Abstract
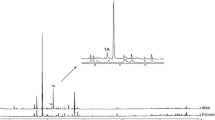
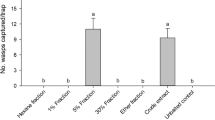
Production of 4-methyl-5-nonanol, and 4-methyl-5-nonanone by two sympatric Asian palm weevils,Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliv.) andR. vulneratus (Panz.) suggested that enantiospecificity of either compound could impart species specificity of pheromone communication. Weevil-produced, racemic 4-methyl-5-nonanol and 4-methyl-5-nonanone and their stereoselectively synthesized optical isomers were subjected to gas chromatographic-electroantennographic detection (GC-EAD) and GC-mass spectrometry (MS) on a chiral Cyclodex-B column. Only theS,S stereoisomer of 4-methyl-5-nonanol was EAD active and was produced by bothR. ferrugineus andR. vulneratus. Production and EAD activity of (S)-4-methyl-5-nonanone exceeded that of its antipode in both weevils. In field experiments in Java. (4S, 5S)-4-methyl-5-nonanol and the stereoisomeric mixture were equally attractive. The 4R,5R stereoisomer was inactive. The corresponding ketone enantiomers neither enhanced nor reduced attraction to (4S,5S)-4-methyl-5-nonanol. Lack of apparent differences betweenR. ferrugineus andR. vulneratus pheromones suggests that synonomy of both weevils should be considered unless other pre- or postzygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms are disclosed in future studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Árn, H., Städler, E., andRauscher, S. 1975. The electroantennographic detector—a selective and sensitive tool in the gas chromatographic analysis of insect pheromones.Z. Naturforsch. 30c:722–725.
Birch, M.C., Light, D.M., andMori, K. 1977. Selective inhibition of response ofIps pini to its pheromone by theS-(—)-enantiomer of ipsenol.Nature 270:738–739.
Birch, M.C., Light, D.L., Wood, L.E., Silverstein, R.M., Bergot, G., West, J.R., andYoung, J.C. 1980. Pheromonal attraction and allomonal interruption ofIps pini in California by the two enantiomers of ipsdienol.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:703–717.
Brown, H., Garg, C.P., andLiu, K.-L. 1971. The oxidation of secondary alcohols in diethyl ether with aqueous chromic acid. A convenient procedure for the preparation of ketones in high epimeric purity.J. Org. Chem. 36:387–390.
Camacho, A.D., Pierce, H.D., Jr., andBorden, J.H. 1993. Geometrical and optical isomerism of pheromones in two sympatricDryocoetes species (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), mediates species specificity and response level.J. Chem. Ecol. 19:2169–2182.
Enders, D., Eichenauer, H., Baus, U., Schubert, H., andKremer, K.A.M. 1984. Asymmetric synthesis via metalated chiral hydrazones. Overall enantioselective α-alkylation of acyclic ketones.Tetrahedron 40:1345–1359.
Fouquet, G., andSchlosser, M. 1974. Improved carbon-carbon linking by controlled copper catalysis.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 13:82–83.
Gries, G., Gries, R., Perez, A.L., Oehlschlager, A.C., Gonzalez, L.M., Pierce, H.D., Jr., Kouda-Bonafos, M., Zebeyou, M., andNanou, N. 1993. Aggregation pheromone of the African palm weevil,Rhynchophorus phoenicis (F).Naturwissenschaften 80:90–91.
Hallett, R.H., Gries, G., Gries, R., Borden, J.H., Czyzewska, E., Oehlschlager, A.C., Pierce, H.D., Jr., Angerilli, N.P.D., andRauf, A. 1993a. Aggregation pheromones of two Asian palm weevils,Rhynchophorus ferrugineus and R. vulneratus.Naturwissenschaften 80:328–331.
Hallett, R. H., Oehlschlager, A.C., Gries, G., Angerilli, N.P.D., Al Shareqi, R.K., Gassouma, M.S., andBorden, J.H. 1993b. Field testing of aggregation pheromones of two Asian palm weevils. PORIM International Palm Oil Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, September 20–25, 1993, Proceedings. In Press.
Lanier, G.N., andWood, D.L. 1975. Specificity of response to pheromones in the genusIps (Coleoptera: Scolytidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 1:9–23.
Light, D.L., andBirch, M.C. 1979. Inhibition of the attractive pheromone response inIps paraconfusus by (R)-(—)-ipsdienol.Naturwissenschaften 66:150–160.
Mori, K., Hiromasa, K., Malosse, C., andRochat, D. 1993. Synthesis of the enantiomers ofsyn-4-methyl-5-nonanol to determine the absolute configuration of the naturally occurring (4S,5S) isomer isolated as the male-produced compound ofRhynchophorus vulneratus andMetamasius hemipterus.Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1993:1201–1204.
Oehlschlager, A.C., Pierce, H.D., Jr., Morgan, B., Wimalaratne, P.D.C., Slessor, K.N., King, G.G.S., Gries, G., Gries, R., Borden, J.H., Jiron, L.J., Chinchilla, C.M., andMexzon, R.G. 1992. Chirality and field activity of rhynchophorol, the aggregation pheromone of the American palm weevil.Naturwissenschaften 79:134–135.
Oehlschlager, A.C., Chinchilla, C.M., Gonzalez, L.M., Jiron, L.F., Mexzon, R., andMorgan, B. 1993a. Development of a pheromone-based trapping system forRhynchophorus palmarum (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 86:1381–1392.
Oehlschlager, A.C., Chinchilla, C.M., andGonzalez, L.M. 1993b. Optimization of a pheromone-baited trap for the American Palm weevil. PORIM International Palm Oil Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, September 20–25, 1993, Proceedings.In Press.
Oehlschlager, A.C., Prior, R.N.B., Perez, A.L., Gries, R., Gries, G., Pierce, H.D., Jr., andLaup, S. 1995. Aggregation pheromone of the Asian palm weevil,Rhynchophorus bilineatus (Montr.), Coleoptera: Curculionidae.J. Chem. Ecol. In press.
Perez, A.L., Gries, R., Gries, G., Hallett, R.H., Oehlschlager, A.C., Pierce, H.D., Jr., Gonzales, L.M., Borden, J.H., andGiblin-Davis, R.M. 1993. Pheromones ofRhynchophorus palm weevils. Paper presented at the 10th Annual ISCE Meeting, Tampa, Florida. July 31–August 4.
Perez, A.L., Gries, G., Gries, R., Giblin-Davis, R.M., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1994. Pheromone chirality of African palm weevil,Rhynchophorus phoenicis (F.) and palmetto weevil,Rhynchophorus cruentatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 20:2653–2671.
Pierce, A.M., Borden, J.H., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1981. Olfactory response to beetle-produced volatiles and host-food attractants byOryzaephilus surinamensis andO. mercator. Can. J. Zool. 59:1980–1990.
Rochat, D.C., Malosse, C., Lettere, M., Ducrot, P.-H., Zagatti, P., Renou, M., andDescoins, C. 1991. Male-produced aggregation pheromone of the American palm weevil,Rhynchophorus palmarum L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Collection, identification, electrophysiological activity and laboratory bioassay.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:2127–2141.
Rochat, D.C., Malosse, C., Lettere, M., Ramirez-Lucas, P., Einhorn, J., andZagatti, P. 1993a. Identification of new pheromone-related compounds from volatiles produced by males of four Rhynchophorinae weevils.C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris. Ser. II 316:1737–1742.
Wattanapongsiri, A. 1966. A revision of the generaRhynchophorus andDynamis (Coleoptera, Curculionidae).Dept. Agric. Sci. Bull. Bangkok 1:1–328.
Weissling, T. J., Giblin-Davis, R. M., Gries, G., Gries, R., Perez, A.L., Pierce, H.D., Jr., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1994. Aggregation pheromone of the palmetto weevil,Rhynchophorus cruentatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 20:505–515.
Zagatti, P., Desmier De Chenon, R., Genty, P., Rochat, D., andMariau, D. 1993. The pheromonal substances of some oil palm insect pest species: Initial studies. PORIM International Palm Oil Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, September 20–25, 1993, Proceedings.In press.
Zar, J.H. 1984. Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, A.L., Hallett, R.H., Gries, R. et al. Pheromone chirality of asian palm weevils,Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliv.) andR. vulneratus (Panz.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Chem Ecol 22, 357–368 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02055104
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02055104