Abstract
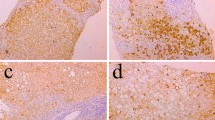
To assess the relationship between hepatitis C virus infection and Fas antigen expression on hepatocytes, we examined changes in hepatic Fas antigen expression in the presence or absence of active hepatitis C virus infection. Twenty patients with chronic hepatitis C infection were treated with interferon and underwent pre- and posttreatment liver biopsies. Patients were classified according to the absence (group A; n=9) or the presence (group B; n=11) of hepatitis C virus RNA (HCV-RNA) in the liver after interferon therapy. An immunohistochemical assay showed Fas antigen staining in hepatocytes membranes and cytoplasm with expression concentrated mainly in periportal areas. The percentage of Fas-positive cells in the liver before treatment was not different between group A (39.5 ± 19.1%) and group B (32.5 ± 15.6%). Hepatic Fas expression was reduced significantly after treatment (24.3 ± 10.6%) compared with the pretreatment values in group A (p < 0.05) but not in group B (25.9 ± 16.9%). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the degree of histologic improvement. These results suggest that hepatic Fas expression is associated with persistent infection of hepatitis C virus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y, Nagata S: The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 66:233–243, 1991
Nagata S: Fas and Fas ligand: A death factor and its receptor. Adv Immunol 57:129–144, 1994
Anel A, Buferne M, Boyer C, Schmit-Verhulst A-M, Golstein P: T cell receptor-induced Fas ligand expression in cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is blocked by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cyclosporin A. Eur J Immunol 24:2469–2476, 1994
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P, Nagata S: Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell 75:1169–1178, 1993
Searle J, Harmon BV, Bishop CJ, Kerr JFR: The significance of cell death by apoptosis in hepatobiliary disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:77–96, 1987
Schupper H, Hayashi P, Scheffel J, Aceituno S, Paglieroni T, Holland PV, Zeldis JB: Peripheral-blood mononuclear cell responses to recombinant hepatitis C virus antigens in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 18:1055–1060, 1993
Koziel MJ, Dudley D, Wong JT, Dienstag J, Houghton M, Ralston R, Walker BD: Intrahepatic cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for hepatitis C virus in persons with chronic hepatitis. J Immunol 149:3339–3344, 1992
Hiramatsu N, Hayashi N, Katayama K, Mochizuki K, Kawanishi Y, Kasahara A, Fusamoto H, Kamada T: Immunohistochemical detection of Fas antigen in liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 19:1354–1359, 1994
Yousuf M, Nakano Y, Tanaka E, Sodeyama T, Kiyosawa K: Persistence of viremia in patients with type-C chronic hepatitis during long-term follow-up. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:812–816, 1992
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagel JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ: Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis, grading, and staging. Hepatology 19:1513–1520, 1994
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate-phenol chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159, 1987
Kanai K, Iwata K, Nakao M, Okamoto H: Suppression of hepatitis C virus RNA by interferon a. Lancet 336:245, 1990
Okamoto H, Okada S, Sugiyama Y, Tanaka T, Sugai Y, Akahane Y, Machida A, Mishiro S, Yoshizawa H, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M: Detection of hepatitis C virus by a two-stage polymerase chain reaction with two pairs of primers deduced from the 5′-noncoding region. Jpn J Exp Med 60:215–222, 1990
Kwok S, Higuchi R: Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature 339:237–238, 1989
Okamoto H, Sugiyama Y, Okada S, Kurai K, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, Tanaka T, Sato K, Tsuda F, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M: Typing hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction with type-specific primers: Application to clinical surveys and tracing infectious sources. J Gen Virol 73:673–679, 1992
Hino K, Okuda M, Konishi T, Ishiko H, Okita K: Serial assay of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum for predicting response to interferon-α. Dig Dis Sci 40:14–20, 1995
Koji T, Kobayashi N, Nakanishi Y, Yoshii A, Hashimoto S, Shibata Y, Anjiki N, Yamamoto R, Aoki A, Ueda T, Kanazawa S, Nakane PK: Immunohistochemical localization of Fas antigen in paraffin sections with rabbit antibodies against human synthetic Fas peptides. Acta Histochem Cytochem 27:459–463, 1994
Simmonds P, Holmes EC, Cha TA, Chan SW, McOmish F, Irvine B, Beall E, Yap PL, Kolberg J, Urdea MS: Classification of hepatitis C virus into six major genotypes and a series of subtypes by phylogenetic analysis of the NS-5 region. J Gen Virol 74:2391–2399, 1993
Hoofnagle JH, Mullen KD, Jones DB, Rustgi V, Bisgeglie AD, Peters M, Waggoner JG, Park Y, Jones EA: Treatment of chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis with recombinant human alpha interferon; A preliminary report. N Engl J Med 315:1575–1578, 1986
Lowin B, Hahne M, Mattmann C, Tschoop J: Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature 370:650–652, 1994
Cohen JJ, Duke CD, Fadok VA, Sellines KS: Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 10:267–293, 1992
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AMJ, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W, Debatin KM, Krammer PH: Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245:301–305, 1989
Kobayashi N, Hamamoto Y, Yamamoto N, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Yonehara S: Anti-Fas monoclonal antibody is cytocidal to human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells without augmenting viral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9620–9624, 1990
Falk MH, Trauth BC, Debatin KM, Klas C, Gregory CD, Rickinson AB, Calender A, Lenoir GM, Ellwart JW, Krammer PH, Bornkamm GW: Expression of APO-1 antigen in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines correlates with a shift towards a lymphoblastoid phenotype. Blood 79:3300–3306, 1992
Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M: A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (anti-Fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 169:1747–1756, 1989
Owen-Schaub LB, Yonehara S, Crump III WL, Grimm EA: DNA fragmentation and cell death is selectively triggered in activated human lymphocytes by Fas antigen engagement. Cell Immunol 140:197–205, 1992
Mita E, Hayashi N, Iio S, Takehara T, Hijioka T, Kasahara A, Fusamoto H, Kamada T: Role of Fas ligand in apoptosis induced by hepatitis C virus infection. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 204:468–474, 1994
Tanaka M, Suda T, Takahashi T, Nagata S: Expression of the functional soluble form of human Fas ligand in activated lymphocytes. EMBO J 14:1129–1135, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, M., Hino, K., Fujii, K. et al. Hepatic fas antigen expression before and after interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Digest Dis Sci 41, 2453–2458 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02100142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02100142