Abstract
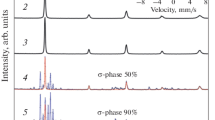
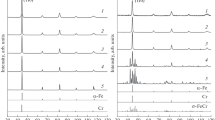
Mössbauer measurements have been performed in situ in the temperature range of 25 to 550°C for three Cr-Fe samples: Cr72Fe28 crystalline alloy (I), as-milled amorphous Cr65Fe35 powders made by mechanical grinding (II) and the same powder annealed at 420°C for 2 h (III). The temperature dependence of isomer shifts for samples I and III follows the variation predicted by the second-order Doppler effect, while for the sample II a deviation has been observed. The Debye temperatures have been determined to be 420, 400 and 380 K for sample I, III and II, respectively. A linear dependence onT 3/2 of quadrupole splitting of the annealed powder is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. Giessen,Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Rapidly Quenched Metals, Vol. 1 (Japan. Inst. of Metals, Sendai, 1982) p. 213.
S.K. Xia, E. Baggio-Saitovitch, F.C. Rizzo Assuncao and V.A.P. Rodrigues, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 5 (1993) 2729.
S.K. Xia, E. Baggio-Saitovitch and F.C. Rizzio Assuncao, J. Alloys Comp. 196 (1993) 177.
K. Nishiyama, F. Dimmling, Th. Kornrumpf and D. Riegel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 37 (1976) 357.
H.E. Mahnke, E. Dafni, M.H. Rafailovich, G.D. Sprouse and E. Vapirev, Phys. Lett. 71A (1979) 112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, S.K., Baggio-Saitovitch, E. Dynamical properties of Cr-Fe amorphous powders obtained from mechanical milling. Hyperfine Interact 83, 267–270 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02074283
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02074283