Abstract
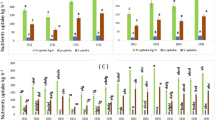
Water extracts of shoot of common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album), yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus) at 1% level significantly reduced soybean seed germination. Soybean seedlings inoculated with broth culture of nodule bacterium were grown for 25 days in N-free nutrient solution amended with cold water extracts of weed residues at 1 and 2% levels. At both levels extracts from residues of all weeds except that of lambsquarters enhanced growth of soybean. Nodulation was generally stimulated by the extracts of five weeds at 1% level except that of lambsquarters. Extracts from lambsquarters at 2% level completely suppressed and at 1% level reduced nodulation by 60%. Extracts from green foxtail (Setaria viridis), Pennsylvania smartweed (Polygonium pensylvanicum) and sunflower at 2% level reduced and at 1% level enhanced nodulation. The residues of lambsquarters shoot incorporated with soil at 0.5 and 1% levels caused 85 and 96% reduction respectively in seed germination and those of Pennsylvania smartweed and sunflower at 1% reduced seed germination by 40–70% but not at 0.5% level. The residues of foxtail and smartweed at both levels enhanced growth and nodulation. Under similar conditions nutsedge at 1% level stimulated nodulation but not growth. The residues of lambsquarters at both levels were inhibitory to nodulation but stimulated growth at 0.5% level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhowmik P C and Doll J D 1982 Corn and soybean response to allelopathic effects of crop and weed residues. Agron. J. 74, 601–606.
Cochran V L, Elliott L E and Papendick R I 1977 The production of phytotoxins from surface crop residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41, 903–908.
Colton C E and Einhellig F A 1980 Allelopathic mechanisms of velvet leaf (Abutilon theophrasti Medic., Malvaceae) on soybean. Am. J. Bot. 67, 1407–1413.
Drost D C and Doll J D 1980 The allelopathic effect of yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus) on corn (Zea mays) and soybeans (Glycine max). Weed Sci. 28, 229–233.
Hoagland D R and Arnon D I 1950 The water culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agric. Exp. Stn. Circ. #347.
Kanchan S D and Jayachandra 1979 Allelopathic effects ofParthenium hysterophorus L. I. Exudation of inhibitors through roots. Plant and Soil 53, 27–35.
Mallik M A B and Tesfai K 1985 Pesticidal effect on soybean-rhizobia symbiosis. Plant and Soil 85, 33–41.
McWhorter C G and Patterson D T 1979 Ecological factors affecting weed competition in soybean.In World Soybean Research Conf. II, Proceed. Ed. F T Corbin. pp 371–392. Westview Press, Boulder, Colorado.
Putnam A R 1983 Allelopathic chemicals, nature's herbicide in action. Chem. Engin. News 61, 34–45.
Rice E L 1964 Inhibition of nitrogen fixing and nitrifying bacteria by seed plants. Ecology 45, 824–837.
Rice E L 1968 Inhibition of nodulation of inoculated legume by pioneer plant species from abandoned fields. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 95, 346–358.
Rice E L 1971 Inhibition of nodulation of inoculated legumes by leaf leachates from pioneer plants species from abandoned fields. Am. J. Bot. 58, 368–371.
Rice E L 1984 Allelopathy, 2nd Edition, Academic Press, New York.
Rice E L, Lin C-Y and Huang C-Y 1981 Effects of decomposing rice straw on growth of and nitrogen fixation by Rhizobium. J. Chem. Ecol. 7, 333–343.
Vincent J M 1970 A manual for the practical study of Root-Nodule Bacteria. Blackwell Scientific Publ, Oxford, UK.
Weston L A and Putnam A R 1985 Inhibition of growth, nodulation and nitrogen fixation of legumes by quackgrass. Crop Sci. 25, 561–565.
Weston L A and Putnam A R 1986 Inhibition of legume seedling growth by residues and extracts of quackgrass (Agropyron repens). Weed Sci. 34, 366–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallik, M.A.B., Tesfai, K. Allelopathic effect of common weeds on soybean growth and soybean-Bradyrhizobium symbiosis. Plant Soil 112, 177–182 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02139993
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02139993