Abstract
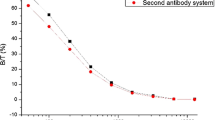
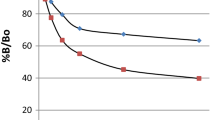
Therapeutic monitoring of theophylline can be accurately performed by radioimmunoassay (RIA). It is radioactive tracer as an essential reagent for the development of very sensitive RIA. Direct radiolabeling of theophylline with125I is very difficult due to the absence of appropriate functional groups. Hence carboxylic acid of theophylline was tagged to tyrosine methyl ester and then radiolabeled. The derivatives of theophylline, bearing a propionic acid and butyric acid side chains at seventh and eight position of theophylline, were synthesised and coupled to tyrosine methyl ester. Theophylline-tyrosine methyl ester conjugates were labeled with125I using chlora mine—T. Radiolabeled theophylline was purified by solvent extraction followed by thin layer chromatography. The purified radiolabeled compound were assessed for their radiochemical purity, specific activity and immunoreactivity. Stability studies of radiolabeled compounds were performed with different solvents at different temperatures. Theophylline serum samples analysed using developed and commercial kits showed the correlation coefficient of 0.961 (n=9).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. H. Jacobs, R. M. Senior, G. Kessler, J. Am. Med. Ass., 235 (1976) 1983.
J. Pollack, F. Kiechel, D. Cooper, M. Weinberger, Pediatrics, 60 (1978) 640.
L. Hendleles, M. Weinberger, New Eng. J. Med., 300 (1979) 1217.
N. Takashi, K. Masayuki, Chem. Pham. Bull., 27 (1979) 893.
C. E. Cook, M. E. Twine, M. Myers, E. Amerson, J. A. Kepler, G. F. Taylor, Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharmacol., 13 (1976) 3497.
A. L. Nesse, L. F. Soyka, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 21 (1977) 633.
E. H. D. Cameron, S. E. Morries, J. J. Scarisbrick, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 1 (1973) 1115.
J. E. T. Corrie, W. A. Ratclifee, J. S. Macpherson, J. Immunol. Method., 51 (1982) 159.
E. D. Horgan, W. J. Riley, Clin. Chem., 19 (1973) 187.
R. Dixon, T. Crews, Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharmacol., 18 (1977) 477.
W. N. Hunter, F. C. Greenwood, Nature, 194 (1962) 495.
C. S. Chiang, Clin. Chem., 33 (1987) 1245.
G. Samuel, N. Sivaprasad, M. Vekatesh, R. Mathew, P. Vavia, H. Bhalla, in: Proc. Intem. Symp. on Radioimmunoassay and Related Procedures: Perspectives in Developing Countries, Organized by IAEA in co-operation with the WHO. Vienna Aug. 26–30, 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhalla, H.L., Vavia, P.R., Samuel, G. et al. Development of radioimmunoassay. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 220, 73–76 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02035351
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02035351