Abstract
Two main types of side effects must be considered in hyperbaric oxygenation: respiratory disturbances or pulmonary changes and central nervous system lesions. The effects on the central nervous system may lead to a tonoclonic seizure. Light- and electron-microscope examination of the brain after experimental hyperbaric oxygen convulsions revealed typical predilection sites for nerve cell alterations which are not identical to localizations of changes caused by other noxious agents. They are regarded as specific changes due to the hyperoxia and their localization in the brain stem correlates to the origin of electrical discharges in hyperbaric oxygen convulsions.
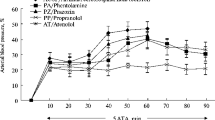
Pharmacological investigations on the symptoms of oxygen intoxication revealed the alternating effects between pulmonary and central nervous system changes.
Zusammenfassung
Neben den Auswirkungen auf die Luftwege und das Lungengewebe sind es v. a. zentralnervöse Erscheinungen, die bei Hyperoxie und hyperbarer Oxygenation zu beachten sind. Sie gipfeln in dem als Paul-Bert-Effekt bekannten Vergiftungsbild hyperbaren Sauerstoffs, einem auch beim Menschen beobachteten tonisch-klonischen Krampfanfall.
Umfangreiche licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen des Zentralnervensystems, die nach tierexperimenteller Sauerstoffkrampferzeugung durchgeführt wurden, zeigten im Stammhirn besondere Prädilektionsstellen für Nervenzellschädigungen, die von anderen Noxen nicht bekannt sind und daher als spezifische Hyperoxiefolgen betrachtet werden.
Sie geben in Zusammenhang mit elektroencephalographischen Befunden Aufschluß über den Sauerstoffkrampf als einen zentrencephal-epileptischen Vorgang.
Pharmakologisch-toxikologische Untersuchungen zeigten ferner, daß im Falle akuter hyperoxischer Vergiftung zentralnervöse und pulmonale Erscheinungen in Wechselbeziehung zueinander stehen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bert, P.: La pression barometrique, recherches de physiologie experimentale. Paris: Masson. 1878. Englische Übersetzung: Barometrique pressure. Researches in experimental physiology. M. A. Hitchcock, F. A. Hitchcock. Columbus, Ohio: College Book Co. 1943
Bean, J. W.: Cerebral O2 in exposure to O2 atmospheric and higher pressures and influence of CO2. Amer. J. Physiol.201, 1192 (1961)
Donald, K. W.: Oxygen poisoning in man. Brit. med. J.1, 667 (1947)
Gillen, H. W.: Oxygen convulsions in man. In: Proceedings of the third international conference on hyperbaric medicine. Ed.: I. W. Brown, B. G. Cox, Washington, D. C.: Nat. Acad. Sci.-Nat. Res. Council. 1966
Jamieson, D., van den Brenk, H. A. S.: Measurement of oxygen tensions in cerebral tissues of rats exposed to high pressures of oxygen. J. appl. Physiol.18, 869 (1963)
Lambertsen, C. J.: Effects of oxygen at high partial pressures. In: Handbook of physiology. Ed.: W. O. Fenn, H. Rahn. Sect. 3, Respiration Vol. II. Amer. Physiol. Soc., Washington, D. C. 1965
Lambertsen, C. J.: Basic requirements for improving diving depth and decompression tolerance. In: Underwater Physiology. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1966
Malorny, G.: Zum Mechanismus der Sauerstoffvergiftung. Habil. Schr. Kiel 1943
Nolte, H.: Die Sauerstoffintoxikation. Z. prakt. Anästh.4, 281 (1968)
Nolte, H.: Histologische Aspekte zum Problem der Sauerstoffintoxikation. In: Überleben auf See. II. Marinemedizinisch-wissenschafliches Symposium: Neue Wege des Tieftauchens und der Tiefseeforschung. Hrsg. Schiffahrtmedizinisches Institut. Kiel 1968
Nolte, H.: Hirngewebsveränderungen bei experimenteller Sauerstoffintoxikation. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)14, 312 (1970)
Nolte, H., Schnakenburg, K. v.: Morphologische und pharmakologisch-toxikologische Aspekte der Hyperoxie. Int. J. clin. Pharmacol.714, 340 (1973)
Nolte, H., Schnakenburg, K. v.: Pharmacological influences on oxygen intoxication in rats. In Vorbereitung
Rucci, F. S.: Changes in electrical activity of the cerebral cortex and some subcortical centers in hyperbaric oxygen. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.22, 231 (1967)
Schnakenburg, K. v., Nolte, H.: Histological Studies of Alterations in the Rat Brain Under Oxygen at High Pressure. Aerospace Med.9, 1013 (1970)
Schnakenburg, K. v.: Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen der Hirngewebsveränderungen bei akuter experimenteller Sauerstoffvergiftung. Virchows Arch. Abt. B Zellpath.8, 230 (1971)
Schnakenburg, K. v., Nolte, H.: Results of Electron Microscopic Studies in the Rat Brain Under Oxygen at High Pressure. Aerospace Med.44 (3), 259 (1973)
Voronov, I. B.: Brain structures and origin of convulsions caused by high oxygen pressure. Int. J. Neuropharmacol.3, 1803 (1967)
Bean, J. W.: Factors influencing clinical oxygen toxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 117/2 (1965)
Pilleri, G.: Zur Anatomie, Physiologie und Pathologie der Formatio reticularis. In: Die retikuläre Formation des Hirnstammes und ihre Bedeutung für das vegetativ-affektive Verhalten. Hrsg.: W. Birkmayer, G. Pilleri. Basel: F. Hoffmann-La Roche 1965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nolte, H., v. Schnakenburg, K. Einflüsse der Hyperoxie auf das Zentralnervensystem. Pneumonologie 149, 87–96 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02151743
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02151743