Summary
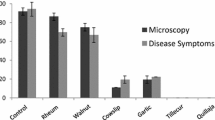
A study of the external and internal fungi associated with different varieties ofSorghum seeds has been made. The varieties tested included eighteen local varieties and twelve newSorghum varieties obtained from the Rockefeller Foundation. The external fungi were studied by preparing suspensions of superficial fungi and growing on potato dextrose agar. The internal fungi were studied by planting surface sterilized seeds on P.D.A. and pure cultures of all these fungi were prepared.
The external fungi found to be associated with the different varieties included different species ofPhycomyces, Circinella, Syncephalastrum, Chaetomium, Curvularia, Cladosporium, Helminthosporium, Montospora, Pullularia, Aspergillus, Penicillium, Cephalosporium, Trichoderma, Phoma, Fusarium.
The internal fungi recovered from these varieties included species ofChaetomium, Cladosporium, Curvularia, Helminthosporium, Heterosporium, Hormodendron, Pullularia, Alternaria, Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Monilia, Penicillium, Fusarium, Phoma, Phomopsis. Varieties 4403B, 1060 and 503 were found to carry a large number of fungi. Variety Black spanish was found to be entirely free from any internal or external fungus. Varieties which were free from endophytic fungi but possess external fungi only were Kaoling 301, African variety 901 and Shallus 475. Three fungi viz.,Pullularia, Heterosporium, Monilia have been recovered from theSorghum seeds for the first time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bain, D. C. (1950) Fungi recovered from seeds ofSorghum vulgare. Phytopathology11 521–522.
Barnett, H. L. (1955) Illustrated genera of Imperfect fungi. Burgess Publishing Co., Minnesota.
Chilton, S. J. P. (1940) The occurrence ofHelminthosporium turcicum in the seed and glumes of Sudan grass. Phytopathology30 533.
Ciccarone, A. (1949) Zonate Leaf Spot of Sorghum in Venezuela. Phytopathology39 760–761.
Dickson, J. G. (1950) Diseases of Field crops, Mc. Graw Hill Book Co., London.
Doyer, L. (1938) Manual for determination of Seed borne diseases. Edited by the International Seed Testing Association.
Gilman, J. C. (1945) A manual of soil fungi. The Iowa State College Press, Ames, Iowa, U.S.A.
Groves, J. W. &A. J. Skolko 1944 Notes on seed borne fungi,Stemphylium. Canad. J. Res.22 190.
Harris, H. B. &E. S. Luttrell (1954) Grain Sorhgum Seed treatment tests and diseases in Georgia. Plt. Disease Reporter39 (4): 329.
Koch, E. &C. Rumbold (1921) Phoma on Sweet Sorghum. Phytopathology11 253.
Leukel, R. W. &J. H. Martin (1943) Seed Rot and Seedling blight of Sorghum. U.S. Dept. Agric. Bull. 839.
Muskett, A. E. (1950) Seed borne fungi and their Significance. Trans. Brit. mycol. Soc.33 1.
Leukel, R. W. &J. H. Martin (1955) Sorghum diseases and their control. U.S. Dept. Agric. Bull., 1959.
Skolko, A. J. &J. W. Groves (1953) Notes on Seed Borne fungiChaetomium. Canad. J. Res.31 779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, V.S., Khan, A.M. Fungi associated with sorghum seeds. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 27, 314–320 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02053790
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02053790