Abstract
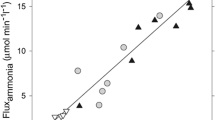
There is abundant evidence to suggest that alterations of excitatory and inhibitory amino acids play a significant role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in both acute and chronic liver diseases. Brain glutamate concentrations are reduced in patients who died in hepatic coma as well as in experimental HE, astrocytic reuptake of glutamate is compromised in liver failure and postsynaptic glutamate receptors (both NMDA and non-NMDA subclasses) are concomitantly reduced in density. Recent studies in experimental acute liver failure suggest reduced capacity of the astrocytic glutamate transporter in this condition. Together, this data suggests that neuron-astrocytic trafficking of glutamate is impaired in HE. Other significant alterations of neuroactive amino acids in HE include a loss of taurine from brain cells to extracellular space, a phenomenon which could relate both to HE and to brain edema in acute liver failure. Increased concentrations of benzodiazepine-like compounds have been reported in human and experimental HE. Clinical trials with the benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil reveal a beneficial effect in some patients with HE; the mechanism responsible for this effect, however, remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basile, A.S., Huges, R.D., Harrison, P.M., Murata, Y., Pannell, L., Jones, E.A., Williams, R., and Skolnick R. (1991). Elevated brain concentrations of 1,4-benzodiazepines in fulminant hepatic failure.N. Engl. J. Med. 325:473–478.
Bassett, M.L., Mullen, K.D., Skolnick, P., and Jones, E.A. (1987). Amelioration of hepatic encephalopathy by pharmacologic antagonism of the GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor complex in a rabbit model of fulminant hepatic failure.Gastroenterology 93:1069–1077.
Bosman, D.K., Deutz, N.E.P., Maas, M.A.W., van Eijk, H.M.H., Smit, J.J.H., de Haan, J.G., and Chamuleau, R.A.F.M. (1992). Amino acid release from cerebral cortex in experimental acute liver failure, studied byin vivo cerebral cortex microdialysis.J. Neurochem. 59:91–99.
Butterworth, R.F., Lavoie, J., Giguère, J.F., and Pomier Layrargues, G. (1988). Affinities and densities of high affinity3H-muscimol (GABA-A) binding sites and central benzodiazepine receptors are unchanged in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 8:1084–1088.
Butterworth, R.F., Le, O., Lavoie, J., and Szerb, J.C. (1991). Effect of portacaval anastomosis on electrically-stimulated release of glutamate from rat hippocampal slices.J. Neurochem. 56:1481–1484.
Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Hepatic encephalopathy. In. (I.M. Arias, J.L. Boyer, N. Fausto, W.B. Jokoby, D.A. Schachter and D.A. Shafritz, eds.)The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology, 3rd edition, Raven Press, New York, pp. 1193–1208.
Butterworth, R.F., Wells, J., and Pomier Layrargues, G. (1995). Detection of benzodiazepine in hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 21:604–605.
Butterworth, R.F. (1996). Taurine in Hepatic Encephalopathy. In (R.J. Huxtable et al., eds.)Taurine: Neurochemistry, Biochemistry and Pharmacology (in press)
Butterworth, J. and Aronson, L. (1996). Selective alterations of amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid of dogs with congenital portal-systemic shunts.Metab. Brain Dis. (in press).
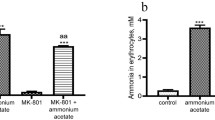
de Kneght, R.J., Kornhuber, J., Schalm, S.W., Rusche, K., Riederer, P., and Tan, J. (1993). Binding of the ligand3H-MK801 to the MK801 binding site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor during experimental encephalopathy from acute liver failure and from acute hyperammonemia in the rabbit.Metab. Brain Dis. 8:81–94.
Ferenci, P., Pappas, S.C., Munson, P.J., and Jones, E.A. (1984). Changes in glutamate receptors on synaptic membranes associated with hepatic encephalopathy or hyperammonemia in the rabbit.Hepatology 4:25–29.
Giguère, J.F., and Butterworth, R.F. (1984). Amino acid changes in regions of the CNS in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Res. 9:1309–1321.
Giguère, J.F., Besnard, A.M., Fournier, H., Bergeron, M. and Butterworth, R.F. (1988). Evidence for a functional imbalance between central GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission in portal-systemic encephalopathy. In (P.B. Soeters, J.H.P. Wilson, A.J. Meijer and E. Holm, eds.)Advances in Ammonia Metabolism and Hepatic Encephalopathy, Elsevier, pp. 287–293.
Hagberg, H., Lehmann, A., Sandberg, M., Nystrom, B., Jacobson, I., and Hamberger, A. (1985). Ischemia-induced shift of inhibitory and excitatory amino acids from intra- to extracellular compartments.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:413–419.
Hilgier, W., and Olson, J.E. (1994). Brain ion and amino acid contents during edema development in hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 62:197–204.
Lavoie, J., Giguère, J.F., Pomier Layrargues, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1987a). Amino acid changes in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 49:692–697.
Lavoie, J., Giguère, J.F., Pomier Layrargues, G., Butterworth R.F. (1987b). Activities of neuronal and astrocytic marker enzymes in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Metab. Brain Dis. 2:283–290.
Maddison, J.E., Watson, W.E.J., Dodd, P.R., and Johnston, G.A.R. (1991). Alterations in cortical3H-kainate and α-3H-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid binding in a spontaneous canine model of chronic hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 56:1881–1888.
Mena, E.E., and Cotman, C.W. (1985). Pathologic concentrations of ammonium ions block L-glutamate uptake.Exp. Neurol. 59:259–263.
Michalak, A., Rose, C., Therrien G., Butterworth, J., and Butterworth, R.F. (1995). Extracellular brain amino acids in relation to deteriorating neurologic status in acute liver failure: Results of anin vivo cerebral microdialysis study.Hepatology, 22:160A, #216.
Michalak, A., Rose, C., Butterworth, J., and Butterworth, R.F. (1996). Extracellular concentrations of neuroactive amino acids in frontal cortex of rats with experimental acute liver failure: results of anin vivo cerebral microdialysis study.Hepatology (in press).
Moroni, F., Lombardi, G., Moneti, G., Cortesini, C. (1983). The release and neosynthesis of glutamic acid are increased in experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 40: 850–854.
Mullen, K.D., Szauter, K.M., Kaminsky, Tolentino, P.D., McCullough, A.J. (1989). Detection and characterization of endogenous benzodiazepine activity in both animal models and humans with hepatic encephalopathy. In (R.F. Butterworth and G. Pomier Layrargues, eds.)Hepatic Encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatment, Clifton, NJ: Humana Press, pp. 287–294.
Norenberg, M.D., Mozes, L.W., Papendick, R.E., and Norenberg, L.B. (1985). Effect of ammonia on glutamate, GABA and rubidium uptake by astrocytes.Ann. Neurol. 18:149.
Norenberg, M.D. (1996). Astrocytes in neuronal degeneration.J. Neurochem 66 (suppl.) S79B (abstract).
Olasmaa, M., Rothstein, J.D., Guidotti, A., Weber, R.J., Paul, S.M., Spector, S., Zeneroli, M.L., Baraldi, M., Costa, E. (1990). Endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligands in human and animal hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. 55:2015–2023.
Pasantes-Morales, H., and Schousboe, A. (1988). Volume regulation in astrocytes: a role for taurine as osmoeffector.J. Neurosci. Res. 20:505–509.
Peterson, C., Giguère, J.F., Cotman, C.W., Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Selective loss of N-methyl-D-aspartate-sensitive L-3H-glutamate binding sites in rat brain following portacaval anastomosis.J. Neurochem. 55:386–390.
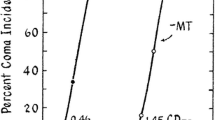
Pomier Layrargues, G., Giguère, J.-F., Lavoie, J., Perney, P., Gagnon, S., D'Amour, M., Well, J., and Buttterworth, R.F. (1994). Flumazenil in cirrhotic patients with hepatic coma: a randomized double blind placebo-controlled crossover trial.Hepatology 19:32–37.
Raghavendra Rao, V.L., Audet, R.M. and Butterworth, R.F. (1995). Increased nitric oxide synthase activities and L-[3H]arginine uptake in brain following portacaval anastomosis.J. Neurochem. 65:677–681.
Rossle, M., Deckert, J., and Jones, E.A. (1989). Autoradiographic analysis of GABA-benzodiazepine receptors in an animal model of acute hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 10:143–147.
Roy, S., Pomier Layrargues, G., Butterworth, R.F., and Huet, P.M. (1988). Hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic and portacaval shunted dogs: lack of changes in brain GABA uptake, brain GABA levels and brain glutamic acid decarboxylase activity and brain postsynaptic GABA receptors.Hepatology 8:845–849.
Schafer, D.F., and Jones, E.A. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy and the γ-aminobutyric acid system.Lancet 1:18–20.
Schmidt, W., Wolf, G., Grungreiff, K., Meier, M., Reum, T. (1990). Hepatic encephalopathy influences high-affinity uptake of transmitter glutamate and aspartate into the hippocampal formation.Metab. Brain Dis. 5:19–32.
Scollo-Lavizzari, G., and Steinmann, E. (1985). Reversal of hepatic coma by benzodiazepine antagonist (Ro15-1788).Lancet 1:1324.
Siesjo, B.K., and Wielock, T. (1986). Epileptic brain damage: pathophysiology and neurochemical pathology. In (A.V. Delgado-Escueta, A.A. Ward, Jr., D.M. Woodbury and R.J. Porter, eds.)Advances in Neurology, vol. 44, Raven Press, New York, pp. 813–847.
Steindl, P., Puspok, A., Druml, W., and Ferenci, P. (1991). Beneficial effect of pharmacological modulation of the GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor on hepatic encephalopathy in the rat: comparison with uremic encephalopathy.Hepatology 14:963–968.
Swain, M., Butterworth, R.F., and Blei, A.T. (1992a). Ammonia and related amino acids in the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute ischemic liver failure in rats.Hepatology 14:449–453.
Swain, M., Bergeron, M., Audet, R., Blei, A.T. and Butterworth, R.F. (1992b). Monitoring of neurotransmitter amino acids by means an indwelling cisterna magna catheter: a comparison of two rodent models of fulminant hepatic failure.Hepatology 16:1028–1035.
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, L.S., Ungerstedt, U. (1987). Brain cortical amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats.Neurochem. Res. 12:265–269.
Wade, J.V., Olson, J.P., Samson, F.E., Nelson, S.P., and Pazdernick, T.L. (1988). A possible role for taurine in osmoregulation within the brain.J. Neurochem. 51:740–745.
Waltz, W., and Allen, A.F. (1987). Evaluation of the osmoregulatory function of taurine in brain cells.Exp. Brain Res. 68:290–298.
Waterfield, C.J., Turton, J.A., Scales, M.D.C., and Timbrell, J.A. (1991). Taurine, a possible urinary marker of liver damage: a study of taurine excretion in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats.Arch. Toxicol. 65:548–555.
Wright, C.E., Tallan, H.H., and Lin Y.Y. (1986). Taurine: biological update.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55:427–453.
Zieve, L., Ferenci, P., Rzepczynski, D., Ebner, J., Zimmerman, C. (1987). A benzodiazepine antagonist does not alter the course of hepatic encephalopathy or neural γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) binding.Metab. Brain Dis. 2:201–205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butterworth, R.F. Neuroactive amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 11, 165–173 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02069503
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02069503