Summary
-
1.
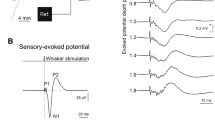
If somatosensory evoked cortical responses are recorded from a subject who is sitting in a dark soundproof chamber, an increasing attenuation of the +5a-potential can be observed preceding the time of the experiment. An awaking stimulus (for instance opening the chamber and talking to the test subject) causes an increase of that +5a-potential.
-
2.
Direct currents of small intensity with positive polarity which are applied extracranially to the human scalp cause changes in the evoked and spontaneous brain activity similar to the changes observed after awaking stimuli.
-
3.
Small direct currents with negative polarity cause an attenuation of the +5a-potential and an increase of the slow components of frequency in the EEG. These changes of the brain activity are similar to those which can be observed with drowsy subjects (before an awaking stimulus).
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Wenn von einer Versuchsperson, die sich in einer dunklen, schalldichten Kammer befindet, somatosensorisch ausgelöste corticale Reizantworten abgeleitet werden, kann man mit zunehmender Versuchsdauer eine größer werdende Dämpfung der Potentialkomponente +5a. (P2) beobachten. Ein Weckreiz (z. B. das Öffnen der Meßkammer und das Sprechen mit der Versuchsperson) hat eine Vergrößerung dieser +5a-Komponente zur Folge.
-
2.
Extracranial am menschlichen Schädel applizierte Gleichströme positiver Polarität und kleiner Intensität (100–400 μA) bewirken in der evozierten und spontanen bioelektrischen Hirnaktivität ähnliche Änderungen, wie sie auch nach Weckreizen beobachtet werden können.
-
3.
Kleine Gleichströme negativer Polarität verursachen eine Dämpfung der +5a-Komponente und eine Zunahme der langsamen Frequenzkomponenten im EEG. Diese Veränderungen der bioelektrischen Hirnaktivität sind ähnlich denen, die auch bei müden Probanden (vor einem Weckreiz) beobachtet werden können.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Asahina, K., Yamanaka, M.: The relationship between steady potential and other electrical activities of cerebral cortex. Jap. J. Physiol.10, 258–266 (1960).
Baumgarten, R. von, Mollica, A., Moruzzi, G.: Modulierung der Entladungsfrequenz einzelner Zellen der Substantia reticularis durch corticofugale und cerebelläre Impulse. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.259, 56–78 (1954).
Bishop, G., O'Leary, J.: The effects of polarizing currents on cell potentials and their significance in the interpretation of central nervous system activity. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.2, 401–416 (1950).
Blackmann, R., Tukey, J.: The measurement of power spectra. New York: Dover Publ. Inc. 1958.
Caspers, H.: Über die Beziehungen zwischen Dendritenpotential und Gleichspannung an der Hirnrinde. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.269, 157–181 (1959).
Creutzfeldt, O., Fromm, G., Kapp, H.: Influence of transcortical d-c currents on cortical neuronal activity. Exp. Neurol.5, 436–452 (1962).
Denney, D., Brookhart, J.: The effect of applied polarization on evoked electro-cortical waves in the cat. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.14, 885–897 (1962).
French, J., Hernández-Peón, R., Livingston, R.: Projections from cortex to cephalic brain stem (reticular formation) in monkey. J. Neurophysiol.18, 74–95 (1955).
Gastaut, H., Régis, H., Lyagoubi, S., Mona, T., Simon, L.: Comparison of the potentials recorted from the occipital, temporal and central regions of the human scalp, evoked by visual, auditory and somato-sensory stimuli. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl.25, 19–28 (1967).
Goff, W., Allison, T., Shapiro, A., Rosner, B.: Cerebral somatosensory responses evoked during sleep in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.21, 1–9 (1966).
Keidel, W. D.: Neuere Ergebnisse der Physiologie des Hörens. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.,- und Kehlk.-Heilk.185, 548–575 (1965).
—, Spreng, M.: Neurophysiological evidence for the Stevens power function in man. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.38, 191–195 (1965).
Kooi, K., Bagchi, B., Jordan, R.: Observations on photically evoked occipital and vertex waves during sleep in man. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.122, 270–280 (1964).
Moruzzi, G., Magoun, H.: Brain stem reticular formation and activation of the EEG. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.1, 455–473 (1949).
Pfurtscheller, G.: Der Einfluß polarisierender Ströme auf die spontane und evozierte Hirnaktivität des Menschen. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.312, 115 (1969).
—, Breuing, G.: Polynomapproximation gemittelter evozierter Hirnspannungsschwankungen. Z. ges. exp. Med.151, 350–355 (1969).
- Johannson, H., Spreng, M.: Reizstärkeunabhängige Änderungen an akustisch ausgelösten corticalen Reizantworten. (Im Druck.)
Scheibel, M., Scheibel, A., Mollica, A., Moruzzi, G.: Convergence and interaction of afferent impulses on single units of reticular formation. J. Neurophysiol.18, 304–331 (1955).
Segundo, J., Naquet, R., Buser, P.: Effects of cortical stimulation on electrocortical activity in monkeys. J. Neurophysiol.18, 235–245 (1955).
Weitzman, E., Kremen, H.: Auditory evoked responses during different stages of sleep in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.18, 65–70 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung und das Rechenzentrum der Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg.
Die Ergebnisse wurden auszugsweise auf der 36. Tagung der Deutschen Physiologischen Gesellschaft vom 25.–27. 9. 1969 in Mainz vorgetragen.
Herrn Professor Dr. W. D. Keidel, Direktor des I. Physiologischen Instituts der Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, möchte ich besonders für die wertvollen Hinweise und Anregungen und die Schaffung ausgezeichneter Arbeitsbedingungen danken.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfurtscheller, G. Änderungen in der evozierten und spontanen Hirnaktivität des Menschen bei extracranialer Polarisation. Z. Gesamte Exp. Med. 152, 284–293 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02044912
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02044912