Summary
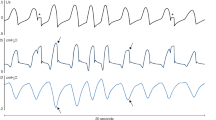
The bioelectrical activities of the chest are recorded by means of two electrodes placed at the lower thorax, with separate amplifiers. The switch system with the shorter time factor and higher amplification, gives the EMG of intercostal musculature. The switch system with the longer time factor and lower amplification gives the EThG. (Electro-thoraco-gram). The latter provides information concerning the type of breathing of the individual patient, as well as changes in respiratory movements of the chest due to an underlying disease, can be differentiated. Furthermore, a tool is provided for objective evaluation of dyspnea and the control of breathing therapy.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde eine bioelektrische Methode vorgestellt die sich aus dem Elektromyogramm (EMG) der Intercostalmuskulatur und dem Elektrothorakogramm (EThG) zusammensetzt. Das EThG registriert mit großer Zeitkonstante die Potentialschwankungen an je einer Elektrode am Vorderende des rechten und linken Intercostalraumes. Das EMG wird simultan pseudounipolar von denselben Elektroden abgenommen und mit kurzer Zeitkonstante geschrieben.
Die Verlaufsform des Elektrothorakogramms ist für bestimmte Atemtypen typisch. Überwiegen der Zwerchfellvertikalbewegung ergibt inspiratorisch positiven Ausschlag, Überwiegen der Thoraxdehnbewegung ergibt inspiratorisch negativen Ausschlag. Es treten auch Mischformen auf, deren Bewegungskomponenten nach diesem Prinzip analysiert werden können. Die Methode eignet sich zur Auswahl der Patienten für die verschiedenen Formen der Atemtherapie und zur Erfolgskontrolle dieser therapeutischen Maßnahmen.
Aus einer zeitlichen Diskrepanz zwischen Maximum der Inspirationsimpulse im EMG und Bewegungsumschlag im EThG läßt sich eine latente Belastungsdyspnoe erkennen und objektivieren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bergsmann, O.: Elektrothorakographie. Wien. Z. inn. Med.50, 2, 49 (1969).
Campbell, E. J. M.: An electromyographic examination of the role of the intercostal muscles in breathing in man. J. Physiol. (Lond.)129, 12 (1955).
Green, J. H., andJ. B. L. Howell: The correlation of intercostal muscle activity with respiratory air flow in conscious human subject. J. Physiol. (Lond.)149, 471 (1959).
Koepke, G. H., A. J. Murphy, J. W. Rae, andD. G. Dickinson: An electromyographie study on some of the muscles used in respiration. Arch. Phys. Rehab.36, 217 (1955).
Jones, D. S., andJ. E. Pauly: Further electromyographic studies on museles of costal respirations in man. Anat. Rec.128, 733 (1957).
Pauly, J. E.: Electromyographic studies of human respiration. Chikago Med. School. Quart.18, 80 (1957).
Rossier, P. H., J. H. Nieporent, H. Pipberger u.R. Kälin: Elektromyographische Untersuchungen der Atemmuskelfunktion an normalen Versuchspersonen. Z. ges. exp. Med.127, 39 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergsmann, O. Untersuchung der Atembewegung mit Elektrothorakographie und Elektromyographie. Beitr. Klin. Tuberk. 139, 326–333 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090941
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090941