Summary
Blood of an African green monkey, experimentally infected with the causative agent of the so called Frankfurt Marburg Syndrome (FMS) was collected 1 day prior to death and the titer of infectious virus determined by subcutaneous inoculation in African green monkeys. All inoculated monkeys died, including those, which received the blood sample diluted 10−10. The longest observed time between inoculation and death of the animals was 25 days.
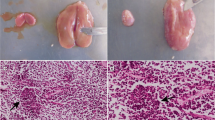
By electronmicroscopy evidence for the presence of virus particles in the liver of the infected African green monkeys was demonstrated. In liver, spleen and lymph nodes virus-specific antigen was shown by immuno fluorescence. The possible meaning of this finding for the diagnosis of spontaneous infections of monkeys with the causative agent of the FMS is discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Einem experimentell mit dem Erreger des sog. Frankfurt-Marburg-Syndroms (FMS) infizierten Cercopithecus aethiops wurde 1 Tag vor seinem Tod Blut entnommen und dieses Blut durch subcutane Verimpfung in weitere Cercopithecusaffen auf seinen Gehalt an infektiösen Viren titriert. Alle inoculierten Affen, einschl. jener, die eine 10−10-Verdünnung der untersuchten Blutprobe erhielten, starben. Die längste beobachtete Zeit zwischen Inoculation des virushaltigen Materials und dem Tod der Tiere betrug 25 Tage.
In der Leber dieser experimentell infizierten Cercopithecusaffen wurden elektronenoptisch Viruspartikel nachgewiesen. In Leber, Milz und Lymphknoten ließ sich fluorescenzserologisch virusspezifisches Antigen nachweisen. Die mögliche Bedeutung dieses Befundes zur Diagnostik einer spontanen Infektion von Affen mit dem Erreger des Frankfurt-Marburg-Syndroms wird diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Gordon Smith, C. E., D. I. H. Simpson, E. T. W. Bowen, andI. Zlotnik: Fatal human disease from vervet monkey. Lancet1967 II, 1119.
Haas, R., G. Maass u.W. Oehlert: Untersuchungen zur Tierpathogenität eines von Cercopithecus aethiops übertragenen menschenpathogenen Erregers. Med. Klin.35, 1359 (1968).
Hennessen, W., O. Bonin u.R. Mauler: Zur Epidemiologie der Erkrankungen von Menschen durch Affen. Dtsch. med. Wschr.93, 582 (1968).
Kissling, R. E., R. Q. Robinson, F. A. Murphy, andS. G. Whitfield: Agent of disease contracted from green monkeys. Science160, 888 (1968).
Maass, G., u.J. Hempel: Reversible Hemmung der Vermehrung des Virus SV-40 durch aromatische Alkohole. Z. med. Mikrobiol. u. Immunol.152, 45 (1966).
- J.Müller, N.Seemayer u. R.Haas: Die Herstellung von Gewebekulturen aus Nieren experimentell mit dem Erreger des Frankfurt-Marburg-Syndroms infizierter Cercopithecus aethiops. (In Vorbereitung.)
Marshall, J. D. E., andCh. W. Smith: Superiority of fluoresceinisothiocyanate for fluorescent antibody technique with a modification of its application. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)98, 898 (1958).
May, G., u.H. Knothe: Bakteriologisch-virologische Untersuchungen über die in Frankfurt a. M. aufgetretenen menschlichen Infektionen durch Meerkatzen. Dtsch. med. Wschr.93, 620 (1968).
Melnick, J. L., andR. McCombs: Classification and nomenclature of animal viruses, 1966. Progr. med. Virol.8, 400 (1966).
Peters, D., u.G. Müller: Die elektronenmikroskopische Erkennung und Charakterisierung des Marburger Erregers. ärztl. Mitt.65, 1831 (1968).
Provisional Committee for Nomenclature of Viruses: Proposals and recommendations. Ann. Inst. Pasteur109, 625 (1965).
Siegert, R., H. L. Shu u.W. Slenczka: Isolierung und Identifizierung des „Marburg-Virus“. Dtsch. med. Wschr.93, 604 (1968).
— — —,D. Peters u.G. Müller: Zur Ätiologie einer unbekannten, von Affen ausgehenden menschlichen Infektionskrankheit. Dtsch. med. Wschr.92, 2341 (1967).
Slenczka, W., H. L. Shu, G. Piepenburg u.R. Siegert: Antigen-Nachweis des „Marburg-Virus“ in den Organen infizierter Meerschweinchen durch Immunfluoreszenz. Dtsch. med. Wschr.93, 612 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Durchgeführt mit finanzieller Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (Unit „Medizinische Virologie“) und des Bundesgesundheitsministeriums.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haas, R., Maass, G., Müller, J. et al. Experimentelle Infektionen von Cercopithecus aethiops mit dem Erreger des Frankfurt-Marburg-Syndroms (FMS). Z. med. Mikrobiol. u. Immunol. 154, 210–220 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02123134
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02123134