Summary
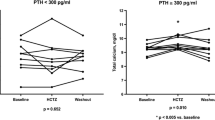
Nifedipine has been shown to lower urinary calcium in “essential” hypercalciuria. However, the mechanism(s) by which this action takes place is completely unknown. This study describes the effect of nifedipine on some calcium-controlling hormones in essential hypercalciuria. Nifedipine (20 mg/day) was administered to ten essential hypercalciuric patients, and urinary PgE2, plasma bicyclic PgE2, 1,25 vitamin D3, and PTH were assayed before and after drug administration. Nifedipine promoted a significant fall in urinary calcium (352.1±87.67 SD vs. 231.2±74.62 mg/24 hr; t=7.35, p<.0001) and PgE2 (343.92±42.71 vs. 245.03±35.41 SD ng/24 hr; t=6.18, p<.0002), as well as in plasma bicyclic PgE2 (310.00±30.91 vs. 200.00±31.62 SD pg/ml; t=9.86, p<.0001) and 1,25 (OH)2 vitamin D3 (32.77±3.23 vs. 26.94±2.94 SD pg/ml; t=6.53, p<.0001), while PTH remained unaltered (18.50±3.63 vs. 19.50±4.09 SD ng/ml; t=0.85, p, ns). Urinary calcium and PgE2 correlated positively before (r=0.81, p<.005) but not after treatment. The fall in urinary PgE2 brought about by nifedipine seems to be due to an inhibition of PgE2 synthesis, since the absolute decrements in both urinary PgE2 and plasma PgE2 metabolites were positively correlated (r=0.79, p<.007). No correlation was found between the absolute decrements of plasma bicyclic PgE2 and 1,25 (OH)2 vitamin D3.
These data seem to suggest that the fall in urinary calcium brought about by nifedipine is insome way related to PgE2 synthesis inhibition and to uncoupling of 1,25 (OH)2 vitamin D3 and PTH action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggio B, Gambaro G, Marchini F, et al. Effect of nifedipine on urinary calcium and oxalate in renal stone formers.Nephron 1986;43:234–235.
Halabe A, Wong NLM, Sisler JW, et al. The effect of calcium antagonists and thiazides in an experimental calciumoxalate stone model.Urol Res 1988;16:240–241.
Houser M, Zimmerman B, Davidman M, et al. Idiopathic hypercalciuria associated with hyperreninemia and high urinary prostaglandin E.Kidney Int 1984;26:176–192.
Buck AC, Lote JC, Sampson WF. The influence of prostaglandins on urinary calcium excretion in idiopathic urolithiasis.J Urol 1983;122:421–426.
Henriquez-La Roche C, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Herrera J, et al. Increased urinary excretion of prostaglandin E in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria.Clin Sci 1988;75:581–587.
Donker AJ, De Jong PE, Statius van Eps LW, et al. Indomethacin in Bartter's syndrome.Nephron 1977;19:200–213.
Betend L, David M, Vincent M. et al. Successful indomethacin treatment of 2 pediatric patients with severe tubulopathies.Helv Pediatr Acta 1979;34:339–344.
Remuzzi G, Imberti L, Grossini M, et al. Increased thromboxane glomerular synthesis as a possible cause of proteinuria in experimental nephrosis.J Clin Invest 1985;75:94–101.
Powell WS. Rapid extraction of oxygenated metabolites of arachidonic acid from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica.Prostaglandins 1980;20:947–957.
Reinhardt TA, Horst RL, Orf JW, et al. A microassay for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D not requiring high performance liquid chromatography: Application to clinical studies.J Clin Endocr Metab 1984;58:91–97.
Winkler MA, De Witt LM, Cheung WJ. Calmodulin and calcium channel blockers.Hypertension 1987;9:217–223.
Yamada M, Matsumoto T, Takahashi N, et al. Stimulatory effect of prostaglandin E2 on 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 synthesis in rats.Biochem J 1983;216:237–240.
Carpenter TO: Mineral regulation of vitamin D metabolism.Bone and Mineral 1989;5:259–269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caló, L., Cantaro, S., Piccoli, A. et al. Effect of nifedipine on urinary excretion of calcium and calcium-controlling hormones in essential hypercalciuria. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 4 (Suppl 5), 983–986 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02018305
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02018305