Abstract
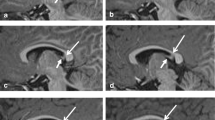
One hundred MRI examinations of normal subjects obtained at 0.5 T were studied in an effort to evaluate the claustrum and to establish a control group for patients with Wilson's disease. The claustrum was detectable unilaterally or bilaterally in 40 out of 100 subjects (40%) on spin-echo long TR (proton density and T2-weighted) MR images as a thin sheet of grey matter enclosed by low signal white matter of the external and extreme capsules. Spin-echo T1-weighted images were negative for the claustrum, however, it was identifiable in 12 out of 25 subjects (48%) studied utilizing the inversion recovery pulse sequence. In addition, eight patients with clinically established diagnoses of Wilson's disease were evaluated. The claustrum was normal (invisible) in four neurologically asymptomatic Wilson's disease patients, however, in 75% (n=3) of the four neurologically symptomatic patients it was bilaterally thickened and bright on long-TR MR images. The bright claustrum appears to be a new sign in Wilson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Starosta-Rubinstein S, Young AB, Kluin K, Hill G, Aisen AM, Gabrielsen T, Brewer GJ (1987) Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease: correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol 44: 365
Aisen AM, Martel W, Gabrielsen TO, Glazer GM, Brewer G, Young AB, Hill G (1985) Wilson disease of the brain: MR imaging. Radiology 157: 137
Lawler GA, Pennock JM, Steiner RE, Jenkins WJ, Sherlock S, Young IR (1983) Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging in Wilson disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 1
Prayer L, Wimberger D, Kramer J, Grimm G, Oder W, Imhof H (1990) Cranial MRI in Wilson's disease. Neuroradiology 32: 211
Wilson SAK (1912) Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain 34: 295
Sener RN (1993) Wilson's disease: MRI demonstration of cavitations in basal ganglia and thalami. Pediatr Radiol 23: 157
Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH (1989) Gray's anatomy, 37th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, p. 1080.
Brugieres P, Combes C, Ricolfi F, Degos JD, Poirier J, Gaston A (1992) Atypical MR presentation of Wilson disease: a possible consequence of paramagnetic effect of copper. Neuroradiology 34: 222
Yuh WTC, Flickinger FW (1988) Unusual MR findings in CNS Wilson disease. AJR 151: 834
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sener, R.N. The claustrum on MRI: Normal anatomy, and the bright claustrum as a new sign in Wilson's disease. Pediatr Radiol 23, 594–596 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014975
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014975