Abstract
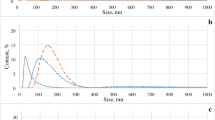
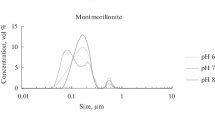
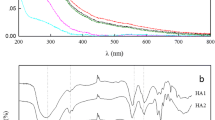
In natural waters trace elements, especially trace metals may be present in a variety of physicochemical forms. They may be associated with forms ranging from simple ions and molecules via hydrolysis products and colloids, pseudocolloids and organic or inorganic particles. The transition between categories is gradual. The presence of species differing in size, charge and density will influence on the transport, mobility and bioavailability of the trace element in question. Fractionation techniques which do not influence the distribution patterns are therefore required for speciation purposes. In the present work dialysis in situ and large membrane (hollow fibers) ultrafiltration are used for fractionation of low molecular weight species, colloids, pseudocolloids and particles. Due to the presence of foreign components transformation processes influence the distribution patterns of trace elements of interest. Sorption to “foreign” surfaces, complexation with agents present and aggregation of colloids (e.g., increasing ionic strength) result in a shift towards higher dimensions while desorption and dispersion processes mobilize the trace elements. Information on several components is therefore needed in speciation studies and a multielemental method of analysis having low determination limits must be applied. Instrumental neutron activation is appropriate to this kind of study because of its high sensitivity for simultaneous determination of a great-number of elements. Size fractionation techniques combined with INAA for the characterization of trace element species in natural waters will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. SALBU, Preconcentration and fractionation techniques in the determination of trace elements in natural waters — their concentration and physico-chemical forms, University of Oslo, 1984.
B. SALBU, H. E. BJØRNSTAD, N. S. LINDSTRØM, E. LYDERSEN, E. M. BREVIK, J. P. RAMBAEK, P. E. PAUS, Talanta, 32 (1985) 907.
B. SALBU, H. E. BJØRNSTAD, H. F. LYSTAD, B. ANDRESEN, Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Nuclear Methods in Environmental and Energy Research, Am. Nucl. Soc. Puerto Rico, 1984.
P. BENES, E. STEINNES, Wat. Res., 8 (1974) 947.
P. BENES, E. T. GJESSING, E. STEINNES, Wat. Res., 10 (1974) 711.
E. LYDERSEN, Thesis, University of Oslo, 1985.
H. E. BJØRNSTAD, B. SALBU, Association of trace elements to colloids, Submitted Anal. Chem.
H. E. BJØRNSTAD, B SALBU, Diffusion rate measurements for distinguishing low molecular weight species in natural waters, in preparation.
B. SALBU, E. STEINNES, A. C. PAPPAS, Anal. Chem., 47 (1975) 1011.
B. SALBU, H. E. BJØRNSTAD, K. BIBOW, J. O. ENGLUND, H. HOVIND, J. P. RAMBAEK, Trace elements in fresh waters from Åstadalen, a high mountain catchment in S. E. Norway, in preparation.
B. SALBU, H. E. BJØRNSTAD, N. S. LINDSTRØM, E. M. BREVIK, J. P. RAMBAEK, J. O. ENGLUND, K. F. MEYER, H. HOVIN, P. E. PAUS, B. ENGER, E. BJERKELUND, Anal. Chim. Acta, 167 (1985) 161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salbu, B. Size fractionation techniques combined with INAA for speciation purposes. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 112, 169–174 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037288
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037288