Abstract
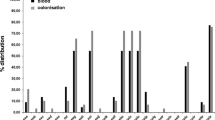
The enterotoxigenicity of 208 strains ofStaphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical specimens and four strains isolated from food was investigated. All strains were examined for production of enterotoxins A, B, C, D, and E in cellophane-over-agar cultures using a modified optimum-sensitivity-plate method. Strains from systemic infections were also examined for production of toxicshock toxin. The overall frequency of enterotoxigenic strains among the clinical isolates was 42 %. Enterotoxin A was the predominant enterotoxin found among positive strains (45/88). Enterotoxins B to E were found in decreasing order of frequency. Twenty-three strains produced two enterotoxins and one strain three toxins. A significant association was observed between multiresistance of strains (defined as resistance against penicillin and at least two other antibiotics) and enterotoxin B production. Strains from phage groups I and III produced predominantly enterotoxin A. Four of the five strains producing toxic shock toxin belonged to phage group I; one was not classifiable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grossmann, R.: Überwachung von Lebensmittelvergiftungen in den USA. Bundesgesundheitsblatt 1982, 25: 289–294.
Sinell, H.-J.: Stand und künftige Aufgaben in der Bekämpfung von Lebensmittelvergiftungen. Bundesgesundheitsblatt 1982, 25: 349–352.
Untermann, F.: Zum Vorkommen von enterotoxinbildenden Staphylokokken bei Menschen. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie und Hygiene (A) 1972, 222: 18–26.
Petras, P., Maskova, L.: Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxigenicity. II. Field strains. Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology and Microbiology and Immunology 1980, 24: 177–182.
Richter, U., Witte, W., Hummel, R., Karsch, W., Mochmann, H.: Enterotoxin production and host specific variety byStaphylococcus aureus strains. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A), 1981, Supplement 10: 1023–1026.
Casman, E. P., Bennett, R. W., Dorsey, A. E., Issa, J. A.: Identification of a fourth staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin D. Journal of Bacteriology 1967, 94: 1875–1882.
Müller, H., Puppel, H., Mannheim, W., Dajani, H., v. Ahn, U.: Fäkale Trägerrate und Enterotoxinbilungsvermögen vonStaphylococcus aureus beim Menschen. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A) 1973, 223: 180–196.
Zak, C., Jeljaszewicz, J., Stochmal, I.: Serological types of enterotoxins produced by strains ofStaphylococcus aureus isolated from feces. In: Jeljaszewicz, J. (ed.): Staphylococci and staphylococcal Infections. Polish Medical Publishers, Warsaw, 1973, p. 526–528.
Payne, D. N., Wood, J. M.: The incidence of enterotoxin production in strains ofStaphylococcus aureus isolated from foods. Journal Applied Bacteriology 1974, 37: 319–325.
Mochmann, H., Akatov, A. K., Khatenever, M. L., Richter, U., Kuschko, I. W., Karsch, W.: Studies on enterotoxin production by strains of staphylococcus of different origin obtained from USSR. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A), 1981, Supplement 10: 377–380.
Mochmann, H., Richter, U., Karsch, W., Witte, W., Meyer, W.: Untersuchungen über die Enterotoxin-Bildung vonStaphylococcus aureus-Stämmen unterschiedlicher Herkunft. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A) 1976, 234, Supplement 5: 434–449.
Osvath-Marton, A., Nagy-Dani, E., Ban, E.: Studies on the correlation of enterotoxin production and resistance ofStaphylococcus aureus strains to antibiotics. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie and Hygiene (A) 1976, 234, Supplement 5: 589–592.
Osvath-Marton, A., Ban, E., Molnar, L.: Occurrence of enterotoxin-producingStaphylococcus aureus strains in enterocolitis of children. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie and Hygiene (A) 1976, 234, Supplement 5: 975–980.
Sourek, J., Vymola, F., Trojanova, M., Zelenkova, L., Matejovska, V., Bergdoll, M. S.: Enterotoxin production byStaphylococcus aureus strains isolated from cases of chronic osteomyelitis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1979, 9: 266–268.
Bergdoll, M. S., Crass, B. A., Reiser, R. F., Robbins, R. N., Davis, J. P.: A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet 1981, i: 1017–1021.
Robbins, R., Gould, S., Bergdoll, M.: Detecting the enterotoxigenicity ofStaphylococcus aureus strains. Applied Microbiology 1974, 28: 946–950.
Bergdoll, M. S.: Immunological aspects of staphylococcal enterotoxins. In: Catsimpoolas, N. (ed.): Immunological aspects of foods. Avi Publishing, Westport, CT, 1977, p. 199–220.
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M. M., Sherris, J. C., Turck, M.: Antibiotic susceptibility testing by standardized single disk method. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1966, 45: 493–496.
Ericsson, H. M., Sherris, J. C.: Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica 1971, Supplement 217: 1–90.
Lenz, W., Brandis, H.: Die Bedeutung der Lysotypie bei Krankenhausinfektionen durchStaphylococcus aureus. In: Thofern, E., Botzenhart, K. (ed.): Infektionserreger in Praxis und Krankenhaus. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart, 1983 (in press).
Bergdoll, M. S., Robbins, R. N., Weiss, K., Borja, C. R., Huang, I. Y., Chu, F. S.: The staphylococcal enterotoxins: similarities. In: Jeljaszewicz, J. (ed.): Staphylococci and staphylococcal Infections. Polish Medical Publishers, Warsaw, 1973, p. 390–396.
Minor, T. E., Marth, E. H.: Staphylococci and their significance in foods. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1976.
Saunders, G. C., Bartlett, M. L.: Double-antibody solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Applied Environmental Microbiology 1977, 34: 518–522.
Lenz, W., Thelen, R., Pickenhahn, P., Brandis, H.: Nachweis von Enterotoxin in Kulturüberständen vonStaphylococcus aureus mit dem ELISA-Test und dem Micro-slide-Test. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A) 1983, 253: 466–475.
Shafer, W. M., Iandolo, J. J.: Transduction of staphylococcal enterotoxin B synthesis: establishment of the toxin gene in a recombination-deficient mutant. Infection and Immunity 1980, 27: 280–282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauff, G., Röhrig, I., Ernzer, U. et al. Enterotoxigenicity ofStaphylococcus aureus strains from clinical isolates. Eur. J, Clin. Microbiol. 2, 321–326 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019461
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019461