilburn J, Sarkar S, Arst HN Jr, Peñalva MA (1995) Activation of theAspergillus PacC transcription factor in response to alkaline ambient pH requires proteolysis of the carboxy-terminal moiety. Genes Dev 9:1622–1632
Raleigh EA, Lech K, Brent R (1989) In: Ausubel FM (ed) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience; NY. Unit 1.4.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd ed). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Serrano R, Kielland-Brandt MC, Fink GR (1986) Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na++K+), K+-and Ca2+-ATPase. Nature 319:689–693
Shah AJ, Tilburn J, Adlard MW, Arst HN Jr (1991) pH regulation of penicillin production inAspergillus nidulans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 77:209–212
Sherman F, Fink GR, Hicks JB (1986) Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Slavík J (1982) Intracellular pH of yeast cells measured with fluorescent probes. FEBS Lett 140:22–26
Tilburn J, Sarkar S, Widdick DA, Espeso EA, Orejas M, Mungroo J, Peñalva MA, Arst HN Jr (1995) TheAspergillus PacC zinc finger transcription factor mediates regulation of both acid-, and alkaline-expressed genes by ambient pH. EMBO J 14:779–790
Werner W, Rey HG, Wielinger H (1970) Z Anal Chem 252:224–225
Xuan J-W, Fournier P, Gaillardin C (1988) Cloning of theLYS5 gene encoding saccharopine dehydrogenase from the yeastYarrowia lipolytica by target integration. Curr Genet 14:5–21
Yamada T, Ogrydziak D (1983) Extracellular acid protease produced bySaccharomycopsis lipolytica. J Bacteriol 154:23–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. A. M. J. J. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordero Otero, R., Gaillardin, C. Dominant mutations affecting expression of pH-regulated genes inYarrowia lipolytica . Molec. Gen. Genet. 252, 311–319 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173777
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173777