Abstract
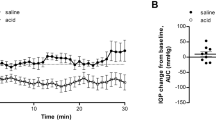
Acetic acid-induced pan colitis in rats leads not only to colonic injury but also to a bystander ileal injury, characterized by decreased fluid and electrolyte absorption without associated histological injury or infiltration of inflammatory cells. To examine the nature of this decreased ileal fluid and electrolyte absorption, we measured effect of acetic acid-induced pancolitis on ileal transmural sodium and chloride transport, as well as on ileal permeability to mannitol and inulin on mucosal sheets mounted in Ussing chambers. In addition, ileal tight junctional morphology was assessed by electron microscopy. In colitic animals, ileal serosal-to-mucosal sodium and chloride transmural fluxes were increased (P<0.05); compatible with the observed decrease in net fluid absorption. Mannitol and inulin ileal serosal-to-mucosal and mucosal-to-serosal ileal fluxes were similarly increased (P<0.05), suggesting that an increase in ileal permeability occurred during acetic acid-induced pancolitis. This increase in ileal permeability was not accompanied by changes in tight junctional ultrastructure. These results suggest that: (1) the decrease in ileal fluid and electrolyte absorption seen during acetic acid-induced rat pancolitis occurred in parallel with a rise in both transcellular and paracellular permeability, and (2) the ileal permeability changes were not accompanied by structural changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanderson IR, Boulton P, Menzies IS, Walker-Smith JA: Improvement of abnormal lactulose/rhamnose permeability in active Crohn's disease of the small bowel by an elemental diet. Gut 28:1073–1076, 1987
Bjarnason I, Zanelli G, Smith T, Prouse P, Williams P, Smethurst P, Delacey G, Gumpel MJ, Levi AJ: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug-induced intestinal inflammation in humans. Gastroenterology 93:480–489, 1987
Hamilton I, Cobden I, Rothwell J, Axon ATR: Intestinal permeability in coeliac disease: The response to gluten withdrawal and singe-dose gluten challenge. Gut 23:202–210, 1982
Madara JL, Stafford J: Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayer. J Clin Invest 83:724–727, 1989
Krugkliak P, Hollander D, Le K, Ma T, Dadufalza VD, Katz KD: Regulation of polyethylene glycol 400 intestinal permeability by endogenous and exogenous prostanoids. Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Gut 31:417–421, 1990
Wellmann W, Fink PC, Benner F, Schmidt FW: Endotoxemia in active Crohn's disease. Treatment with whole gut irrigation and 5-aminosalicylic acid. Gut 27:814–820, 1986
Empey LR, Cui N, Fedorak RN: Acetic acid-induced colitis results in bystander ileal injury. Agents Actions 38:76–84, 1993
Pantzar N, Ekstrom GM, Wang Q, Westrom BR: Mechanisms of increased intestinal [51Cr]EDTA absorption during experimental colitis in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 39:2327–2333, 1994
McLeod AD, Fedorak RN, Friend DR, Tozer TN, Cui N: A glucocorticoid prodrug facilitates normal mucosal function in rat colitis without adrenal suppression. Gastroenterology 106:405–413, 1994
Fedorak RN, Empey LR, MacArthur C, Jewell LD: Misoprostol provides a colonic mucosal protective effect during acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Gastroenterology 98:615–625, 1990
Charney AN, Goldfarb AS, Egnor RW: Effects of pH and cyclic adenosine monophosphate on ileal electrolyte transport in the rat and rabbit. Gastroenterology 100:410–418, 1991
O'Loughlin EV, Gall DG: Small intestinal absorption and secretion of fluid and electrolytes.In Gastrointestinal Secretion. JS Davison (ed). London, Wright, 1989, pp 157–170
Moore R, Pothoulakis C, LaMont JT, Carlson S, Madara JL:C. difficile toxin A increases intestinal permeability and induces Cl− secretion. Am J Physiol 259(2 pt 1):G165-G172, 1990
Hollander D: The intestinal permeability barrier. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:721–726, 1992
Hollander D: Crohn's disease—a permeability disorder of the tight junction? Gut 29:1621–1624, 1988
Jodal M, Fihn BM, Sjoqvist A: Effect of glucose on passive transport of extracellular probes across the rat small intestinal epitheliumin vivo. Gastroenterology 106:241, 1994
Atisook K, Carlson S, Madara JL: Effects of phlorizin and sodium on glucose-elicited alterations of cell junctions in intestinal epithelia. J Am Physiol 258 (1 pt 1):C77-C85, 1990
Flick JA, Tai YH, Levine SL, Watson AM, Montrose JM, Madara JL, Donowitz M: Intracellular Ca2+ regulation of tight junction resistance in T84 monolayer-a protein kinase C effect. Gastroenterology 100:A686, 1991
Phillips TE, Phillips TL, Neutra MR: Macromolecules can pass through occluding junctions of rat ileal epithelium during cholinergic stimulation. Cell Tissue Res 247:547–554, 1987
Madara JL, Barenberg D, Carlson S: Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: Further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J Cell Biol 102:2125–2136, 1986
Schulzke J, Fromm M, Bentzel CJ, Zeitz M, Menge H, Reicken E: Ion transport in the experimental short bowel syndrome of the rat. Gastroenterology 102:479–504, 1992
Weiss SJ: Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med 320:365–376, 1989
Nash S, Stafford J, Madara JL: Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on the barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest 80:1104–1113, 1987
Von Ritter C, Grisham MB, Hollwarth M, Inauen W, Granger DN: Neutrophil-derived oxidants mediate formyl-methionylleucyl-phenylalanine-induced increases in mucosal permeability in rats. Gastroenterology 97:778–780, 1989
Hollander D, Vadheim CM, Brettholz E, Petersen GM, Delahunty T, Rotter JI: Increased intestinal permeability in patients with Crohn's disease and their relatives. Ann Intern Med 105:883–885, 1986
Sartor RB, Bond TM, Schwab JH: Systemic uptake and intestinal inflammatory effects of luminal bacterial cell wall polymers in rat with acute colonic injury. Infect Immun 56:2101–2108, 1988
Hobson CH, Butt TJ, Ferry DM, Hunter J, Chadwick VS, Broom MF: Enterohepatic circulation of bacterial chemotactic peptide in rats with experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 94:1006–1013, 1988
Cui N, Friend DR, Fedorak RN: A budesonide prodrug accelerates treatment of colitis in rats. Gut 35:1439–1446, 1994
Jacobson K, McHugh K, Collins SM: Distal colitis causes changes in enteric nerve function at distant non-inflamed sites in the gut. Gastroenterology 104 (part 2):A717, 1993
Gross V, Andus T, Caesar I, Roth M, Scholmerich J: Evidence for continuous stimulation of interleukin-6 production in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 103:1120–1121, 1990
Alstead EM, McConnell JS, Exley AR, Hodgson HJF, Cohen J: Relationship between endotoxin, tumour necrosis factor-α and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:325–328, 1991
Andus T, Gross V, Casar I, Krumm D, Hosp J, David M, Scholmerich J: Activation of monocytes during inflammatory bowel disease. Pathobiology 59:166–170, 1991
McKay DM, Croitoru K, Brattsand R, and Perdue MH: TNFα causes epithelial (T84) permeability and secretory abnormalities in a co-culture model of inflammation. Gastroenterology 106:A732, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, N., Madsen, K.L., Friend, D.R. et al. Increased permeability occurs in rat ileum following induction of pancolitis. Digest Dis Sci 41, 405–411 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02093836
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02093836