Abstract
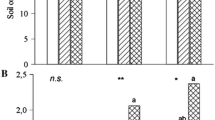
A pot culture experiment was conducted on a loamy sand soil to study the effect of FYM and Fe on dry matter yield and uptake of nutrients by oats (Avena sativa) crop in green-house. Application of Fe @ 5 and 20 ppm increased dry matter yield by 5.11 and 11.55 per cent, respectively. The per cent increase in dry matter yield over control with the application of 0.5 and 1.0 percent FYM was 19.06 and 30.07, respectively. Application of FYM increased concentration and uptake of P significantly. Phosphorus uptake increased by 23.60, 54.38, 91.01 and 134.61 per cent over control with 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 per cent FYM, respectively. Phosphorus concentration decreased at 20 ppm Fe but uptake increased significantly at 5 ppm Fe. Concentration and uptake of Ca increased with increasing amounts of Fe and application of FYM decreased concentration of Ca but uptake increased upto 1.0 per cent FYM over control. The Mg concentration and uptake decreased significantly with increased amount of Fe. Application of FYM also decreased Mg concentration but its uptake increased upto 1.0 per cent FYM and then decreased.
Iron concentration and uptake increased upto 2 per cent FYM and then decreased. Whereas concentration of Fe decreased with increased amount of applied Fe but its uptake increased nonsignificantly with increased amount of added Fe.
Managenese concentration and uptake decreased significantly with increased amount of applied Fe. Managenese concentration increased upto 0.5 per cent FYM but its uptake continued increasing with increasing amounts of applied FYM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basak, M. N. 1956 Effect of bulk organic manures on nutrition of rice. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci.4, 95–203.
Cheng, K. L. and Bray, R. H. 1951 Determination of calcium and magnesium in soil and plant material. Soil Sci.72, 449–455.
Dahiya, S. S. 1973 Studies on the availability and uptake of iron as affected by salinity, alkalinity and CaCO3 taking pea (Pisum sativum L.) as an indicator crop. Ph. D. Diss. (Unpublished), H.A.U., Hissar.
Dahiya, S. S. and Singh, R. 1980 Effect of farm yard manure and CaCO3 on the dry matter yield and nutrient uptake by oats (Avena sativa). Plant and Soil56, 391–402.
Koenig, R. A. and Johnson, C. R. 1942 Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in biological material. Ind. Engg. Chem. Analyst.14, 155–156. (1942).
Kumar, V. and Awasthi, K. S. 1977 Efficiency of different manures in relation to their effect on yield and nutrient uptake by grain sorghum. Agrochimica21, 327–334.
Singh, J. P. 1975 A study on the long-term effect of FYM and inorganic fertilizers on the yield of wheat and some soil properties. M. Sc. thesis (Unpublished), HAU, Hissar.
Singh, M. and Dahiya, S. S. 1976 Effect of calcium carbonate and iron on the availability and uptake of iron, manganese, phosphorus and calcium in pea (Pisum sativum). Plant and Soil54, 511–520.
Twyman, E. S. 1951 The iron and manganese requirements of plants. New Phytol.50, 210–226.
Watanabe, F. S., Lindsay, W. L. and Olson, S. R. 1965 Nutrient balance involving phosphorus, iron and zinc. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am.29, 562–565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Dahiya, S.S. Effect of farm yard manure and iron on dry matter yield and nutrients uptake by oats (Avena sativa). Plant Soil 56, 403–412 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143034
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143034