Abstract
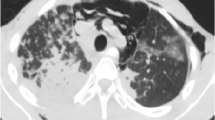
Two infants with recurrent obstructive symptoms attracted attention because of massive radiologically detected unilateral pulmonary hyperinflation. Further diagnostic procedures including bronchoscopy, revealed a pulmonary tuberculosis with lymph nodes encroaching on the bronchi. Steady improvement of clinical symptoms and hyperinflation was noted under combined antituberculotic therapy including systemic steroids.
Conclusion
Our two cases demonstrate that the differential diagnosis of unilateral pulmonary hyperinflation and wheezing in infancy should consider valvular stenosis by encroaching lymph nodes due to pulmonary tuberculosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrazone C, Hofer M, Nussle D, Suter S, Rochat T (1993) Childhood tuberculosis at a Swiss university hospital: a 2-year study. Eur J Pediatr 152:805–809
Giammona ST, Poole CA, Zelkowitz P, Skrovan C (1969) Massive lymphadenopathy in primary tuberculosis in children. Am Rev Respir Dis 100: 480–489
Hageman J, Shulman S, Schreiber M, Luck S, Yogev R (1980) Congenital tuberculosis: critical reappraisal of clinical findings and diagnostic procedures. Pediatrics 66:980–984
Inselman LS, Kendig EL (1990) Tuberculosis. In: Chernick V (ed) Kendig's disorders of the respiratory tract in children 5th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 730–769
Myers JP, Perlstein PH, Light IJ, Towbin RB, Dincsoy HP, Dincsoy MY (1981) Tuberculosis in pregnancy with fatal congenital infection. Pediatrics 67: 89–94
Nemir RL, O'Hare D (1985) Congenital tuberculosis- review and diagnostic guidelines. Am J Dis Child 139:284–287
Pineda PR, Leung A, Muller NL, Allen EA, Black WA, FitzGerald JM (1993) Intrathoracic paediatric tuberculosis. Tubercle Lung Dis 74:261–266
Schaaf HS, Gie RP, Beyers N, Smuts N, Donald PR (1993) Tuberculosis in infants less than 3 months of age. Arch Dis Child 69:371–374
Starke JR, Jacobs RF, Jereb J (1992) Resurgence of tuberculosis in children. J Pediatr 120:839–855
Toppet M, Malfroot A, Derde MP, Toppet V, Spehl M, Dab I (1990) Corticosteroids in primary tuberculosis with bronchial obstruction. Arch Dis Child 65:1222–1226
Worthington MG, Brink JG, Odell JA, Buckels J, Groot MK de, Klein M, Gunning AJ (1993) Surgical relief of acute airway obstruction due to primary tuberculosis. Ann Thorac Surg 56: 1054–1062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niggemann, B., Klettke, U., Magdorf, K. et al. Two cases of pulmonary tuberculosis presenting with unilateral pulmonary hyperinflation in infancy. Eur J Pediatr 154, 413–415 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072118