Abstract
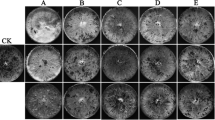
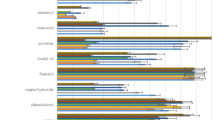
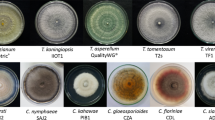
The effect ofStachybotrys atra on fungi, actinomycetes and bacteria was studied in agar culture. Of the 27 genera and 52 species of fungi, 6 species of actinomycetes and 5 genera and 10 species of bacteria tested,S. atra was found to inhibit 95.7 % fungi, all the actinomycetes and 83.3 % of bacteria.Aspergillus ustus, 2 unidentified species ofFusarium, Rhizobium trifolii andPseudomonas spp. were however not inhibited. In experiments in soil,S. atra inhibited the growth ofTrichoderma viride. S atra was ineffective whereT. viride andS. atra were inoculated simultaneously or whereT. viride was added 7 days earlier. Besides,S. atra was not found to controlMacrophomina phaseoli infection on cotton. Soil culture ofS. atra showed phytotoxic effect on cotton seedlings.S. atra produced a dark brown to black thermostable toxic metabolite in the medium. The culture filtrate retarded the growth ofM. phaseoli in agar culture. Despite the importance ofS. atra as a fungistatic agent with wide antimicrobial spectrum, the use ofS. atra as a protectant against plant pathogens seems to be limited because of its phytotoxicity on cotton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. C. &Haensler, C. M. (1935) Antagonistic action ofTrichoderma onRhizoctonia and other soil fungi.Phytopathology 25:244–252.
Aytoun, R. S. C. (1953) The genusTrichoderma; its relationship withArmillaria mellea (Vahl. ex Fr.) Quel. andPolyporus schweinitzii Fr., together with preliminary observations on its ecology in woodland soils.Trans. Bot. Soc. Edin. 36:99–144.
Brian, P. W. &Hemming, H. G. (1947) Production of antifungal and antibacterial substances by fungi; Preliminary examination of 166 strains of Fungi Imperfecti.J. Gen. Microbiol. 1:158–167.
Butler, E. J. &Jones, S. G. (1949) Plant Pathology. Macmillan & Co. London.
Ghaffar, A. (1968) Interaction of soil fungi withMacrophomina phaseoli (Maubl.) Ashby, the cause of root rot of cotton.Mycopath. Mycol. Appl. 34:196–201.
Ghaffar, A. (1969) Biological control of white rot of onion. I. Interactions of soil micro-organisms withSclerotium cepivorum Berk.Mycopath. Mycol. Appl. 38:101–111.
Ghaffar, A., Zentmyer, G. A. &Erwin, D. C. (1969) Effect of organic amendments on severity ofMacrophomina root rot of cotton.Phytopathology 59:1267–1269.
Ghaffar, A. &Fatima, K. (1970) Inhibition ofTrichoderma viride byStachybotrys atra. Sci. & Ind. 7:88–90.
Jefferys, E. G. (1952) The stability of antibiotics in soil.J. Gen. Microbiol. 7:295–312.
Keen, B. A. &Raczkowski, H. (1921) The relation between clay content and certain physical properties of soil.J. Agri. Sci. 11:441–449.
Morton, D. J. (1954) Antagonistic effects of the soil microflora uponSclerotium rolfsii.Phytopathology 44:499.
Siminoff, P. &Gottlieb, D. (1951) The production and role of antibiotics in the soil. I. The fate of streptomycin.Phytopathology 41:420–430.
Vasudeva, R. S. (1935) Studies in the root rot disease of cotton in the Punjab.Ind. J. Agri. Sci. 5:496–512.
Verona, O. (1946) Influenza di liquidi colturali fungini sullo sviluppo dei microbi del suolo. (The influence of fungal cultural liquids on the development of soil microorganisms.)Ann. Fac. Agr. Pisa, N.S. VII:147–156. (Abst. inRev. Appl. Myc. 26:557).
Weindling, R. (1932)Trichoderma lignorum as a parasite of other soil fungi.Phytopathology 22:837–845.
Wright, J. M. (1956) Biological control of a soil bornePythium infection by seed inoculation.Plant & Soil 8:132–140.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, Z.L., Ghaffar, A. Inhibition of fungi, actinomycetes and bacteria by Stachybotrys atra. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 47, 241–251 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02051662
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02051662