Abstract
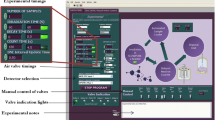
Apparatus is being developed for short irradiation and rapid counting at the NIST Reactor, optimized for accurate neutron activation analysis via activation products ranging in half-life from about 500 ms to 500 s. This facility is designed to irradiate a sample either in a well-thermalized neutron flux at 3·1013 n·cm−2·s−1, or in a higher flux with a larger fast and epithermal component. The design transfer time for a 1-ml rabbit is 500 ms, measured to 10 ms precision. Timing information for both irradiation and counting will be transferred automatically to the activation analysis workstation computer. The γ-ray spectrometer system is selected and tuned for accurate measurement at high and varying counting rates, using loss-free counting (LFC) technology. A detailed calibration and characterization of this system has been performed. Accurate measurement requires that attention be paid to the systematic and random errors to which LFC is subject, but this requirement is minor compared to the advantages of undistorted spectral shape, the ability to solve the decay equations exactly, and the wider useful range of counting rates in the spectrometer system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. S. Carter, T. M. Raby, in Use and Development of Low and Medium Flux Research Reactors,O. K. Harling, J. L. Clark, P. v. d. Hardt (Eds), Karl Thiemig, Munich, 1984, p. 180.
D. A. Becker, P. D. LaFleur, J. Radioanal. Chem., 19 (1974) 149.
R. E. Williams, Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc., 72 (1995) 312.
R. M. Lindstrom, R. F. Fleming, in: NBS Techn. Note 969,F. J. Shorten (Ed.), U.S. Govt. Print. Off., Washington, 1978, p. 78.
D. A. Becker, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 110 (1987) 393.
D. A. Becker, R. M. Lindstrom, J. K. Langland, R. R. Greenberg, J. Trace Microprobe Tech., submitted.
R. R. Greenberg, R. F. Fleming, R. Zeisler, Environ. Internat., 10 (1984) 129.
R. M. Lindstrom, R. F. Fleming, Radioact. Radiochem., 6 (1995) No. 2, 20.
G. P. Westphal, J. Radioanal. Chem., 70 (1982) 387.
R. M. Lindstrom, M. J. J. Ammerlaan, S. S. Then, J. Trace Microprobe Tech., submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contributions of the National Institute of Standards and Technology are not subject to copyright.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindstrom, R.M., Becker, D.A., Langland, J.K. et al. The NIST rapid irradiation and counting system. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 215, 47–50 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02109876
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02109876