Abstract
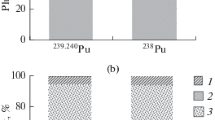
Geochemical association of plutonium in the coastal environment of Trombay has been studied. A sequential leaching method was employed for chemical partitioning of plutonium in sediments. The results show that 95±15% of plutonium was extracted by different leaching reagents out of which 85±14% was associated with organic matter and hydrous oxide and 9±4% with residual fraction.
The presence of significant fraction of Pu bound with organic matter of the sediment is an important factor in determining the extent to which an element becomes available to bottom feeding biota and so enters the aquatic food chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. C. PILLAI, N. N. DEY, E. MATHEW, B. U. KOTHARI, in: Impacts of Nuclear Releases into the Aquatic Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1975, p. 277.
K. C. PILLAI, E. MATHEW, in: Transuranic Nuclides in the Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1975, p. 25.
V. M. MATKAR, E. MATHEW, N. N. DEY, M. C. ABANI, K. C. PILLAI, Indian J. Marine Sci., 12 (1983) 72.
B. M. SANKHESARA, A. K. MORE, M. D. BORKAR, V. M. MATKAR, K. C. PILLAI, XIV IARP Conference, 1978.
V. M. MATKAR, K. C. PILLAI, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Articles, 138 (1990) 1.
J. J. ALBERT, M. A. WAHLGREN, R. N. MULLER, K. A. ORLANDINI, Radiological and Environmental Research Division Annual Report, ANAL 75–60, Part III, 1975, p. 36.
D. N. EDGINGTON, J. J. ALBERTS, M. A. WAHLGREN, J. O. KARTTUNM, C. A. REEVE, Transuranic Nuclides in the Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1976, p. 493.
D. N. EDGINGTON, Techniques for Identifying Transuranics Speciation in Aquatic Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1981, p. 3.
J. A. HETHERINGTON, Mar. Sci. Commun., 4 (1978) 239.
C. T. COOK, M. S. BAXTER, H. J. DUNCAN, J. TOOLE, R. MALCOLMSON, Nucl. Instr. Methods Phys. Res., 233 (1984) 517.
D. N. EDGINGTON, J. A. ROBBINS, in: Impacts of Nuclear Releases into the Aquatic Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1975, p. 245.
J. J. ALBERTS, R. N. MULLER, J. Environ. Qual., 8 (1979) 20.
CLIDE, ORR, JR., J. M. DALLAVALLE, The MacMillan Co., New York, 1959, p. 43.
R. CHESTER, M. J. HUGHES, Chem. Geol., 2 (1967) 249.
R. CHESTER, S. R. ASTOW, Techniques for Identifying Trans Uranic Speciation in Aquatic Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1981, p. 173.
E. MATHEW, V. M. MATKAR, K. C. PILLAI, J. Radioanal. Chem., 62 (1981) 265.
M. V. M. DESAI, A. K. GANGULY, BARC, 1970, p. 488.
S. R. ASTON, D. S. STANNERS, Nature (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matkar, V.M., Narayanan, U., Bhat, I.S. et al. Geochemical association of plutonium in sediments of the Trombay coastal environment. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 156, 119–127 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037428
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037428