Abstract
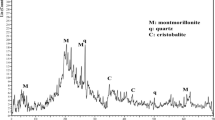
The sorption and desorption of uranium, thorium and mercury on a western Anatolian montmorillonite, obtained from the deposit located in Kula, were studied by application of a batch technique. The clay used is a tertiary clay originally found in a rather large geological formation of west Anatolia. It is nearly pure montmorillonite. Its cation exchange capacity (CEC) determination was performed for ammonium acetate by the Mehlich procedure. The mean CEC was found to be 83 meq/100 g, which, taking into account that CEC determinations were carried out on unfractionated material, is in good agreement with previously reported data. The concentration ranges were between 70–1500 ppm for mercury and 100–2000 ppm for thorium and uranium. The relative importance of test parameters, e.g., pH, clay particle size, groundwater composition, contact time and solid/water ratio, which determine the distribution coefficients was studied. The sorption coefficients varied between 2.7–6.4 ml/g for U, 0.22–1.59 ml/g for Th and 152.4–427.2 ml/g for Hg. The differences of distribution coefficients are discussed. The data could be fitted to Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. The quantities of the sorbed and desorbed Th were much lower than its theoretical CEC's. This attitude was attributed to the blocking of montmorillonite by cation islands sorbed in the interlayer. Hg is sorbed most strongly. The experimental results indicate that the montmorillonites studied should be effective components of the buffer and backfill material and lead to eventual immobilization of these elements, which are environmentally dangerous.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fujiki, 6th Int. Conf. Water Poll. Res. Paper No. 12 (1972).
D.E. Robertson, D.S. Sklarew, K.B. Olsen, N.S. Bloam, E.A. Crecelies, C.W. Apts, Research Project 2020-3, Final Report, Batelle Pacific Northwest Laboratories (1987).
L.H. Baetsle,Waste Management, 2 (1990) 907.
European Catalogue of Geological Formations Having Favorable Characteristics for the Disposal of Solidified High-level and Long-lived Radioactive Wastes, CEC Report EUR 6891 (1980).
L.H. Baetsle et al., R. Heremans et al., H. Beale et al. (Ed. by R. Simon and S. Orlowski), Harwood Academic Publishers, EUR 6871 (1980), Proc. First Eur. Conf., Luxemburg, (1980), pp. 442, 468, 488.
R.T. Di Giulio, E.A. Ryan,Water Air Soil Poll., 33 (1987) 205.
D. Schmidt, P. Freimann P.,Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem., 317 (1984) 385.
N. Garisto, F. Garisto,Ann. Nucl. Energy, (1990), VI., 17, 4, 183.
J. Bell, T.H. Bates,Sci. Tot. Env., 69 (1988) 297.
P. F. Salter, L.L. Ames, J.J. Mc.Garrah, Rockwell Hanford Operations Report, RHO-BWL-LD-48 (1981).
B. Alard, G.W. Beal, T. Krajewski,Nucl. Tech., 49 (1980) 474.
J.J.W. Higgo,Prog. Nucl. Energy, 19 (2) (1987) 173.
J.D. Rhoades, Methods of Soil Analysis, Am. Soc. Agron., Wisconsin, (1982) pp. 149.
M. Polemio, J.D. Rhoades,Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J., 41 (1977) 524.
A. Mehlich,Soil Sci., 66 (1948) 429.
I. Carlsen, P. Bo, Environ. Migr. Long-Lived Radionuclides Proc. Int. Sym., Vienna, (1981), IAEA-SM-257/82, pp. 97.
K.H. Lieser, B. Gleitsmann, T.H. Steinkopff,Radiochim. Acta, 40 (1986) 33.
J.J.W. Higgo,Prog. Nucl. Energy, 19 (2) (1987) 173.
R.E. Grim, Clay Mineralogy, Mc Graw Hill, New York (1968) pp. 56.
J.J. Fritz, J.J. Ford,Anal. Chem., 25 (1953) 1640.
Methodes d'Analyse, Presse Universitaire de France, Paris, (1964 and 1970), Vol. 3, pp. 134 and Vol. 5, pp. 260.
H. Freundlich, Colloid and Capil. Chem., Methuen, London (1926).
I. Langmuir,J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 40 (1918) 1361.
H. Akçay, F. Kurtulmuş,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., Letters, 200 (1995) 529.
H. Akçay, S. Kilinç,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., Letters, 212 (1996) 173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akçay, H., Kilinç, S. & Karapire, C. A comparative study on the sorption and desorption of Hg, Th and U on clay. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry Letters 214, 51–66 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02165058
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02165058