Abstract
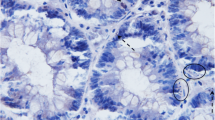
Colonic carcinogenesis is accompanied by progressive genetic changes and alterations in growth control. To examine whether abnormalities of apoptosis are involved in carcinogenesis, we examined epithelial apoptosis in formalin-fixed normal and neoplastic colon by terminal uridine deoxynucleotide nick end-labeling (TUNEL) histochemistry. In normal colon, resection margins, and hyperplastic polyps, TUNEL-positive cells comprised around 3% of total colonocytes, with over 85% of these cells located in surface epithelium between crypts. In adenomas, there were significantly fewer TUNEL-positive cells at the luminal surface than normal (1.82±0.51% of epithelial cells, compared with 12.1±2.3%,P<0.05) and a trend to increased numbers at the crypt base (2.70±0.98% compared with 0.65±0.15%). Carcinomas contained fewer TUNEL-positive cells than normal (1.7±0.27%), and they are randomly distributed. Transitional mucosa had significantly more TUNEL-positive colonocytes than normal (11.0±3.0%,P<0.005), both at the surface and crypt base. These results show that colonocyte apoptosis normally occurs mainly in luminal cells but that early during carcinogenesis the distribution and quantity of apoptotic cells changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morson BC: The polyp-cancer sequence in the large bowel. Proc R Soc Med 67:451–454, 1974
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B: A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–767, 1990
Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, Sargeant L, Krapcho K, Wolff EE, Burt RW, Hughes JP, Warrington J, McPherson J, Wasmuth J, LePaslier D, Abderrahim H, Cohen D, Leppert M, White R: Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis gene. Cell 66:589–600, 1991.
Kinzler KW, Nilbert MC, Su LK, Vogelstein B, Bryan TM, Levy DB, Smith KJ, Preisinger AC, Hedge P, McKechnie D, Finniear R, Markham A, Groffen J, Boguski M, Altshul SF, Horii A, Hiroshi A, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y, Nishisho L, Nakamura Y: Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science 253:661–665, 1991
Modrich P: Mismatch repair, genetic instability and cancer. Science 266:1959–1960, 1994
Lipkin M, Blattner WA, Gardner EJ, Burt RW, Lynch H, Deschner E, Winawer S, Fraumeni JF: Classification and risk assessment of individuals with familial polyposis, Gardner's syndrome, and familial non-polyposis colon cancer from [3H]-thymidine labeling patterns in colonic epithelial cells. Cancer Res 44:4201–4207, 1984
Risio M, Lipkin M, Candelaresi G, Bertone A, Coverlizza S, Rossini PF: Correlations between rectal mucosal cell proliferation and the clinical and pathological features of nonfamilial neoplasia of the large intestine. Cancer Res 51:1917–1921, 1991
Terpstra OT, van Blankenstein M, Dees J, Eilers GAM: Abnormal pattern of cell proliferation in entire colonic mucosa of patients with colon adenoma or cancer. Gastroenterology 92:704–708, 1987
Anti M, Marra G, Armelao F, Percesepe A, Fiscarelli R, Ricciuto GM, Valenti A, Rapacinni GL, De Vitis I, D'Agostini G, Brighi S, Vecchio FM: Rectal epithelial cell proliferation patterns as predictors of adenomatous colorectal polyp recurrence. Gut 34:525–530, 1993
Risio M, Coverlizza S, Ferrari A, Candelares GL, Rossini FP: Immunohistochemical study of epithelial cell proliferation in hyperplastic polyps, adenomas and adenocarcinoma of the large bowel. Gastroenterology 94:899–906, 1988
Johnston PG, O'Brien MJ, Dervan PA, Carney DN: Immuno-histochemical analysis of cell kinetic parameters in colonic adenocarcinomas, adenoma and normal mucosa. Hum Pathol 20:696–700, 1989
Risio M, Rossini PF: Cell proliferation in colorectal adenomas containing invasive carcinoma. Anticancer Res 13:43–48, 1993
Croitoru K, Riddell RH: Reduce, reuse, recycle: Shedding light on shedding cells. Gastroenterology 105:1243–1246, 1993
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA: Identification of programmed cell death via specific labelling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501, 1992
Hall PA, Coates PJ, Ansari B, Hopwood W: Regulation of cell numbers in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract: The importance of apoptosis. J Cell Sci 107:3569–3577, 1994
Sträter J, Koretz K, Günthert AR, Möller P:In situ detection of enterocytic apoptosis in normal colonic mucosa and in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 37:819–823, 1995
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462, 1995
Bedi A, Pasricha PJ, Akhtar AJ, Barber JP, Bedi GC, Giardiello FM, Zehnbauer BA, Hamilton SR, Jones RJ: Inhibition of apoptosis during development of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 55:1811–1816, 1995
Coates PJ: Molecular methods for the identification of apoptosis in tissues. J Histotechnol 17:261–267, 1994
Kressel M, Groscurth P: Distinction of apoptotic and necrotic cell death byin situ labelling of fragmented DNA. Cell Tissue Res 278:549–556, 1994
Shu S, Ju G, Fan L: The glucose oxidase-DAB-nickel method in peroxidase histochemistry of the nervous system. Neurosci Lett 85:169–171, 1988
Ijiri K: Apoptosis (cell death) induced in mouse bowel by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine, methylazoxymethanol acetate and gamma rays. Cancer Res 49:6342–6346, 1989
Enright H, Hebbel R, Nath K: Internucleosomal cleavage of DNA as the sole criterion for apoptosis may be artifactual. J Lab Clin Med 124:63–68, 1994
Potten CS: The significance of spontaneous and induced apptosis in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:179–195, 1992
Itzkowitz S, Kim YS: Polyps and benign neoplasms of the colon.In: Gastrointestinal Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management, 4th ed. Sleisinger MH, Fordtran JS (eds). Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1993, pp 1403–1430
Arai T, Kino I: Role of apoptosis in modulation of the growth of human colorectal tubular and villous adenomas. J Pathol 176:37–44, 1995
Lightdale C, Lipkin M, Deschner E:In vivo measurements in familial polyposis: Kinetics and location of proliferating cells in colonic adenomas. Cancer Res 42:4280–4283, 1982
Ruoslahti E, Reed JC: Anchorage dependence, integrins and apoptosis. Cell 77:477–478, 1994
Hague A, Moorgehen M, Hicks D, Chapman M, Paraskeva C: Bcl-2 expression in human colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. Oncogene 9:3367–3370, 1994
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens LC, Lee JJ, Levin B: bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 55:237–241, 1995
Reed JC: Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 124:1–6, 1994
Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer S: Bcl2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6961–6965, 1991
Heerdt BG, Houston MA, Augenlicht LH: Potentiation by short-chain fatty acids of differentiation and apoptosis in human colonic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 54:3288–3294, 1994
Rubinfield B, Souza B, Albert I, Muller O, Chamberlain SH, Masiarz FR, Munemitsu S, Polakis P: Association of the APC gene product with β-catenin. Science 262:1731–1734, 193
Su L-K, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW: Association of the APC tumor suppressor protein with catenins. Science 262:1734–1737, 1993
Rotello FJ, Lieberman RC, Lepoff RB, Gerschenson LE: Characterization of uterine epithelium apoptotic cell death kinetics and regulation by progesterone and RU 486. Am J Pathol 140:449–456, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the American Cancer Society Institutional Review Grant IRG-177C, Columbia Presbyterian Cancer Center and the US National Dairy Council.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moss, S.F., Scholes, J.V. & Holt, P.R. Abnormalities of epithelial apoptosis in multistep colorectal neoplasia demonstrated by terminal deoxyuridine nick end labeling. Digest Dis Sci 41, 2238–2247 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02071407
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02071407