Abstract
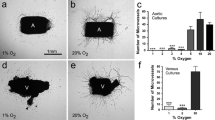
Hypoxic injury of vascular endothelial cells is hypothesized to be the initial cellular event in the formation of an atherosclerotic lesion. We studied the effect of various oxygen tensions on rabbit aortic endothelial cells in culture to determine macrophage adhesion and analyzed endothelial cell-conditioned media for fibroblast mitogenesis and transforming growth factor beta production. Fibroblast mitogenesis assay of endothelial cell-conditioned media revealed decreased activity at lower oxygen tensions. Further study revealed an inverse relationship between oxygen tension and aortic endothelial cell production of transforming growth factor beta despite lower total numbers of viable aortic endothelial cells at lower oxygen tensions. When rabbit aortic endothelial cells grown at various oxygen tensions were incubated with five day old bone marrow macrophages, an increase in macrophage adherence to aortic endothelial cells was noted at low oxygen tensions. Our observations suggest that aortic endothelial cell hypoxia leads to the production of transforming growth factor beta, a known monocyte chemoattractant. Monocytes may marginate and then adhere to endothelial cells, their adherence being augmented by endothelial cell hypoxia. This may contribute to the initial cellular events in the formation of an atherosclerotic lesion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
VIRCHOW R. Phlogose und thrombose im gefasssystem. In:Gessamlte Abhandlungen zur Wissenschaftlichen Medizin. Frankfurt-am-Main: Meidlinger Sohn und Co., 1856, pp 485.
SCHWARTZ SM. Disturbances in endothelial integrity.Ann NY Acad Sci 1982;401:228–233.
VAN FURTH R, HIRSCH JG, FEDORKO MF. Morphology and peroxidase cytochemistry of mouse promonocytes, monocytes, and macrophages.J Exp Med 1970;132:794–812.
VAN FURTH R, DIESSELHOFF-DEN DULK MMC. The kinetics of promonocytes and monocytes in the bone marrow.J Exp Med 1970;132:813–828.
HAUSER P, GILBERT V. The isolation and cultivation of rabbit bone marrow mononuclear phagocytes.Exp Cell Res 1978;111:353–361.
VAN FURTH R. An approach to the characterization of mononuclear phagocytes involved in pathological processes.Agents and Actions 1976;6:91–98.
FAGGIOTO A, ROSS R, HARKER L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation.Arteriosclerosis 1984;4:341–356.
ROSENFELD ME, TSUKADA T, GOWN AM, et al. Fatty streak initiation in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic and comparably hypercholesterolemic fat-fed rabbits.Atherosclerosis 1987;7:9–23.
WOLINSKY H, GLAGOV S. Comparison of abdominal and thoracic aortic medical structure in mammals: deviation of man from the usual pattern.Circ Res 1969;25:677–686.
MOSS AJ, SAMUELSON P, Angell C, et al. Polarographic evaluation of transmural oxygen availability in intact muscular arteries.J Atheroscler Res 19;8:803–810.
HAM AM.Histology. Toronto: J.B. Lippincott Co., 1969; pp 581–603.
NIINIKOSKI J, HEUGHEN C, HUNT TK. Oxygen tensions in the aortic wall of normal rabbits.Atherosclerosis 1973;17:353–359.
HEUGHEN C, NIINIKOSKI J, HUNT TK. Oxygen tensions in the lesions of experimental atherosclerosis of rabbits.Atherosclerosis 1973;17:361–367.
RUTHERFORD B.Vascular Surgery. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co., 1984, 19–45.
GARCIA CA, RUIZ RS. Diabetes and the eye.CIBA Clinical Symposia 1984;36:4.
BJORKERUD S, BONDJERS G. Arterial repair and atherosclerosis after mechanical injury: permeability and light microscopic characteristics of endothelial cells in non-atherosclerotic and atherosclerotic lesions.Atherosclerosis 1971;13:355–363.
BIERMAN EL. Atherosclerosis and other forms of atherosclerosis. In: ISSELBACHER KJ, ADAMS RD, BRAUNWALD E, et al. (eds).Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. Toronto: McGraw-Hill, 1980, pp 1156–1166.
HARRISON CV. Experimental arterial disease produced by cholesterol and vitamin D.J Pathol Bact 1933;36:447–453.
COGAN DG, KUWABARA T. Lipid keratopathy and atheroma.Circulation 1958;18:519–525.
LE COMPTE PM. Reactions of the vasa vasorum in vascular disease. In: BLUMENTHAL HT (ed).Cowdy's Atherosclerosis: A Survey of the Problem. Springfield: Charles C. Thomas, 1967, pp 212–214.
GANFIELD RA, ABBOUD FM, HEISTAD DD, et al. Vascular oxygen consumption and the myogenic response to increased wall tension.Circulation 1971;43/44:II-78.
ROMANOVSKA L, JANDOVA R, PREROVSKY I. Evaluation of structural changes in the arterial wall in juvenile hypertension.Cor et Vasa 1982;24:118–127.
GEIRINGER E. Intimal vascularization and atherosclerosis.J Pathol Bacteriol 1951;63:201–211.
NEREN RM, CORNHILL JF. The role of fluid mechanics in atherogenesis.J Biomech Eng 1980;102:181–189.
SPENCE JD, PERKINS DG, KLINE RL, et al. Hemodynamic modification of aortic atherosclerosis: effects of propanolol vs hydralazine in hypertensive hyperlipidemic rabbits.Atherosclerosis 1984;50:325–333.
HEH P, LOSENBER I. Atherosclerosis in rabbit aorta induced by systemic hypoxia.Angiology 1961;20:1–8.
KJELDSEN K, ASTREP P, WENSTREP J. Reversal of rabbit atherosclerosis by hyperoxia.J Atherosclerosis Res 1970;10:173–178.
BJORKERUD S, BONDJERS G. Endothelial integrity and viability in the aorta of the normal rabbit and rat as evaluated with dye exclusion tests and interference contrast microscopy.Atherosclerosis 1986;15:285–300.
RISBERG B, STERBERG B, BYLOCK A. Endothelial surface ultrastructure following hypoxia and hyperoxia.Artery 1986;13(5):287–306.
HOFNER G, SPEIR E, EPSTEIN S, et al. Hypoxia enhances endothelial cell production and release of heparin binding growth activities.Clin Res 1988;36(3):541A.
WAHL SM, HUNT DA, WAKEFIELD LM, et al. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production.Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1987;84:5788–5792.
DUSTIN ML, ROTHLEIN R, BHAN AK, et al. Induction by IL-1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1).J Immunol 1986;137:245–254.
POBER JS, COLLINS T, GIMBRONE MA Jr, et al. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon.J Immunol 1986;137:1893–1896.
ROTHLEIN R, DUSTIN ML, MARLIN SD, et al. A human intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) distinct from LFA-1.J Immunol 1986;137:1270–1274.
HSU S-M, RAINE L, FANGER H. Use of avidin-biotinperoxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures.J Histochem Cytochem 1981;29:577–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Santilli, S.M., Fiegel, V.D., Aldridge, D.E. et al. Rabbit aortic endothelial cell hypoxia induces secretion of transforming growth factor beta and augments macrophage adhesion in vitro. Annals of Vascular Surgery 5, 429–438 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02133047
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02133047