Abstract
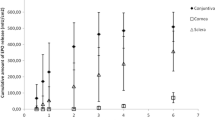
Changes in iron (Fe) concentration and total-iron-binding capacity (TIBC) of the intraocular fluids were measured during endotoxin-induced ocular inflammation in rabbits over a 3-week time course. In the aqueous humor, both Fe and TIBC increased to peak levels 24 h after intravitreal injection of endotoxin (10 ng) and gradually decreased to baseline levels by 3 weeks. In the uninflamed eye, the TIBC of the aqueous was only 23% saturated. During inflammation the TIBC became more highly saturated over time, reaching 50% at 3 weeks. In the vitreous humor the picture was more complicated due to the presence of slight hemorrhage. Noncellular Fe and TIBC increased to peak levels by 7 days, while TIBC approached 100% saturation. Both returned to baseline by 21 days. The influx of the partially saturated plasma protein transferrin through disrupted blood-ocular barriers most likely accounts for the increased TIBC in the inflamed eye and could provide some protection against the potentially harmful effects of Fe arising from tissue necrosis and hemolysis subsequent to hemorrhage. Under conditions of the model of inflammation studied here, the TIBC was not exceeded at any time during the 3 weeks. However, with more severe and long-lasting inflammation or when there is greater hemorrhage, the TIBC could be exceeded. This could lead to greater, and perhaps irreversible, damage to ocular tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dernouchamps JP, Vaerman JP, Michiels J, Heremans JF (1974) La transferrine des liquides endoculaires chez le lapin. Ophthalmologica 170: 72–83
Fleisher LN, McGahan MC (1986) Time course for prostaglandin synthesis by rabbit lens during endotoxin-induced ocular inflammation. Curr Eye Res 5: 629–634
Forrester JV, Lee WR, Williamson J (1978) The pathology of vitreous hemorrhage. I. Gross and histological appearances. Arch Ophthalmol 96: 703–710
Gutteridge JMC (1984) Tissue damage by oxy-radicals: the possible involvement of iron and copper complexes. Med Biol 62: 101–104
Hogan MJ, Kimura SJ, Thygeson P (1950) Signs and symptoms of uveitis. I. Anterior uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 47: 155–170
McGahan MC, Bito LZ (1983) The pathophysiology of the ocular microenvironment. I. Preliminary report on the possible involvement of copper in ocular inflammation. Curr Eye Res 2: 883–885
McGahan MC, Fleisher LN (1986) A micromethod for the determination of iron and total iron-binding capacity in intraocular fluids and plasma using electrothermal atomic absorption spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 156: 397–402
McGahan MC, Fleisher LN (1986) Antioxidant activity of aqueous and vitreous humor from the inflamed rabbit eye. Curr Eye Res 5: 641–645
Stocks J, Gutteridge JMC, Sharp RJ, Dormandy TL (1974) The inhibition of lipid autooxidation by human serum and its relation to serum proteins and a-tocopherol. Clin Sci Mol Med 47: 223–233
Toth KM, Clifford DP, Berger EM, White CW, Repine JE (1984) Intact human erythrocytes prevent hydrogen peroxide-mediated damage to isolated perfused rat lungs and cultured bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 74: 292–295
Underwood EJ (1978) Trace elements in human and animal nutrition. Academic Press, New York
Van Bockxmeer FM, Martin CE, Constable LJ (1983) Ironbinding proteins in vitreous humor. Biochim Biophys Acta 758: 17–23
White A, Handler P, Smith EL (1968) Principles of biochemistry, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 747
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGahan, M.C., Fleisher, L.N. Inflammation-induced changes in the iron concentration and total iron-binding capacity of the intraocular fluids of rabbits. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 226, 27–30 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172712
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172712