Abstract
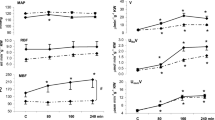
Sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), inorganic phosphate (Pi) and water excretion were measured in nondiuretic (ND) and extracellular fluid (ECF) volume expanded (VE) conscious restrained rats four weeks after denervation or sham-denervation of the left kidney. On the day of the study the animals were lightly anaesthetized with ether and the femoral vessels on one side were catheterized. Urine was collected from both kidneys. The animals were allowed to recover for 3 hours and studied in a restraining chamber. In ND animals isotonic saline containing inulin and para-amino-hippuric acid (PAH) were given at a rate of 0.067±0.002 (SE) ml/min/kg body weight (BW). In VE animals the infusion rate was 0.24±0.04 ml/min/kg BW. Kidney catecholamine content was measured after the experiments. Clearances of PAH and of inulin (GFR) were the same in both kidneys. Urine volume (V), sodium excretion (UNaV/GFR), inorganic phosphate excretion (UPiV/GFR) and calcium excretion (UCaV/GFR) were significantly higher in the denervated kidneys. Values in sham denervated kidneys were not greater than those of the right kidney. Denervation was proven by demonstrating absent or very low catecholamine content in the kidneys.
The results demonstrate that: (a) chronic renal denervation in rats leads to diuresis and natriuresis even in the conscious state, thus confirming previous results from our laboratory; (b) such changes occur independently of the state of the ECF volume and of renal haemodynamic changes; (c) the increased excretion of Ca++ and Pi after denervation demonstrates that renal nerves affect the reabsorption of these ions either independently or by way of their effect on sodium reabsorption. These data allow us to suggest that a renal tubular dysfunction, which was proved in anaesthetized denervated animals, can also be observed in the conscious state.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DiBona, G. F.: Neurogenic regulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption.Am. J. Physiol, 233, 73 (1977).
Takács, L., Bencsáth, P., Szalay, L.,: Decreased proximal tubular transport capacity after renal sympathectomy. Proc. 7th Int. Congr. Nephrol., Montreal, 1978, pp. 553–558.
Gottschalk, C. W.: Renal nerves and sodium excretion.Annu. Rev. Physiol., 41, 229 (1979).
Szalay, L., Bencsáth, P., Takács L.: Impaired proximal tubular transport functions in anesthetized splanchnicotomized dogs.Experientia, 33, 42 (1977).
Szalay, L., Colindres, R. E., Jackson, R., Adkinson, J. T., Lassiter, W. E., Gottschalk, C. W.: Phosphate (Pi) transport in chronically denervated rat kidneys (Under publication).
Szénási, G., Bencsáth, P., Lehoczky, E., Takács, L.: Tubular transport and urinary excretion of phosphate after renal denervation in the anesthetized rat.Am. J. Physiol., 240, 481 (1981).
Surtshin, A., Schmandt, W. P.: Comparison of continuously collected urines from the two normal kidneys and some effects of unilateral denervation.Am. J. Physiol., 185, 418 (1956).
Berne, R. M.: Hemodynamics and sodium excretion of denervated kidney in anesthetized and unanesthetized dog.Am. J. Physiol., 171, 148 (1952).
Smith, H. W.: The Kidney: Structure and Function in Health and Disease. New York-Oxford 1951, pp. 411–460.
Lifschitz, M. D.: Lack of a role for the renal nerves in renal sodium reabsorption in conscious dogs.Clin. Sci. Mol. Med., 54, 567 (1978).
Sadowski, J., Kurkus, J., Gellert, R.: Reinvestigation of denervation diuresis and natriuresis in conscious dogs.Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim., 87, 663 (1979).
Sadowski, J., Kurkus, J., Gellert, R.: Denervated and intact kidney responses to saline load in awake and anesthetized dogs.Am. J. Physiol., 237, 262 (1979).
Sadowski, J., Kurkus, J.: A search for a defect of proximal transport in denervated kidneys of conscious dogs.Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim., 89, 149 (1981).
Rogenes, P. R., Gottschalk, C. W.: Renal function in conscious rats with chronic unilateral renal denervation.Am. J. Physiol., 242 140 (1982).
Walsh, G. M., Ferrone, R. A.: Ether-induced vasodilation in the rat.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 24, 67 (1979).
Coyle, J. T., Henry, D.: Catecholamines in fetal and newborn rat brain.J. Neurochem., 21, 61 (1973).
Davidson, W. D., Sackner, M. A.: Simplification of the anthrone method for the determination of inulin in clearance studies.J. Lab. Clin. Med., 62, 351 (1963).
Bratton, A. C., Marshall, E. K. Jr.: A new coupling component for sulfanilamide determination.J. Biol. Chem., 128, 537 (1939).
Chen, P. S., Jr., Toribara, T. Y., Warner, H.: Microdetermination of phosphorus.J. Anal. Chem., 28, 1756 (1956).
Hill, J. B.: Automated fluorometric method for determination of serum calcium.Clin. Chem., 11, 122 (1965).
Pastoriza-Munoz, E., Colindres, R. E., Lassiter, W. E., Lechene, C.: Effect of parathyroid hormone on phosphate reabsorption in rat distal convolution.Am. J. Physiol., 235, 321 (1978).
Lassiter, W. E., Gottschalk, C. W., Mylle, M.: Micropuncture study of renal tubular reabsorption of calcium in normal rodents.Am. J. Physiol., 204, 771 (1963).
Gitelman, H. J., Kukolj, S., Welt, L. G.: The influence of the parathyroid glands on the hypercalcemia of experimental magnesium depletion in the rat.J. Clin. Invest., 47, 118 (1968).
LeGrimellec, Ch., Poujeol, P., deRouffignac, C.:3H-inulin and electrolyte concentrations in Bowman's capsule in rat kidney. Comparison with artificial ultrafiltration.Pfluegers Arch., 354, 117 (1975).
Bernstein, D. S., Aliapoulios, M. A., Hattner, R. S., Wachman, A., Rose, B.: Serum calcium ion activity: effects of thyrocalcitonin and parathyroid extract in the rat.Endocrinology, 85, 589 (1969).
Sutton, R. A., Dirks, J. H.: The renal excretion of calcium: a review of micropuncture data.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 53, 979 (1975).
de Takats, G., McDonald, G. O., Harridge, W. M.: The vicious circle in hypertension.Surgery, 43, 113 (1958).
de Takats, G.: Sympathectomy for hypertension.Am. J. Sur. 127, 521 (1974).
Hix, E. L.: A new approach to ureteral exteriorization for bilateral renal studies.J. Appl. Physiol., 8, 114 (1955).
Hix, E. L.: Uretero-renal reflex facilitating renal vasoconstrictor responses to emotional stress.Am. J. Physiol., 192, 191 (1958).
Szalay, L., Bencsáth, P., Takács, L.: Effect of splanchnicotomy on the renal excretion of inorganic phosphate in the anesthetized dog.Pfluegers Arch., 367, 283 (1977).
Szalay, L., Takács, L.: Renal excretion of calcium and phosphate in normal and thyroparathyroidectomized dogs.Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung., 53, 216 (1979).
Pitts, R. F., Gurd, R. S., Kessler, R. H., Hierholzer, K.: Localization of acidification of urine, potassium and ammonia secretion and phosphate reabsorption in the nephron of the dog.Am. J. Physiol., 104, 125 (1958).
Wilde, W. S., Malvin, R. L.: Graphical placement of transport segments along the nephron from urine concentration pattern developed with stop flow technique.Am. J. Physiol., 195, 153 (1958).
Strickler, J. C., Thompson, D. D., Klose, R. M., Giebisch, G.: Micropuncture study of inorganic phosphate excretion in the rat.J. Clin. Invest., 43, 1596 (1964).
Amiel, C., Kuntziger, H., Richet, G.: Micropuncture study of handling of phosphate by proximal and distal nephron in normal and parathyroidectomized rat. Evidence for distal reabsorption.Pfluegers Arch., 317, 93 (1970).
Bencsáth, P., Bonvalet, J. P., deRouffignac, C.: Tubular factors in denervation diuresis and natriuresis. In: H. Wirz, F. Spinelli (eds): Recent Advances in Renal Physiology. Karger, Basel 1972, pp. 96–106.
Bello-Reuss, E., Colindres, R. E., Pastoriza-Munoz, E., Mueller, R. A., Gottschalk, C. W.: Effects of acute unilateral renal denervation in the rat.J. Clin. Invest., 56, 208 (1975).
Vaziri, D. N., Nellans, R. E., Brueggemann, R. M., Barton, C. H., Martin, D. C.: Renal tubular dysfunction in transplanted kidneys.South. Med. J., 72, 530 (1979).
Norwell, J. E., Weitsen, H. A., Dwyer, J. J.: Degeneration and regeneration of adrenergic nerves in the autotransplanted kidney.Transplantation 7, 218 (1969).
Norwell, J. E., Weitsen, H. A., Sheppek, C. G.: The intrinsic innervation of human renal homotransplants.Transplantation, 9, 168 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szalay, L., Colindres, R.E., Jackson, R. et al. Effects of chronic renal denervation in conscious restrained rats. International Urology and Nephrology 18, 3–18 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082643
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082643