Summary
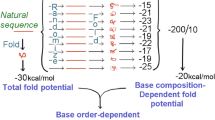
We present a phenomenological theory expressing the constraints operating on the (G+C) contents of the three codon positions, i.e., first, second, and third bases of codons, by using the smallest number of constraint parameters having clear physical and genetic meaning. Theoretical curves displaying base composition at each of the three codon sites are given. The agreement between the theoretical curves and the data points of 1277 genes is quite good irrespective of the species from which the DNAs originated; the curves might be universal ones and the constraint parameters might have general biological meanings in relation to the DNA/RNA and protein functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1985) Codon usage and geonome composition. J Mol Evol 22:363–365
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1986) Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol 24:1–11
Blake RD, Hinds PW, Earley S, Hillyard AL, Day GR (1986) Evolution and functional significance of the bias in codon usage. In: Sarma RH, Sarma MH (eds) Biomolecular stereodynamics. Proceedings of a conversation in the discipline of biomolecular stereodynamics, ed 4. Adenine Press, New York, pp 271–286
Cox EC, Yanofsky C (1967) Altered base ratios in the DNA of anEscherichia coli mutator strain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 58:1895–1902
Curnow RN, Kirkwood TBL (1989) Statistical analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid sequence data—a review. J R Statist Soc A 152:199–220
Dayhoff MO, Eck RV, Park CM (1972) A model of evolutionary change in proteins. In: Dayhoff MO (ed) Atlas of protein sequence and structure vol 5, chapter 9. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington DC
Freese E (1962) On the evolution of the base composition of DNA. J Theor Biol 3:82–101
Ikemura T, Ozeki H (1983) Codon usage and transfer RNA contents: organism-specific codon-choice patterns in reference to the isoacceptor contents. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 47:1087–1097
Jukes TH, Bhushan V (1986) Silent nucleotide substitutions and G+C content of some mitochondrial and bacterial genes. J Mol Evol 24:39–44
Kimura M (1981) Possibility of extensive neutral evolution under stabilizing selection with special reference to nonrandom usage of synonymous codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5773–5777
Kimura M, Crow JF (1978) Effect of overall phenotypic selection on genetic change at individual loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:6168–6171
Kurland CG (1987) Strategies for efficiency and accuracy in gene expression. 1. The major codon preference: a growth optimization strategy. Trends Biochem Sci 12:126–128
Nishikawa K, Kubota Y, Ooi T (1983) Classification of proteins into groups based on amino acid composition and other characters. II. Grouping into four types. J Biochem 94:997–1007
Ohama T, Muto A, Osawa S (1990) Role of GC-biased mutation pressure on synonymous codon choice inMicrococcus luteus, a bacterium with a high genomic CG-content. Nucleic Acids Res 18:1565–1569
Osawa S, Jukes TH, Muto A, Yamao F, Ohama T, Andachi Y (1987) Role of directional mutation pressure in the evolution of the eubacterial genetic code. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 52:777–789
Rushbrooke GS (1949) Introduction to statistical mechanics. Clarendon, Oxford
Sueoka N (1962) On the genetic basis of variation and heterogeneity of DNA base composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 48:582–592
Sueoka N (1988) Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2653–2657
Wada A, Suyama A (1985a) Third letters in codons counter-balance the (G+C)-content of their first and second letters. FEBS Lett 188:291–294
Wada A, Suyama A (1985b) Homogenous double-helix-stability in individual genes. In: Sarma RH, Sarma MH (eds) Biomolecular stereodynamics. Proceedings of a conversation in the discipline of biomolecular stereodynamics, ed 4. Adenine Press, New York, pp 255–269
Wada A, Suyama A (1986) Local stability of DNA and RNA secondary structure and its relation to biological functions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 47:113–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, A., Suyama, A. & Hanai, R. Phenomenological theory of GC/AT pressure on DNA base composition. J Mol Evol 32, 374–378 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101277
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101277