Abstract
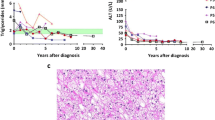
Progressive liver failure or hepatic complications of the primary disease led to orthotopic liver transplantation in eight children with glycogen storage disease over a 9-year period. One patient had glycogen storage disease (GSD) type I (von Gierke disease) and seven patients had type IV GSD (Andersen disease). As previously reported [19], a 16.5-year-old-girl with GSD type I was successfully treated in 1982 by orthotopic liver transplantation under cyclosporine and steroid immunosuppression. The metabolic consequences of the disease have been eliminated, the renal function and size have remained normal, and the patient has lived a normal young adult life. A late portal venous thrombosis was treated successfully with a distal splenorenal shunt. Orthotopic liver transplantation was performed in seven children with type N GSD who had progressive hepatic failure. Two patients died early from technical complications. The other five have no evidence of recurrent hepatic amylopectinosis after 1.1–5.8 postoperative years. They have had good physical and intellectual maturation. Amylopectin was found in many extrahepatic tissues prior to surgery, but cardiopathy and skeletal myopathy have not developed after transplantation. Post-operative heart biopsies from patients showed either minimal amylopectin deposits as long as 4.5 years following transplantation or a dramatic reduction in sequential biopsies from one patient who initially had dense myocardial deposits. Serious hepatic derangement is seen most commonly in types I and IV GSD. Liver transplantation cures the hepatic manifestations of both types. The extrahepatic deposition of abnormal glycogen appears not to be problematic in type I disease, and while potentially more threatening in type IV disease, may actually exhibit signs of regression after hepatic allografting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GSD:
-
glycogen storage disease
References
Alper CA, Johnson AM, Birtch AG, Moore FD (1969) Human C'3: Evidence for the liver as the primary site of synthesis. Science 163286–163288
Alper CA, Raum D, Awdeh Z, Petersen BH, Taylor PD, Starzl TE (1980) Studies of hepatic synthesis in vivo of plasma proteins, including orosomucoid, transferrin, alpha-1-antitrypsis, C8, and Factor B. Clin Immunol Immunopath 16:84–89
Anderson DH (1952) Studies on glycogen disease with report of a case in which the glycogen was abnormal. In: Johns Hopkins Press Baltimore, Carbohydrate metabolism. Najjar A (ed) pp:28–42
Bannayan GA, Dean WJ, Howell RR (1976) Type IV glycogen storage disease. Am J Clin Path 66:702–709
Brown BI (1986) Debranching and branching enzyme deficiencies. In: Engel AG, Banker BQ (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1653–1661
Brown BI, Brown DH (1966) Lack of an α-1,4-glucan: α-1,4-glucan 6-glycosyl transferase in a case of type IV glycogenosis. Proc Nat Acad Sci. USA 56:725–729
Brown BI, Brown DH (1989) Branching enzyme activity of cultured amniocytes and chrionic villi: prenatal testing for type IV glycogen storage disease. Am J Hum Genet 44:378–381
Cori GT, Cori CF (1952) Glucose-6-phosphatase in the liver in glycogen storage disease. J Biol Chem 199:661–667
Ferguson IT, Mahon M, Cumming WJ (1983) An adult case of Andersen's disease-Type IV glycogenosis. A clinical, histochemical, ultrastructural and biochemical study. J Neurol Sci 60:337–351
Greene HL, Slonim AE, Burr IM (1979) Type I glycogen storage disease: a metabolic basis for advances in treatment. Adv Pediatr 26:63–92
Guerra AS, Van Diggelen OP, Carneiro F, Tsou RM, Simoes S, Santos NU (1986) A juvenile variant of glycogenosis IV (Andersen disease) Eur J 145:179–181
Greene GM, Weldon DC, Ferrans VJ, Cheatham JP, McComb RD, Brown BI, Gumbiner CH, Vanderhoff JA, Itkin PG, McManus BM (1987) Juvenile polysaccharidosis with cardioskeletal myopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 111:977–982
Harding MW, Galat A, Uehling DE, Schreiber SL (1989) A receptor for the immunosuppressant FK506 is a cis-trans peptidyl-prolyl isomerase. Nature 341:758–760
Hers HG, Van Hoof F, De Barsy T (1989) Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. 6th edn. McGraw Hill, New York pp 425–453
Illingworth B, Corti GT (1952) Structures of glycogen and amylopectins: III. Normal and abnormal human glycogen. J Biol Chem 199:653–660
Ishihara T, Yokota T, Yamashita Y, Takahashi M, Kawano H, Uchino F, Kamei T, Matsumoto N, Kusunose Y, Yamada M (1987) Comparative study of the intracytoplasmic inclusions in Lafora disease and Type IV glycogenosis by electron microscopy. Acta Pathol Jpn 37:1591–1601
Kashiwagi N, Groth CG, Starzl TE (1968) Changes in serum haptoglobin and group specific component after orthotopic liver homotransplantation in humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 128:247–250
Kashiwagi N (1969) Specila immunochemical studies. In: Starzl TE (ed) Experience in hepatic transplantation. WB Saunders Co, Philadelphia, 163:286–288
Malatack JJ, Iwatsuki S, Gartner JL, Zitelli BJ, Roe T, Starzl TE (1983) Liver transplantation for type I glycogen storage disease. Lancet I:1073–1075
Mazzaferro V, Porter K, Scotti-Foglieni CL, Ventakataramanan R, Makowka L, Rossaro L, Froncavilla A, Todo S, Van Thiel D, Starzl TE (1990) The hepatotrophic effect of cyclosporine. Surgery 107:533–539
McMaster KR, Powers JM, Hennigar GR Jr, Wohlbmann HJ, Farr OH Jr (1979) Nervous system involvement in Type IV Glycogenosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 103:105–111
Merrill DA, Kirkpatrick CH, Wilson WEC, Riley CM (1964) Change in serum haptoglobin type following human liver transplantation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 116:748–751
Nordlie RC (1971) Glucose-6-phosphatase, hydrolytic and synthetic activities. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes. Academic Press, New York, pp 543–610
Raum D, Marcus D, Alper CA, Levey R, Taylor PD, Starzl TE (1980) Synthesis of human plasminogen by the liver. Science 208:1036–1037
Reed GB, Dixon JFP, Neustein HB (1969) Type IV glycogen. Lab Invest 19:546–557
Schochet SS, McCormick WF, Zellweger H (1970) Type IV glycogenosis
Servidei S, Riepe R, Langston C, Tani LY, Bricher JT, Crisp-Lindgren JT, Travers H, Armstrong D, Di Mauro S (1987) Severe cardiopathy in branching enzyme deficiency. J Pediatr 111:51–56
Siekierka JJ, Hung SHY, Poe M, Lin CS, Sigal NH (1989) A cytosolic binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK 506 has peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity but is distinct from cyclophilin. Nature 341:755–757
Starzl TE, Marchioro TL, Rowlands DT Jr, Kirkpatrick CH, Wilson WEC, Rifkind D, Waddell WR (1964) Immunosuppression after experimental and clinical homotransplantation of the liver. Ann Surg; 160:411–439
Starzl TE, Watanabe K, Porter KA, Putnam CW (1976) Effects of insulin, glucagon, and insulin/glucagon infusions on liver morphology and cell division after complete portacaval shunt in dogs. Lancet I:821–825
Starzl TE, Koep LJ, Halgrimson GC, Hood J, Schroter GPJ, Porter KA, Weil R (1979) Fifteen years of clinical liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 77:375–388
Starzl TE, Ieatsuki S, Van Thiel DH, Gartner JC, Zitelli BJ, Malatack JJ, Schade RR, Shaw BW Jr, Hakala TR, Rosenthal JT, Porter KA (1982) Evolution of liver transplantation. Hepatology 2:614–636
Starl TE, Demetris AJ, Van Thiel DH (1989) Medical progress: Liver transplantation. N Engl J Med (Part I) 321:1014–1022
Starzl TE, Porter KA, Mazzaferro V, Todo S, Fung J, Francavilla A. Hepatotrophic effects of FK 506 in dogs. Transplantation (in press)
Zellweger H, Mueller S, Ionasescu V, Schochet SS, McCormick W (1972) Glycogenosis IV: a new cause of infantile hypotonia. J Pediatr 80:842–844
Zitelli BJ, Malatack JJ, Gartner JC, Shaw BW Jr, Iwatsuki S, Starzl TE (1983) Orthotopic liver transplantation in children with hepatic-based metabolic disease. Transplant Proc (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selby, R., Starzl, T.E., Yunis, E. et al. Liver transplantation for type I and type IV glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 152 (Suppl 1), 71–76 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072093
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072093