Abstract
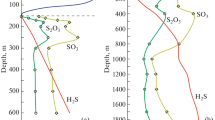
Vertical profiles of total sulfur and organic carbon have been measured in two deep-sea piston cores from the southwestern Japan Sea where sulfate reduction is proceeding within the sediments. The content of total sulfur, most of which is present as pyrite, increases gradually with increasing depth, showing several peaks. The amount of diagenetically deposited sulfide-sulfur is estimated using a steady-state model that considers vertical change in the diffusion coefficient. It is suggested that two-thirds to three-fourths of the observed total sulfur content has been deposited diagenetically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai, F., T. Oba, H. Kitazato, Y. Horibe and H. Machida (1981): Late Quaternary tephrochronology and paleo-oceanography of the sediments of the Japan Sea. Quat. Res. (Tokyo),20, 209–230 (in Japanese).
Berner, R. A. (1964a): Distribution and diagenesis of sulfur in some sediments from the Gulf of California. Mar. Geol.,1, 117–140.
Berner, R. A. (1964b): An idealized model of dissolved sulfate distribution in recent sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,28, 1497–1503.
Berner, R. A. (1972): Sulfate reduction, pyrite formation, and the oceanic sulfur budget. In: The Changing Chemistry of the Oceans, ed. by D. Dyrssen and D. Jagner, Almqvist and Wiksell, Stockholm, p. 347–361.
Berner, R. A. (1980): Early Diagenesis: A Theoretical Approach. Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, 241pp.
Didyk, B. M., B. R. T. Simoneit, S. C. Brassell and G. Eglinton (1978): Organic geochemical indicators of palaeoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation. Nature,272, 216–222.
Filipek, L. H. and R. M. Owen (1980): Early diagenesis of organic carbon and sulfur in outer shelf sediments from the Gulf of Mexico. Am. J. Sci.,280, 1097–1112.
Goldhaber, M. B., R. C. Aller, J. K. Cochran, J. K. Rosenfeld, C. S. Martens and R. A. Berner (1977): Sulfate reduction, diffusion and bioturbation in Long Island Sound sediments: Report of the FOAM group. Am. J. Sci.,277, 193–237.
Goldhaber, M. B. and I. R. Kaplan (1974): The sulfur cycle. In: The Sea, Vol. 5, ed. by E. D. Goldberg, Wiley, New York, p. 569–655.
Goldhaber, M. B. and I. R. Kaplan (1980): Mechanisms of sulfur incorporation and isotope fractionation during early diagenesis in sediments of the Gulf of California. Mar. Chem.,9, 95–143.
Horibe, Y. (ed.) (1981): Preliminary Report of the Hakuho Maru Cruise KH-77-3 (Pegasus Expedition), Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, 55pp.
Ichikura, M. and H. Ujiié (1976): Lithology and planktonic foraminifera of the Sea of Japan piston cores. Bull. Nat. Sci. Mus. (Tokyo), Ser. C,2, 151–178.
Ishizuka, T. (1981): Paleoenvironment of the Japan Sea during the last twenty to thirty thousand years. Bull. Geol. Surv. Japan,32, 192–193 (in Japanese).
Kobayashi, K. and M. Nomura (1972): Iron sulfides in the sediment cores from the Sea of Japan and their geophysical implications. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,16, 200–208.
Li, Y. -H. and S. Gregory (1974): Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,38, 703–714.
Machida, H. and F. Arai (1976): The very widespread tephra — The Aira-Tn. Kagaku,46, 339–347 (in Japanese).
Manheim, F. T. (1970): The diffusion of ions in unconsolidated sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,9, 307–309.
Manheim, F. T. and L. S. Waterman (1974): Diffusimetry (diffusion constant estimation) on sediment cores by resistivity probe. Init. Rep. Deep Sea Drilling Proj.,22, 663–670.
Masuzawa, T. and Y. Kitano (1983): Interstitial water chemistry in deep-sea sediments from the Japan Sea. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,39, 171–184.
Masuzawa, T., Y. Kitano and H. Wada (1979): Partition of manganese and distribution of sulfur, organic carbon, and nitrogen in a 10-m core from the Japan Sea. J. Earth Sci., Nagoya Univ.,26/27, 1–17.
McDuff, R. E. and R. A. Ellis (1979): Determining diffusion coefficients in marine sediments: a laboratory study of the validity of resistivity techniques. Am. J. Sci.,279, 666–675.
Miyake, Y., Y. Sugimura and E. Matsumoto (1968): Ionium-thorium chronology of the Japan Sea cores. Rec. Oceanogr. Works Japan,9, 189–195.
Murray, J. W., V. Grundmanis and W. M. Smethie, Jr. (1978): Interstitial water chemistry in the sediments of Saanich Inlet. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,42, 1011–1026.
Nitani, H. (1972): On the deep and bottom waters in the Japan Sea. In: Research in Hydrography and Oceanography, Hydrographic Department of Japan, Tokyo, p. 151–201.
Okada, A. and M. Shima (1973): Authigenic minerals in the sediments of Japan Sea. Sci. Papers Inst. Phys. Chem. Res.,67, 148–154.
Thiede, J. and T. H. van Andel (1977): The paleoenvironment of anaerobic sediments in the Late Mesozoic South Atlantic Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,33, 301–309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuzawa, T., Kitano, Y. Sulfate reduction and sulfide deposition in deep-sea sediments from the southwestern Japan Sea. Journal of the Oceanographical Society of Japan 39, 251–258 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02070395
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02070395