Summary
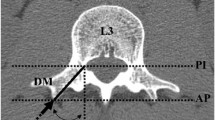
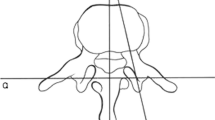
The geometric properties of 380 vertebral pedicles, ranging from T6 to L5, were analysed. Measurement were made directly from the specimens as well as from roentgenograms. The parameters considered were the horizontal and vertical pedicle diameters, pedicle angles in the transverse and sagittal planes, and the transverse and anteroposterior widths of the spinal canal and vertebral body. In addition, the length of the pedicle and the length of the pedicle including the vertebral body to the anterior cortex were measured along the pedicle axis and in a line parallel to the midline of the vertebral body. The smallest horizontal and vertical pedicle diameters were found at vertebral levels from T6 to T10. The correlation between pedicle widths and screw dimensions is obvious. In the transverse plane, the pedicle angle diverged from the vertebral body at all levels, except at T12. In the sagittal plane, the pedicles were angled cephalad from T6 to L3 and slightly caudally at L5. Knowledge of the length of the pedicle to the anterior vertebral body cortex is very important for safe screw purchase. At all levels, with the exception of T12, this length was found to be significantly greater along the pedicle axis than along a line parallel to the midline of the vertebral body.
Résumé
Les caractéristiques géométriques de 380 pédicules vertébraux, compris entre T6 et L5, ont été analysées. Les différentes mesures ont été pratiquées directement sur les pièces anatomiques et sur leurs images radiographiques. Le diamètre horizontal et vertical du pédicule vertébral, son angle avec le plan transversal et sagittal, le diamètre transversal et ventrodorsal du canal rachidien et du corps vertébral ont été pris en considération. La longueur du pédicule seule, ainsi que sa longueur associée à celle du corps vertébral jusqu'au cortex ventral ont été mesurées le long de l'axe pédiculaire et sur une ligne parallèle à la ligne médiane. Les diamètres pédiculaires horizontaux et verticaux les plus étroits ont été mis en évidence aux niveaux compris entre T6 et T10. La corrélation entre la largueur pédiculaire et la dimension des vis utilisées en clinique est évidente. Sur le plan transversal, le pédicule forme un angle plus ou moins divergent à partir du corps vertébral, à l'exception de T12. Sur le plan sagittal le pédicule a une direction crâniale de T6 à L3 et légèrement caudale pour L5. La connaissance de la distance comprise entre la limite dorsale du pédicule et le cortex ventral du corps vertébral est très importante pour pouvoir insérer une vis avec sûreté. Cette distance est significativement plus grande le long de l'axe pédiculaire par rapport à une ligne parallèle à l'axe médian à tous les niveaux sauf pour T12.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenstein S (1976) Measurements of the lumbar spinal canal in 2 racial groups. Clin Orthop 115: 42–46
Kortmann HR (1986) Die Morphometrie der Pedikel an der thorakolumbalen und lumbalen Wirbelsäule (in preparation)
Krag MH, Beynnon BD, Pope MH, Frymoyer JW, Haugh LD, Weaver DL (1986) An internal fixator for posterior application to short segments of the thoracic, lumbar, or lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop 203: 75–98
Louis R (1982) Chirurgie du rachis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Louis R (1986) Fusion of the lumbar and sacral spine by internal fixation with screw plates. Clin Orthop 203: 18–33
Magerl FP (1984) Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop 189: 125–141
Magerl FP (1985) External spine skeletal fixation. In: Weber BG, Magert FP (eds) The external fixation. Springer-Verlag, New York
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Lapresle P, Mazel C (1984) A secret in spine surgery: the pedicle. 51st Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Atlanta, Georgia, February
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C (1986) Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop 203: 7–17
Saillant G (1976) Etude anatomique des pédicules vertébraux: application chirurgicale. Rev Chir Orthop 62: 151–160
Steffee AD, Biscup RS, Sitkowski DJ (1986) Segmental spine plate with pedicle screw fixation. Clin Orthop 203: 45–53
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Widell EH, Thomas JC, Holland WR, Field BT, Spencer CW (1986) A biomechanical study of intrapeduncular screw fixation in the lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop 203: 99–112
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, Widell EH, Knight GW, Patwardhan AG, Thomas JC, Rothman SL, Fields BT (1987) Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine 12: 160–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchesi, D., Schneider, E., Glauser, P. et al. Morphometric analysis of the thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicles, anatomo-radiologic study. Surg Radiol Anat 10, 317–322 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02107905
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02107905