Abstract
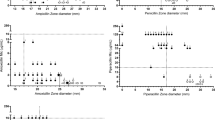
Using regression analysis to correlate MIC values and inhibition zone diameters, an attempt was made to establish criteria for interpreting the results of the agar diffusion test with norfloxacin discs (10 mcg). The test was performed on DST agar in accordance with ICS recommendations. The correlation was moderate (r=−0.8547); the regression equation was x=−0.30y + 15.80, where x was log2 MIC + 9 and y the inhibition zone diameter. The position of the MIC breakpoints of norfloxacin and the distribution of the MIC values of the bacterial population did not permit precise inhibition zone breakpoints to be established. To allow a safety margin it is recommended that for the meantime norfloxacin inhibition zones be interpreted as sensitive from 15 mm onwards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M. M., Sherris, J. C., Turck, M.: Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1966, 45: 493–496.
Ericsson, H. M., Sherris, J. C.: Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica 1971, Supplement 217: 1–90.
Shungu, D. L., Weinberg, E., Gadebusch, H. H.: Tentative interpretive standards for disk diffusion susceptibility testing with norfloxacin (MK-0366, AM-715). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1983, 23: 256–260.
Woods, S. J., Shadomy, S.: Disk diffusion susceptibility tests with norfloxacin (MK-0366, AM-715): confirmation of proposed interpretive criteria. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 2: 242–244.
Boppana, V. K., Swanson, B. N.: Determination of norfloxacin, a new nalidixic acid analog, in human serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 21: 808–810.
NCCLS Proposed Standard: PSM-7: Standard methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria which grow aerobically. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Villanova, PA, 1980, p. 1–31.
DIN 58940, Teil 4, Beiblatt 2: Methoden zur Empfindlichkeitsprüfung von bakteriellen Krankheitserregern (außer Mykobakterien) gegen Chemotherapeutika. Bewertungsstufen der minimalen Hemmkonzentration. Liste der durchschnittlichen Tagesdosierungen. Beuth-Verlag, Berlin, 1982.
Metzler, C. M., DeHaan, R. M.: Susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria: statistical and clinical considerations. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1974, 130: 588–594.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimm, H. Criteria for interpretation of agar diffusion susceptibility tests of norfloxacin performed by the ICS method. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2, 245–248 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029526
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029526