Summary
1. The effects of bath-applied recombinant human interleukin-1 (rhIL-1) and interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) on the calcitonin (CT)-induced outward current recorded from identified neurons (R9–R12) ofAplysia kurodai were investigated with conventional voltage-clamp and pressure ejection techniques.
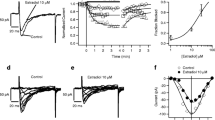
2. Micropressure ejection of CT onto the soma of the neuron induced a slow outward current [I o(CT); 4–6 nA in amplitude, 30–40 sec in duration] associated with a decrease in input membrane conductance.
3.I o(CT) was increased by hyperpolarization.
4. The extrapolated reversal potential was +10 mV. Additionally,I o(CT) was sensitive to changes in (Na+)o but not to changes in (K+)o, (Ca2+)o, and (Cl−)o.
5. Micropressure-ejected forskolin produced a slow outward current similar to that induced by CT.
6. Bath-applied rhIL-1 and rhIL-2 (10–40 U/ml) reduced the CT-induced current in identifiedAplysia neurons without affecting the resting membrane conductance or the holding current.
7. The inhibitory effects of both cytokines on the current were completely reversible. Heat-inactivated rhIL-1 and rhIL-2 were without effect.
8. These results suggest that the immunomodulators, IL-1 and IL-2, can modulate the CT-induced outward current associated with a decrease in Na+ conductance in the nervous system ofAplysia. Therefore, the study suggests that these cytokines may also serve as neuromodulators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo, D. M., Lapchak, P. A., Collier, B., and Quirion, R. (1989). Localization of interleukin-2 immunoreactivity in the rat brain: Interaction with the cholinergic system.Brain Res. 498257–266.
Beck, G., and Habicht, G. S. (1986). Isolation and characterization of a primitive interleukin-1-like protein from an invertebrate,Asterias forvesi.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 837429–7433.
Beck, G., Vasta, G. R., Marchalonis, J. J., and Habicht, G. S. (1989). Characterization of interleukin-1 activity inTunicates.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 92B93–98.
Beckner, S. K., and Farrar, W. L. (1986). Interleukin-2 modulation of adenylate cyclase. Potential role of protein kinase C.J. Biol. Chem. 2613043–3047.
Bindoni, M., Perciavalle, V., Berretta, S., Belluardo, N., and Diamantstein, T. (1988). Interleukin 2 modifies the bioelectric activity of some neurosecretory nuclei in the rat hypothalamus.Brain Res. 46210–14.
Blatteis, C. M. (1990). Neuromodulative actions of cytokines.Yale J. Biol. Med. 63133–146.
Dafny, N., Prieto-Gomez, B., and Reyes-Vazquez, C. (1985). Does the immune system communicate with the central nervous system?J. Neuroimmunol. 91–12.
Dinarello, C. A. (1986). Multiple biological properties of recombinant human interleukin-1 (beta).Immunology 172301–305.
Evans, S. W., Beckner, S. K., and Farrar, W. L. (1987). Stimulation of specific GTP binding and hydrolysis activities in lymphocyte membrane by interleukin-2.Nature 325166–168.
Farrar, W. L., and Anderson, W. B. (1985). Interleukin-2 stimulates association of protein kinase C with plasma membrane.Nature 315233–235.
Farrar, W. L., Hill, J. M., Harle-Bellan, A., and Vinocur, M. (1987). The immunological brain.Immunol. Rev. 100361–378.
Fischer, J. A., Tobler, P. H., Henke, H., and Tschop, F. A. (1983). Salmon and human calcitonin-like peptides coexist in the human thyroid and brain.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 571314–1316.
Frazier, W. T., Kandel, E. R., Kupfermann, I., Waziri, R., and Coggeshall, R. E. (1967). Morphological and functional properties of identified neurons in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica.J. Neurophysiol. 301288–1351.
Giulian, D., and Lachman, L. B. (1985). Interleukin-1 simulation of astroglial proliferation after brain inuury.Science 228497–499.
Giulian, D., Baker, T. J., Shih, L.-C. N., and Lachman, L. B. (1986). Interleukin-1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia.J. Exp. Med. 164594–604.
Giulian, D., Young, D. G., and Woodward, J. (1988). Interleukin-1 is an astroglial growth factor in the developing brain.J. Neurosci. 8 709–714.
Hori, T., Shibata, M., Nakashima, M., Asami, A., Asami, T., and Koga, H. (1988). Effects of interleukin-1 and arachidonate on the preoptic and anterior hypothalamic neurons.Brain Res. Bull. 2075–82.
Hughes, T. K., Chin, R., Smith, E. M., Leung, M. K., and Stefano, G. B. (1991). Similarities of signal system in vertebrates and invertebrates. Detection, action and interactions of immunoreactive monokines in theMytulus edulis.Adv. Neuroimmunol. 159–70.
Miller, L. G. Galpern, W. R., Dunlap, K., Dinarello, C. A., and Turner, T. J. (1991). Interleukin-1 augmentsγ-aminobutyric acid A receptor function in brain.Mol. Pharmacol. 39105–108.
Nakashima, T., Hori, T., Mori, T., Kuriyama, K., and Mizuno, K. (1989). Recombinant human interleukin-1β alters the activity of preoptic thermosensitive neurons in vitro.Brain Res. Bull. 23209–213.
Oomura, Y. (1988). Chemical and neuronal control of feeding motivation.Physiol. Behav. 44555–560.
Paemen, L. R., Porchet-Hennere, E., Masson, M., Leung, M. K., Hughes, T. K., and Stefano, G. B. (1992). Glial localization of interleukin-1α in invertebrate ganglia.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 12463–473.
Plata-Salaman, C. R., and French-Mullen, J. M. H. (1992). Interleukin-1β depresses calcium currents in CA1 hippocampal neurons at pathophysiological concentrations.Brain Res. Bull. 29221–223.
Plata-Salaman, C. R., Oomura, Y., and Kai, Y. (1988). Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1β: Suppression of food intake by direct action in the central nervous system.Brain Res. 448106–114.
Primi, M. P., and Bueno, L. (1986). Centrally mediated stimulation of jejunal water and electrolyte secretion by calcitonin in dogs.Am. J. Physiol. 250G172-G176.
Sasayama, Y., Kotoh, A., Oguro, C., Kambegawa, A., and Yoshizawa, H. (1991). Cells showing immunoreactivity for calcitonin or calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the central nervous system of some invertebrates.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 83406–414.
Sawada, M., Hara, N., and Ichinose, M. (1992). Interleukin-2 inhibits the GABA-induced Cl− current in identifiedAplysia neurons.J. Neurosci. Res. 33461–465.
Sawada, M., Hara, N., and Maeno, T. (1991a). Tumor necrosis factor reduces the ACh-induced outward current in identifiedAplysia neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 131217–220.
Sawada, M., Hara, N., and Maeno, T. (1991b). Ionic mechanism of the outward current induced by extracellular ejection of interleukin-1 onto identified neurons ofAplysia.Brain Res. 545248–256.
Sawada, M., Ichinose, M., Ishikawa, S., and Sasayama, Y. (1993). Calcitonin induces a decreased Na+ conductance in identified neurons ofAplysia.J. Neurosci. Res. 36200–208.
Seamon, K. B., Padgett, W., and Daly, J. W. (1981). Forskolin: Unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and intact cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 783363–3367.
Shimizu, N., and Oomura, Y. (1986). Calcitonin-induced anorexia in rats: Evidence for its inhibitory action on lateral hypothalamic chemosensitive neurons.Brain Res. 367128–140.
Smith, K. A. (1988). Interleukin-2: Inception, impact and implications.Science 2401169–1176.
Stefano, G. B. (1989). Role of opioid neuropeptides in immunoregulation.Prog. Neurobiol. 33149–159.
Stefano, G. B. (1992). Invertebrate and vertebrate neuroimmune and autoimmunoregulatory commonalties involving opioid peptides.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 12357–366.
Szucs, A., Stefano, G. B., Hughes, T. K., and S-Roza, K. (1992). Modulation of voltage-activated ion currents on identified neurons ofHelix pomatia L. by interleukin-1.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 12429–438.
Tancredi, V., Zona, C., Veltotti, F., Eusebi, F., and Santoni, A. (1990). Interleukin-2 suppresses established long-term potentiation and inhibits its induction in the rat hippocampus.Brain Res. 525149–151.
Weigent, D. A., and Blalock, J. E. (1987). Interactions between the neuroendocrine and immune systems: Common hormones and receptors.Immunol. Rev. 10079–108.
Zona, C., Palma, E., Santoni, A., Grassi, F., and Eusebi, F. (1990). Interleukin-2 reduces voltage-activated Na+-currents in embryonic rat hippocampal neurons.Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 16181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, M., Ichinose, M. & Stefano, G.B. Inhibition of the calcitonin-induced outward current in identifiedAplysia neurons by interleukin-1 and interleukin-2. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14, 175–184 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090783
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090783