Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to determine the concentration of interleukin-1α in human embryo culture medium with or without oviductal cell coculture and to correlate the interleukin-1α levels with pregnancy.
Methods: Culture media from 32 in vitrofertilization and embryo transfer cycles were assayed for interleukin-1α by immunoassay technique. Human embryos were cultured in Earles' balanced salt solution supplemented with 15% preovulatory serum (sEBSS) in 16 of these cycles, while embryos in the rest of the cycles were cocultured with human oviductal cells in sEBSS.
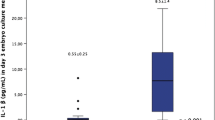
Results: Both sEBSS and spent sEBSS after embryo culture contained low or undetectable levels of interleukin-1α in the pregnant and nonpregnant cycles. On the other hand, oviductal cells significantly increased the amount of interleukin-1α immunoreactivity in the conventional culture medium or coculture medium (P<0.001, Mann-Whitney rank sum test). The concentrations of interleukin-1α in the spent sEBSS after oviductal cell culture and after coculture with human embryos were 1.5±1.0 and 1.3±0.9 pg/ml, respectively. There was no difference in the interleukin-1α concentration between the pregnant and the nonpregnant coculture cycles.
Conclusions: These data showed that human oviductal cells produced interleukin-1α immunoreactivity in a coculture system. However, this production could not be used as a marker for successful embryo implantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daya S, Clark DA: Identification of two species of suppressive factor of differing molecular weight released by in vitro fertilized human oocytes. Fertil Steril 1988;49:360–363
Clark DA, Lee S Fishel S, Mahadevan M, Goodall H, Ah Moye M, Schechter O, Stedronska-Clark J, Daya S, Underwood J, Craft I, Mowbray J: Immunosuppressive activity in human in vitro fertilization (IVF) culture supernatants and prediction of the outcome of embryo transfer: A multicenter trial. J in Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1989;6:51–58
Sheth KV, Parhar RS, Roca GL, Hamilton CJCM, Al-Sedairy ST, Jabbar FA: Predication of successful implantation by measuring interleukin-1-alpha and immunosuppressive factor(s) in preimplantation embryo culture fluid. Fertil Steril 1991;55:952–957
Jones KP, Edwin SS, Warnock SH, Mitchell MD, Urry RL: Immunosuppressive activity and alpha interferon concentrations in human embryo culture media as an index of potential for successful implantation. Fertil Steril 1992;57:637–640
Armstrong DT, Chaouat G, Guichard A, Cedard L, Andreu G, Denver L: Lack of correlation of immunosuppressive activity secreted by human in vitro fertilization (IVF) ova with successful pregnancy. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1989;6:15–21
Hardy RI, Anderson DJ, Hill JA: Lack of correlation between interleukin-1-α in preimplantation culture media and pregnancy outcome. Fertil Steril 1993;61:Abstr O-139
Sifer DB, Romero R, Berlinsky D, Haning RV Jr: Absence of cytokine production by preimplantation human embryos. Adv Res Int 1993;30:105–107
Austgulen K, Arntzen KJ, Vatten LJ, Kahn J, Sunde A: Prediction of cytokines (interleukin-1, interleukin-6, transforming growth factor-β) and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors in embryo culture fluids during in vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod 1995;10:171–176
Bongso A, Ng SC, Sathananthan H, Ng PL, Rauff M, Ratnam S: Improved quality of human embryos when co-cultured with human ampullary cells. Hum Reprod 1989;4:706–713
Yeung WSB, Ho PC, Lau EYL, Chan STH: Improved development of human embryos in vitro by a human oviductal cell coculture system. Hum Reprod 1992;7:1144–1149
Bongso A, Ng SC, Fong CY, Anandakumar C, Marshall B, Edirisinghe R, Ratnam S: Improved pregnancy rate after transfer of embryos grown in human fallopian tubal cell coculture. Fertil Steril 1992;58:569–574
Meinert CL: Randomization and the mechanics of treatment masking.In Clinical Trials: Design, Conduct and Analysis, CL Meinert (ed.). New York/Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1986 pp. 90–112
Simon C, Pellicer A, Plan ML: Interleukin-1 system crosstalk between embryo and endometrium in implantation. Hum Reprod 1995;10 (Suppl 2):43–54
De los Santos MJ, Mercader, A Frances A, Portoles E, Remohi H, Pellicer A, Simon C: Role of endometrial factors in regulating secretion of components of the immunoreactive human embryonic interleukin-1 system during embryonic development. Biol Reprod 54:563–574
Dinarello CA: Interleukin-1 and its related cytokines. Adv Immunol 1989;44:153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, W.S.B., Lau, E.Y.L., Chan, A.Y.F. et al. The production of interleukin-1α immunoreactivity by human oviductal cells in a coculture system. J Assist Reprod Genet 13, 772–775 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066496
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066496