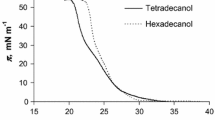
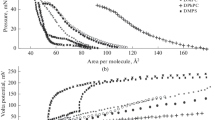
Summary
Mixed monolayers are of technological importance and also of interest because of their relevance to many natural systems. Determination of the miscibility of the components is necessary before an understanding of the molecular interactions can be reached. The variation of collapse pressure with monolayer composition can be used to obtain information on the degree of miscibility. Since kinetic effects can alter the collapse, the collapse pressures were measured for monolayers of cholesterol with either ethyl palmitate or triglycerides above and below the melting points of the alkyl compounds. Consideration of partial molecular areas and of the two dimensional phase rule indicates that immiscible collapsed phases can occur. The criterion of enhanced surface pressure stability in mixed monolayers only applies when the components are miscible both in the monolayer and collapsed phase. When the latter situation occurs a theoretical analysis of the variation of collapse pressure with monolayer composition is possible. Reasonable agreement between theory and experiment is found.
Zusammenfassung
Die Bestimmung der Mischbarkeit der Komponenten in gemischten, monomolekularen Filmen ist Voraussetzung für ein Verständnis von molekularen Reaktionen zwischen den Filmkomponenten. Die Beziehung zwischen Kollabierungsdruck und chemischer Zusammensetzung in gemischten, monomolekularen Filmen kann zu Aussagen über den Grad der Mischbarkeit der Komponenten herangezogen werden. Da kinetische Effekte den Filmdruck am Kollabierungspunkt beeinflussen können, wurde der Kollabierungsdruck von zwei gemischten monomolekularen Filmen [(1) Cholesterin und Palmitinsäureäthylester; (2) Cholesterin und Triglyceride] bei Temperaturen oberhalb und unterhalb des Schmelzpunktes der Alkylverbindungen bestimmt. Die Berücksichtigung des partiellen Flächenbedarfes per Molekül und der zweidimensionalen Phasenregel lassen auf das Vorliegen von unmischbaren Phasen nach der Kollabierung schließen. Das Phänomen der erhöhten Filmstabilität in gemischten, monomolekularen Filmen trifft nur zu, wenn die Komponenten sowohl im Film als auch in der Phase, welche nach der Kollabierung vorliegt, vollkommen mischbar sind. Wenn dies der Fall ist, dann kann eine theoretische Analyse der Beziehung zwischen Kollabierungsdruck und Zusammensetzung des monomolekularen Films durchgeführt werden. Eine gute Übereinstimmung zwischen Theorie und Experiment liegt vor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaines, G. L., Insoluble Monolayers at Liquid-Gas Interfaces, Chap. 6 (New York 1966).
Demel, R. A., L. L. M. van Deenen and B. A. Pethica, Biochim. Biophys. Acta135, 11 (1967).
Demel, R. A. and P. Joos, Chem. Phys. Lipids1, 35 (1968).
Chapman, D., N. F. Owens, M. C. Phillips and D. A. Walker, Biochim. Biophys. Acta183, 458 (1969).
Dervichian, D. G., in: Surface Science in Chemistry and Biology, edited byJ. F. Danielli, K. G. A. Pankhurst andA. C. Riddiford, p. 70 (London 1958).
Cadenhead, D. A. and M. C. Phillips, Advances in Chem. Series84, 131 (1968).
Crisp, D. J., in: Surface Chemistry, Supplement to Research, p. 23 (London 1949).
Gaines, G. L., J. Colloid and Interface Sci.21, 315 (1966).
Defay, R., I. Prigogine, A. Bellemans andD. H. Everett, Surface Tension and Adsorption, Chap. 6 (London 1966).
Crisp, D. J., in: Surface Chemistry, Supplement to Research, p. 17 (London 1949).
Joos, P., Bull. Soc. Chim. Belges78, 207 (1969).
Joos, P. and R. A. Demel, Biochim. Biophys. Acta183, 447 (1969).
Joos, P., R. Ruyssen, J. Miñones Trillo, S. Garcia Fernandez and P. Sans Pedrero, J. Chim. Phys.66, 1665 (1969).
Wu, S. and J. R. Huntsberger, J. Colloid and Interface Sci.29, 138 (1969).
Gaines, G. L., Insoluble Monolayers at Liquid-Gas Interfaces, p. 144 (New York 1966).
Phillips, M. C. and D. Chapman, Biochim. Biophys. Acta163, 301 (1968).
Cadenhead, D. A. and M. C. Phillips, J. Colloid and Interface Sci.24, 491 (1967).
Alexander, A. E. and J. H. Schulman, Proc. Roy. Soc.A 161, 115 (1937).
Defay, R., I. Prigogine, A. Bellemans andD. H. Everett, Surface Tension and Adsorption, p. 166 (London 1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 6 figures and 1 table
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, M.C., Joos, P. The collapse pressures and miscibilities of mixed insoluble monolayers. Kolloid-Z.u.Z.Polymere 238, 499–505 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02085578
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02085578