Abstract
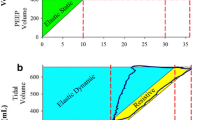
The dependence of differentiated capnogram parameters — maximum steepness (m 1), plateau steepness (m 2) and their quotient (m 1/m 2=Q) — on the RV% values are reported. A close correlation could be found between them 2 and Q values.
There was furthermore a significant difference between the differentiated capnogram parameters of control persons and that of patients with non-obstructive and obstructive emphysema. The average RV values and differentiated capnogram parameters of emphysematous patients with severe obstruction differed significantly from the same values of emphysematous patients with mild or without any obstruction.
The authors show that conclusions can be drawn from differentiated capnogram values for determining the degree of obstructive ventilatory failure and the arterial blood gas tensions.
Zusammenfassung
Die Verfasser untersuchten den Zusammenhang zwischen den Differentialkapnogrammgrößen (m 1-,m 2- und Q-Werten) und den prozentualen Residualvolumenwerten. Die Korrelation derm 2- und Q-Werte mit Residualvolumenwerten ist eng. Die Differentialkapnogrammparameter von Kontrollpersonen unterscheiden sich von denjenigen der nichtobstruktiv- bzw. obstruktiv-emphysematösen Krankengruppen signifikant, dabei besteht aber eine signifikante Differenz zwischen Differentialkapnogrammwerten von nichtobstruktiv-und obstruktiv-emphysematösen Patienten. Aufgrund der zwischen Differentialkapnogramm-parametern und Blutgaswerten bestehenden Korrelation ist die Folgerung von Kapnogrammgrößen auf Blutgaswerte möglich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Filley, G. F.: Emphysema ans chrobic bronchitis: Clinical manifestations and their physiologic significance. Med. Clin. of North. Amer.51 283 (1967).
Galgóczy, G., Megyesi, Cs., Mándi, A.: Eine Methode zur quantitativen Bewertung der Kapnogramm (URAS)-Kurve. Beitr. Klin. Tuberk.141 362 (1970).
—— Mága, R., Mándi, A.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zwischen differenzierter Kapnogrammkurve und atemmechanischen Parametern. Pneumonology144 113 (1971).
Herberg, D., Krüger, R., Mulch, G., Utz, G.: Zur Pathophysiologie der CO2-Retention bei obstruktiven bronchopulmonalen Erkrankungen. Respiration27 236 (1970).
Hoffbrand, B. J.: The expiratory capnogram: A measure of ventilation, perfusion inequalities. Thorax21 518 (1966).
Isawa, T., Wasserman, K., Taplin, G. V.: Lung scintigraphy and pulmonary function studies in obstructive airway disease. Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis.102 161 (1970).
Kochsiek, K.: Atemmechanische Untersuchungen beim schweren obstruktiven Lungenemphysem. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med.66 185 (1960).
King, T. K. C., Briscoe, W. A.: Blood gas exchange in emphysema: an example illustrating method of calculation. J. Appl. Phys.23 672 (1967).
Levine, E. R.: Special problems of emphysema. Modern Treatment6 331 (1969).
Mathes, K., Ulmer, W. T.: Untersuchungen über die pathophysiologische Bedeutung des Emphysems (I–III). Dtsch. Arch. Klin. Med.204 255 (1957).
Mottley, H. L.: Problem of obstructive disease. Modern Treatment6 233 (1969).
Nolte, D., Grebe, S., Schraub, H.: Nachweis von Verteilungsstörungen durch Doppel-Scintigraphie der Lungen. Beitr. Klin. Tuberk.141 147 (1969).
Otto, H., Zeilhofer, R., Reissinger, O.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Klinik und Symptomatik morphologisch gesicherter Emphysem-Fälle. Praxis d. Pneumonologie23 776 (1969).
Park, S. S., Janis, M., Schim, Ch. S., Williams, M. H., Jr.: Relationship of bronchitis and emphysema to altered-pulmonary function. Ann. Rev. Resp. Disp.102 927 (1970).
Riccabona, G., Mathie, F., Leitner, E.: Erste Ergebnisse einer nuklearmedizinischen Lungenfunktionsdiagnostik. Wiener Klin. Wschr.82 765 (1970).
Sibel, E. M., Landis, G. A., Moser, K. M.: Inhalation lung scanning evaluation. Radioaerosol versus radioxenon techniques. Diseases of the chest.56 284 (1969).
—— Moser, K. M.: The relation between spirometric measurements and arterial blood gas analysis in patients with chronic air flow obstruction. Thorax25 598 (1970).
Snider, G. L.: Problems of restrictive thoracopulmonary disease. Modern Treatment6 26 (1969).
Ulmer, W. T.: Untersuchungen zur Analyse der alveolären Ventilationsstörung bei chronischem cor pulmonale. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Kreisl.-Forsch.21 360 (1955).
Van Meerten, R. J.: Expiratory gas concentration curves for examination of uneven distribution of ventilation and perfusion in the lung. Respiration27 552 (1970).
Venrath, H.: Über die Messung der regionalen Durchblutung und Belüftung der Lungen. Med. Welt21 1276 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galgóczy, G., Mága, R. & Mándi, A. Differentialkapnographische Diagnose der verschiedenen Verteilungsstörungen. Pneumonologie 147, 21–28 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02089909
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02089909