Abstract
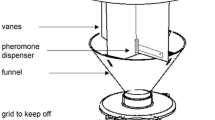
The alarm pheromone system ofLeptoglossus zonatus (Dallas) adults was shown to be composed of hexyl acetate, hexanol, hexanal, and hexanoic acid. Single components tested in the field elicited dispersive behavior of over 70% of adults. 2-(E)-Hexenal, found in the secretion of nymphs, but not in the exudates of adults, was also active against adults. In addition, first-instar nymphs responded to the four components of the alarm pheromone of adults as well as to 2-(E)-hexenal, a component of their own alarm pheromone system. Adults and nymphs possess different alarm pheromone systems, which are not specific to their own life stage. That hemipteran alarm pheromone systems are not species-specific was supported by the fact that both adult and nymphL. zonatus responded to butanoic acid, an alarm pheromone of Alydidae, which was not found in this Coreidae species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.C. 1969. A revision of the genusLeptoglossus Guerin (Hemiptera: Coreidae).Entomol. Am. 45:35–140.
Anonymous. 1992. Software for statistical visualization on the Apple Macintosh. JMP introductory guide. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, North Carolina.
Aldrich, J.R. 1988. Chemical ecology of the Heteroptera.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 33:211–238.
Aldrich, J.R., andYonke, T.R. 1975. Natural products of abdominal and metathoracic scent glands of coreid bugs.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 68:955–959.
Aldrich, J.R., Oliver, J.E., Lusby, W.R., Kochansky, J.P., andLockwood, J.A. 1987. Pheromone strains of the cosmopolitan pest,Nezara viridula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae).J. Exp. Zool. 244:171–175.
Blum, M.S. 1985. Alarm pheromones, pp. 193–223,in G.A. Kerkut and L.I. Gilbert (eds.). Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology. Pergamon Press, New York.
Kou, R., Tang, D.S., andChow, Y.S. 1989. Alarm pheromone of pentatomid bug,Erthesina fullo (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 15:2695–2702.
Leal, W.S., andKadosawa, T. 1992a. (E)-2-Hexenyl hexanoaate, the alarm pheromone of the bean bugRiptortus clavatus (Heteroptera: Alydidae).Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 56:1004–1005.
Leal, W.S., andKadosawa, T. 1992b. Chemical ecology ofRiptortus clavatus. Proceedings, 36th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry. p. 186.
Leal, W.S., Kadosawa, T., andNakamori, H. 1993. Aggregation pheromone of the bean bugRiptortus clavatus. Proceedings, 37th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry. p. 212.
Levinson, H.Z., Levinson, A.R., Müller, B., andSteinbrecht, R.A. 1974. Structure of sensilla, olfactory perception, and behaviour of the bedbug,Cimex lectularius, in response to its alarm pheromone.J. Insect Physiol. 20:1231–1248.
Lockwood, J.A., andStory, R.N. 1987. Defensive secretion of the southern green stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) as an alarm pheromone.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 80:686–691.
Nault, L.R., andPhelan, P.L. 1984. Alarm pheromones and sociality in pre-social insects, pp. 237–256,in W.J. Bell and R.T. Cardé (eds.). Chemical Ecology of Insects. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts.
Panizzi, A.R. 1989. Desempenho de ninfas e adultos deLeptoglossus zonatus (Dallas, 1852) (Hemiptera: Coreidae) em diferentes alimentos.An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 18:375–389.
Schaefer, C.W., andMitchell, P.L. 1983. Food plants of the Coreoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera).Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 76:591–615.
Solomon, J.C., andFroeschner, R.C. 1981. Notes on food resources and behavior of the family Coreidae (Hemiptera) in a semi-deciduous tropical forest.Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 83:428–431.
Todd, J.L., andBaker, T.C. 1993. Response of single antennal neurons of female cabbage loopers to behaviorally active attractants.Naturwissenschaften 80:183–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares Leal, W., Ricardo Panizzi, A. & Carla Niva, C. Alarm pheromone system of leaf-footed bugLeptoglossus zonatus (Heteroptera: Coreidae). J Chem Ecol 20, 1209–1216 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059755
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059755