Abstract
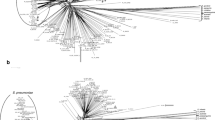
Seventy-seven clinical isolates ofXanthomonas maltophilia (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) were consecutively collected from the Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, ribotyped and compared with the ribotypes of 25 other clinical and reference strains ofXanthomonas maltophilia. Using restriction enzymeEcoRI, 20 different ribotypes were observed, with 78 isolates displaying the five most common types. Using another enzyme,BamHI, these 78 isolates were further subdivided into 16 different ribotypes. Three patients harboured two strains with different ribotypes. No type was found related to only one department and no single-strain outbreak was detected. The origin of this wealth of different strains in hospital patients needs to be established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodey GP: Epidemiological studies ofPseudomonas species in patients with leukemia. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1970, 260: 82–89.
Khardori N, Elting L, Wong E, Schable B, Bodey GP: Nosocomial infections due toXanthomonas maltophilia (Pseudomonas maltophilia) in patients with cancer. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1990, 12: 997–1003.
Victor MA, Arpi M, Bruun B, Jønsson V, Hansen MM:Xanthomonas maltophilia bacteremia in immunocompromised hematological patients. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1994, 26: 163–170.
Orr K, Gould FK, Sisson PR, Lightfoot NF, Freeman R, Burdess D: Rapid inter-strain comparison by pyrolysis mass spectrometry in nosocomial infection withXanthomonas maltophilia. Journal of Hospital Infection 1991, 17: 187–195.
Sanders CC, Sanders WEJ: β-lactam resistance in gram-negative bacteria: global trends and clinical impact. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1992, 15: 824–839.
Elting LS, Khardori N, Bodey GP, Fainstein V: Nosocomial infection caused byXanthomonas maltophilia: a case-control study of predisposing factors. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1990, 11: 134–138.
Hulisz DT, File TM: Predisposing factors and antibiotic use in nosocomial infections caused byXanthomonas maltophilia. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1992, 13: 489–490.
Schable B, Rhoden DL, Hugh R, Weaver RE, Khardori N, Smith PB, Bodey GP, Anderson RL: Serological classification ofXanthomonas maltophilia (Pseudomonas maltophilia) based on heat-stable O antigens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1989, 27: 1011–1014.
Schable B, Villarino ME, Favero MS, Miller JM: Application of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis to epidemiologic investigations ofXanthomonas maltophilia. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1991, 12: 163–167.
Bingen EH, Denamur E, Lambert-Zechovsky NY, Bourdois A, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Cezard J-P, Navarro J, Elion J: DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism differentiates crossed from independent infections in nosocomialXanthomonas maltophilia bacteremia. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1991, 29: 1348–1350.
Talon D, Bailly P, Leprat R, Godard C, Deconnink E, Cahn J-Y, Michel-Briand Y: Typing of hospital strains ofXanthomonas maltophilia by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Journal of Hospital Infection 1994, 27: 209–217.
Gemer-Smidt P: Ribotyping of theAcinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1992, 30: 2680–2685.
Morrison AJ, Hoffmann KK, Wenzel RP: Associated mortality and clinical characteristics of nosocomialPseudomonas maltophilia in a university hospital. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 24: 52–55.
Elting LS, Bodey GP: Septicemia due toXanthomonas species and non-aeruginosaPseudomonas species: an increasing incidence of catheter-related infections. Medicine 1990, 69: 296–306.
Rosenthal SL: Sources ofPseudomonas andAcinetobacter species found in human culture materials. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1974, 62: 807–811.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerner-Smidt, P., Bruun, B., Arpi, M. et al. Diversity of nosocomialXanthomonas maltophilia (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) as determined by ribotyping. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 14, 137–140 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02111874
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02111874