Abstract
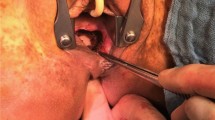
PURPOSE: During transsphincteric fistula surgery, laying open the entire fistula track can cause grave damage. Thus, a surgical procedure that excises the primary abscess only is preferable. However, the primary abscess of a transsphincteric fistula is located in the postanal space. When creating an appropriate drainage wound after excision of the primary abscess, damage to the drainage wound itself can be severe. This article illustrates an alternative procedure. METHODS: We have developed a new method in which we excise only the primary abscess of a transsphincteric fistula and use the muscle flap at the bottom of the wound to fill in the dead space left by the excision. This procedure takes advantage of the availability of the muscle flap and allows for a smaller wound and faster wound healing. RESULTS: During the past 17 years, during which 328 transsphincteric fistula procedures have been performed using the muscle-filling technique, we have experienced a recurrence rate of only 1.5 percent (5 cases). CONCLUSION: The muscle-filling technique is an effective alternative procedure for transsphincteric fistulas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Hanley PH. Conservative surgical correction of horse-shoe abscess and fistula. Dis Colon Rectum 1965;8:364–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Iwadare, J., Sumikoshi, Y. & Sahara, R. Muscle-filling procedure for transsphincteric fistulas. Dis Colon Rectum 40 (Suppl 10), S102–S103 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02062030
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02062030