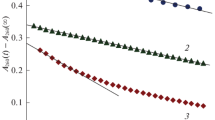
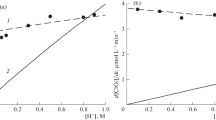
Abstract
The chemistry of aqeous ozone, O3, and ozonide, O −3 , is of great interest from a technological, environmental and scientific point of view. The literature about their aqueous chemistry is extensive, the reaction mechanisms are still not well understood. The ozonide anion is a free radical that is too unstable in aqueous media to be studied by classical means. Some properties of the aqueous ozonide radical ion have been elucidated earlier by means of the pulse radiolysis technique. The OH− catalyzed chain decomposition of aqueous ozone, 2O3→3O2, has not yet been rationalized in terms of a detailed mechanism. We have investigated the reaction mechanisms using pulse radiolysis in combination with a high pressure cell, rapid mixing and numerical simulation of the experiments. This study makes it possible to give a detailed description of the reaction mechanisms in terms of uni- and bimolecular reactions and provides kinetic data sufficient for computer simulations of aqueous O3/O −3 chemistry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. L. EVANS (Ed.), Ozone in Water and Waste Water Treatment, Ann Arbor, MI, 1972.
R. G. RICE, A. NETZER (Eds), Handbook of Ozone Technology and Application, Ann Arbor, MI, 1982.
W. J. MASSCHLEIN (Ed.), Ozonation Manual for Water and Wastewater Treatment, Wiley, New York, 1982.
L. NEWMAN (Ed.), Gas-Liquid Chemistry of Natural Walters Abstracts of papers presented at Brookhaven National Laboratory, April 1984, BNL 51757 Vols 1 and 2.
J. HOIGNE, H. BADER, Water Res., 17 (1983) 173 and 185.
J. HOIGNE, H. BADER, W. R. HAAG, J. STAEHELIN, Water Res., 19 (1985) 993.
J. STAEHELIN, J. HOIGNE, 5th Ozon-Weltkongress, Wasser Berlin 1981, Colloquium Verlag, West Berlin, 1981, p. 623.
M. TERAMOTO, S. IMAMURA, N. YATAGAI, Y. NISHIKAWA, H. TERANISHI, J. Chem. Eng. Japan, 14 (1981) 383.
J. A. ROTH, D. E. SULLIVAN, Ozone Sci. Eng., 5 (1983) 37.
J. WEISS, Faraday Soc., 31 (1935) 685.
M. PELEG, Water Res., 10 (1976) 361.
J. HOIGNE, H. BADER, Water Res., 10 (1976) 377.
E. J. HART, K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, Anal. Chem., 55 (1983) 46.
D. BAHNEMANN, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 86 (1982) 252.
K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 87 (1983) 1951.
J. HOIGNE, H. BADER, Wasser, 48 (1977) 283.
K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, E. J. HART, to be published.
K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, E. BJERGBAKKE, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 88 (1984) 4144.
R. F. HAMPSON, Chemical Kinetic and Photochemical Data Sheet for Atmospheric Reactions. Report No. FAA-EE-80-17, 1980.
R. E. BÜHLER, J. STAEHELIN, J. HOIGNE, J. Phys. Chem., 88 (1984) 2560.
J. STAEHELIN, R. E. BÜHLER, J. HOIGNE, J. Phys. Chem., 88 (1984) 5999.
D. S. GORBENKO-GERMANOV, I. V. KOZLOVA, Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSR, 210 (1973) 851.
D. S. GORBENKO-GERMANOV, I. V. KOZLOVA, Zh. Fiz. Khim., 48 (1974) 166.
L. FORNI, D. BAHNEMANN, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 86 (1982) 255.
B. H. J. BIELSKI, J. M. GEBICKI, Advances in Radiation Chemistry, Vol. 2, M. BURTON, J. L. MAGEE (Eds), Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1970, p. 248.
G. CZAPSKI, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 22 (1971) 171.
K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, E. BJERGBAKKE, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 88 (1984) 269.
U. K. KLÄNING, K. SEHESTED, T. WOLFF, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I, 80 (1984) 2969.
U. K. KLÄNING, K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, J. Phys. Chem., 89 (1985) 760.
H. CHRISTENSEN, K. SEHESTED, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 16 (1979) 183.
K. SEHESTED, J. HOLCMAN, E. BJERGBAKKE, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 86 (1982) 2066.
G. E. ADAMS, W. J. BOAG, B. D. MICHAEL, Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 281 (1966) 321.
E. BJERGBAKKE, O. L. RASMUSSEN, Chemsimul — A Program Package for Numerical Simulation of Chemical Reaction Systems, Risø National Laboratory, DK 4000 Roskilde, Denmark, 1984, Risø-R-395.
E. BJERGBAKKE, K. SHEESTED, O. L. RASMUSSEN, H. CHRISTENSEN, Input Files for Computer Simulation of Water Radiolysis. Risø National Laboratory, DK 4000 Roskilde, Denmark 1984, Risø-M-2430.
J. HOLCMAN, K. SEHESTED, E. BJERGBAKKE, E. J. HART, J. Phys. Chem., 86 (1982) 2069.
J. STAEHELIN, J. HOIGNE, Envir. Sci. Technol., 16 (1982) 676.
R. W. MATTHEWS, D. F. SANGSTER, J. Phys. Chem., 69 (1965) 1938.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sehested, K., Holcman, J., Bjergbakke, E. et al. Use of pulse radiolysis for the study of the chemistry of aqueous ozone and ozonide solutions. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 101, 239–250 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042424
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042424