Summary
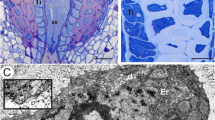
The sieve areas inPinus resinosa consist of groups of plasmalemma-lined pores joined in the middle of the wall by large compound median cavities. Numerous membranes extend into the pores from aggregates of smooth, tubular endoplasmic reticulum opposite the sieve areas and merge in the median cavities. A compound median cavity arises through the union of smaller simple median cavities, each of which is initially associated with a single plasmodesma. Callose platelets were not associated with developing pores, but the pores of most fully-developed sieve areas were lined with callose. Sieve cells also have connections with albuminous cells. The connections on the sieve-cell side of the wall are similar to sieve-area pores, those on the albuminous-cell side to plasmodesmata. These connections also are associated with compound median cavities containing many membranes. The albuminous cells contain protoplasmic components similar to those of other parenchymatous cells including chloroplasts, cytoplasmic fibers, and microbodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri, F. J., andR. F. Evert, 1968: Observations on albuminous cells inPinus. Planta (Berl.)78, 93–97.
Alosi, M. C., andF. J. Alfieri, 1972: Ontogeny and structure of the secondary phloem inEphedra. Amer. J. Bot.59, 818–827.
Behnke, H.-D., andG. S. Paliwal, 1973: Ultrastructure of phloem and its development inGnetum gnemon, with some observations onEphedra campylopoda. Protoplasma78, 305–319.
Campbell, R., 1972: Electron microscopy of the development of needles ofPinus nigra var. maritima. Ann. Bot.36, 711–720.
Chafe, S. C., andM. E. Doohan, 1972: Observations on the ultrastructure of the thickened sieve cell wall inPinus strobus (L). Protoplasma75, 67–78.
Esau, K., 1969: The Phloem. In: Handbuch der Pflanzenanatomie (W. Zimmermann, P. Ozenda, andH. D. Wulff, eds.). Histologie, Vol. 5, pt. 2. Berlin-Stuttgart: Borntraeger.
Esau, K., V. I. Cheadle, andE. B. Risley, 1962: Development of sieve-plate pores. Bot. Gaz.123, 233–243.
—, andR. H. Gill, 1973: Correlations in differentiation of protophloem sieve elements ofAllium cepa root. J. Ultrastruct. Res.44, 310–328.
Evert, R. F., andF. J. Alfieri, 1965: Ontogeny and structure of coniferous sieve cells. Amer. J. Bot.52, 1058–1066.
—,C. H. Bornman, V. Butler, andM. G. Gilliland, 1973: Structure and development of sieve areas in leaf veins ofWelwitschia. Protoplasma76, 23–34.
—, andW. F. Derr, 1964: Callose substance in sieve elements. Amer. J. Bot.51, 552–559.
—,B. P. Deshpande, andS. E. Eichhorn, 1971: Lateral sieve-area pores in woody dicotyledons. Canad. J. Bot.49, 1509–1515.
Harris, W. M., 1972: Ultrastructural observations onPinaceae leaf phloem. New Phytol.71, 169–173.
Kollmann, R., undW. Schumacher, 1962: Über die Feinstruktur des Phloems vonMetasequoia glyptostroboides und seine jahreszeitlichen Veränderungen. II. Vergleichende Untersuchungen der plasmatischen Verbindungsbrücken in Phloemparenchymzellen und Siebzellen. Planta (Berl.)58, 366–386.
— —, 1963: Über die Feinstruktur des Phloems vonMetasequoia glyptostroboides und seine jahreszeitlichen Veränderungen. IV. Weitere Beobachtungen zum Feinbau der Plasmabrücken in den Siebzellen. Planta (Berl.)60, 360–389.
Murmanis, L., andR. F. Evert, 1966: Some aspects of sieve cell ultrastructure inPinus strobus. Amer. J. Bot.53, 1065–1078.
Neuberger, D., andR. F. Evert, 1974: Structure and development of the sieve-element protoplast in the hypocotyl ofPinus resinosa. Amer. J. Bot.61, 360–374.
Northcote, D. H., andF. B. P. Wooding, 1966: Development of sieve tubes inAcer pseudoplatanus. Proc. Roy. Soc. B163, 524–537.
Parameswaran, N., 1971: Zur Feinstruktur der Assimilatleitbahnen in der Nadel vonPinus silvestris. Cytobiologie3, 70–88.
—, undW. Liese, 1970: Zur Cytologie der Strasburger-Zellen in Coniferennadeln. Naturwiss.57, 45–46.
Spurr, A. R., 1969: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43.
Srivastava, L. M., 1969: On the ultrastructure of cambium and its vascular derivatives. III. The secondary walls of the sieve elements ofPinus strobus. Amer. J. Bot.56, 354–361.
—, andT. P. O'Brien, 1966: On the ultrastructure of cambium and its vascular derivatives. II. Secondary phloem ofPinus strobus L. Protoplasma61, 277–293.
Timell, T. E., 1973: Ultrastructure of the dormant and active cambial zones and the dormant phloem associated with formation of normal and compression woods inPicea abies (L.) Karst. Technical Publication No. 96, State University of New York, College of Environmental Science and Forestry, Syracuse, New York.
Wooding, F. B. P., 1966: The development of the sieve elements ofPinus pinea. Planta (Berl.)69, 230–243.
—, 1968: Fine structure of callus phloem inPinus pinea. Planta (Berl.)83, 99–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation (GB 8330 and GB 31417) to R. F.Evert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuberger, D.S., Evert, R.F. Structure and development of sieve areas in the hypocotyl ofPinus resinosa . Protoplasma 84, 109–125 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02075947
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02075947