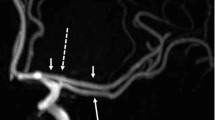
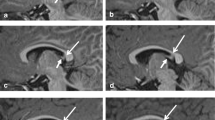
Summary
Arteriovenous malformations in anatomically important cortical regions are not explicitly non-operable. Decisive for surgery is much more the type and extent of lesion than its localisation. In the widespread cavernous type the normal cerebral tissue does not exist and the specific function of the area is carried out by the surrounding cortex. Its radical removal can be performed without any neurological consequences, if it is limited closely to the borders of the lesion. Out of 60 patients 4 illustrative cases of arteriovenous malformations localised in the speech and motoric regions, successfully removed are reported.
Zusammenfassung
Arteriovenöse Malformation in wichtigen kortikalen Gehirngebieten sind nicht ausnahmslos inoperabel. Für die Operationsindikation ist vielmehr der Typ und die Ausdehnung der Läsion als ihre Lokalisation entscheidend. Bei ausgedehnten arteriovenösen Mißbildungen vom kavernösen Typus existiert an ihrer Stelle kein normales Hirngewebe und die spezifischen Funktionen werden von der Rinde in der Umgebung geleistet. Die Malformation kann sogar ohne neurologische Folgen radikal exstirpiert werden, wenn die Operation die Grenzen der Mißbildung nicht überschreitet. Aus einem Krankengut von 60 Fällen werden 4 Beispiele von arteriovenösen Malformationen beschrieben, die im Bereich der Sprachzentren und des motorischen Cortex lagen und radikal exstirpiert werden konnten.
Résumé
Les malformations artério-veineuses des régions corticales anatomiquement importantes ne sont pas expressément inopérables. L'intervention chirurgicale est bien plus indiquée par le type et l'étendue de la lésion que par sa localisation. Il n'y a pas de tissu cérébral normal dans les grandes malformations du type caverneux et la fonction spécifique de cette zone est assurée par le cortex voisinant. Il est possible de procéder à une résection radicale sans aucune séquelle neurologique si l'intervention est strictement limitée au bord de la lésion. Du nombre total de 60 malades l'auteur présente 4 cas de malformations artério-veineuses localisées dans les zones du language et dans les zones motrices opérés avec succès.
Riassunto
Le malformazioni arterovenose di importanti regioni corticali non sono necessariamente inoperabili. Decisiva per la scelta chirurgica sono il tipo e l'estensione della lesione più che non la localizzazione. Nel tipo cavernoso esteso, il tessuto cerebrale normale non esiste e le funzioni specifiche di quel tessuto sono sostenute dalla corteccia limitrofa. L'asportazione radicale di questo tipo di malformazione può essere effettuata senza provocare deficit neurologici, se essa è limitata ai confini della malformazione. Su 60 pazienti operati, l'Autore illustra 4 casi di malformazioni artero-venosa localizzate in regione motoria o nell'area del linguaggio, rimosse chirurgicamente con successo.
Resumen
Las malforrnaciónes arteriovenosas en las regiones corticales anatómicamente importantes no son expresamente inoperables. La intervención quirúrgica está más indicada según el tipo y extensión de la lesión que por su localización. En las grandes malformaciones de tipo cavernoso no existe tejido cerebral normal y la función especifica de esta zona está mantenida por la corteza circundante. Se puede proceder a la resección radical sin ocasionar secuelas neurológicas, siempre que ésta se limite a los bordes de la lesión. De un total de 60 enfermos el autor presenta 4 casos de malformaciones arterio-venosas localizadas en las zonas motoras y del lenguaje y que fueron operados con buen resultado.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achsloch, J., J. Brihaye, A. Lereymaeker, G. Hoffmann etS. Thirty, A propos des 66 angiomes artério-veineux supratentoriels: Bases du problème thérapeutique. Excerpta Med. Ier Congr. intern. de chir. neurol. Bruxelles15 (1957), 57–58.
Anderson, F. M., andM. A. Korbin, Arteriovenous Anomalies of the Brain. Neurology8 (1958), 89–101.
Baker, B. S., Discussion des rapports sur “Les angiomes supratentoriels”, Ier Congr. intern. de neurochir. Excerpta med.15 (1957), 53–54.
Basset, C. R., Surgical experiences with arteriovenous anomalies of the brain. J. Neurosurg.8 (1951), 59–74.
Björkesten, G., andH. Troupp, Arteriovenous malformations of the brain. Acta psychiat. neurol. (Kbh.)34 (1959), 429–437.
Corrin, B., Three cases of intracranial vascular malformations in infants. J. clin. Path.12 (1959), 412–418.
Decker, K., Röntgendiagnostische Betrachtungen supratentorieller arteriovenöser Gefäßmißbildungen. Ier Congr. intern, de Neuroch. Acta med. belg. (1957), 237–248.
Dickmann, G. H., La conduite thérapeutique dans les angiomes supratentoriels. Excerpta med. Ier Congr. internat. de chir. neurol. Bruxelles15 (1957), 62.
Girard, P. F., etM. Tommasi, Réflexions concernant la pathologie générale des angiomes artérioveneux. Neurochir.9 (1963), 423–427.
Hamby, W. B., The pathology of supratentorial angiomes. Ier Congr. intern. de neuroch. Bruxelles. Acta med. belg. (1957), 193–204.
Höök, O., andC. Johanson, Intracranial arteriovenous aneurysms. A. M. A. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat.80 (1958), 39–54.
Kaplan, H. A., S. M. Aronson andE. J. Browder, Vascular malformations of the brain. An anatomical study. J. Neurosurg.18 (1961), 630–635.
Mc Kissock, W., andJ. Hankinson, The surgical treatment of the supratentorial angiomas. Ier Congr. intern. de neurochir. Bruxelles (1957), 222–236.
Krayenbühl, H., Discussion des rapports sur “Les angiomes supratentoriels”. Ier Congr. intern. de neurochir. Bruxelles15 (1957), 249–251.
Laine, E., J. M. Delandsbeer, P. Pruvot, J. Delahousse, C. Lopez-Pinto, J. L. Christiaens, A. Bertram etJ. Mme. Pruvot, Considérations cliniques, électroencéphalographiques et radiologiques tirées de l'étude de notre série d'anévrysmes artério-veineux ou cirsoides sus-tentoriels. Neurochir.9 (1963), 391–403.
Milletti, M., Discussion des rapports sur “Les angiomes supratentoriels”. Ier Congr. intern. de Neurochir. Bruxelles (1957), 249–251.
Norlén, G., Arteriovenous aneurysms of the brain. Report of ten cases of total removal of the lesion. J. Neurosurg.6 (1949), 475–494.
Olivecrona, H., Die arteriovenösen Aneurysmen der Carotis und Vertebralis-Gebiete. Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk.176 (1957), 263–280.
Olivecrona, H., andJ. Landenheim, Congenital arteriovenous aneurysms of the carotid and vertebral arterial systems. Springer, 1957.
Paterson, J. H., andW. McKissock, A clinical survey of intracranial angiomas with special reference to their mode of progression and surgical treatment. A report of 110 cases. Brain79 (1956), 233–266.
Pool, J. L., Treatment of arteriovenous malformations of the cerebral hemispheres. J. Neurosurg.19 (1962), 236–241.
Tönnis, W., W. Schiefer andW. Walter, Signs and symptoms of supratentorial arteriovenous aneurysms. J. Neurosurg.15 (1958), 471–480.
Wolf, G., Das Syndrom der Subarachnoidealblutung. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiat.28 (1960), 363–418.
Petr B., andM. Kroó, Příspěvky k rozpoznání a léčbě intrakraniálních aneurysmat. Naše Vojsko 1954, 134–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunc, Z. The possibility of surgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations in anatomically important cortical regions of the brain. Acta neurochir 13, 361–379 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02074419
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02074419